Question:
Which three options are types of Layer 2 network attack? (Choose three)
- Spoofing attacks
- Vlan Hopping
- botnet attacks
- DDOS attacks
- ARP Attacks
- Brute force attacks
Explanation: 
(DHCP) Spoofing attack is a type of attack in that the attacker listens for DHCP Requests from clients and answers them with fake DHCP Response before the authorized DHCP Response comes to the clients. The fake DHCP Response often gives its IP address as the client default gateway -> all the traffic sent from the client will go through the attacker computer, the attacker becomes a “man-in-the-middle”.
The attacker can have some ways to make sure its fake DHCP Response arrives first. In fact, if the attacker is “closer” than the DHCP Server then he doesn’t need to do anything. Or he can DoS the DHCP Server so that it can’t send the DHCP Response.
VLAN Hopping: By altering the VLAN ID on packets encapsulated for trunking, an attacking device can send or receive packets on various VLANs, bypassing Layer 3 security measures. VLAN hopping can be accomplished by switch spoofing or double tagging.
1) Switch spoofing:
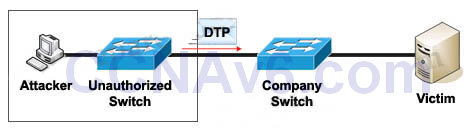
The attacker can connect an unauthorized Cisco switch to a Company switch port. The unauthorized switch can send DTP frames and form a trunk with the Company Switch. If the attacker can establish a trunk link to the Company switch, it receives traffic to all VLANs through the trunk because all VLANs are allowed on a trunk by default.
(Instead of using a Cisco Switch, the attacker can use a software to create and send DTP frames).
2) Double-Tagging:
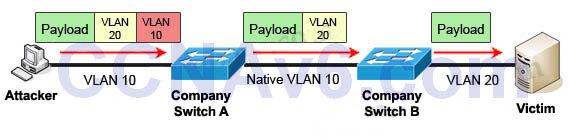
In this attack, the attacking computer generates frames with two 802.1Q tags. The first tag matches the native VLAN of the trunk port (VLAN 10 in this case), and the second matches the VLAN of a host it wants to attack (VLAN 20).
When the packet from the attacker reaches Switch A, Switch A only sees the first VLAN 10 and it matches with its native VLAN 10 so this VLAN tag is removed. Switch A forwards the frame out all links with the same native VLAN 10. Switch B receives the frame with an tag of VLAN 20 so it removes this tag and forwards out to the Victim computer.
Note: This attack only works if the trunk (between two switches) has the same native VLAN as the attacker.
ARP attack (like ARP poisoning/spoofing) is a type of attack in Which a malicious actor sends falsified ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) messages over a local area network. This results in the linking of an attacker’s MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate computer or server on the network. This is an attack based on ARP Which is at Layer 2.
Exam with this question: CCNA v3.0 (200-125) Study Guide – Exam Dumps
Exam with this question: CCNA SECFND 210-250 Dumps – Certification Practice Exam Answers
Please login or Register to submit your answer
