Question:
A network administrator is troubleshooting an EIGRP problem on a router and needs to confirm the IP addresses of the devices with which the router has established adjacency. The retransmit interval and the queue counts for the adjacent routers also need to be checked. What command will display the required information?
- Router# show ip eigrp neighbors
- Router# show ip eigrp interfaces
- Router# show ip eigrp adjacency
- Router# show ip eigrp topology
Explanation: Below is an example of the “show ip eigrp neighbors” output.
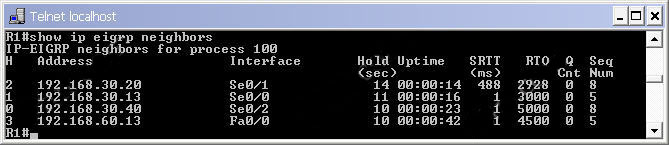
Let’s analyze these columns:
+ H: lists the neighbors in the order this router was learned
+ Address: the IP address of the neighbors
+ Interface: the interface of the local router on which this Hello packet was received
+ Hold (sec): the amount of time left before neighbor is considered in “down” status
+ Uptime: amount of time since the adjacency was established
+ SRTT (Smooth Round Trip Timer): the average time in milliseconds between the transmission of a packet to a neighbor and the receipt of an acknowledgement.
+ RTO (Retransmission Timeout): if a multicast has failed, then a unicast is sent to that particular router, the RTO is the time in milliseconds that the router waits for an acknowledgement of that unicast.
+ Queue count (Q Cnt): shows the number of queued EIGRP packets. It is usually 0.
+ Sequence Number (Seq Num): the sequence number of the last update EIGRP packet received. Each update message is given a sequence number, and the received ACK should have the same sequence number. The next update message to that neighbor will use Seq Num + 1.
In this question we have to check the RTO and Q cnt fields.
Exam with this question: CCNA v3.0 (200-125) Study Guide – Exam Dumps
Please login or Register to submit your answer
