Question:
Refer to the exhibit. Baseline documentation for a small company had ping round trip time statistics of 36/97/132 between hosts H1 and H3. Today the network administrator checked connectivity by pinging between hosts H1 and H3 that resulted in a round trip time of 1458/2390/6066. What does this indicate to the network administrator?
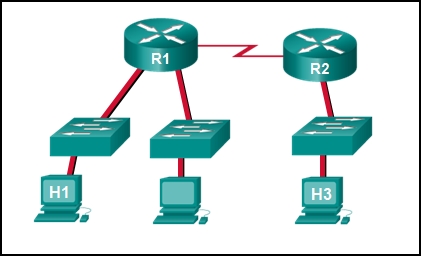
- Connectivity between H1 and H3 is fine.
- H3 is not connected properly to the network.
- Something is causing interference between H1 and R1.
- Performance between the networks is within expected parameters.
- Something is causing a time delay between the networks.
Explanation: Ping round trip time statistics are shown in milliseconds. The larger the number the more delay. A baseline is critical in times of slow performance. By looking at the documentation for the performance when the network is performing fine and comparing it to information when there is a problem, a network administrator can resolve problems faster.
Exam with this question: ITN (Version 7.00) - Building and Securing a Small Network Exam
Exam with this question: CCNA 1 (v5.1 + v6.0) Chapter 11 Exam Answers
Please login or Register to submit your answer
