Refer to the exhibit. SW1 is the root bridge and SW2 is the backup root bridge. An administrator wants to prevent SW4 and SW5 from ever becoming root bridges, but still allow SW2 to maintain connectivity to SW1 via SW3 if the link connecting SW1 to SW2 fails. On which two ports in this topology should the administrator configure root guard to accomplish this? (Choose two.)
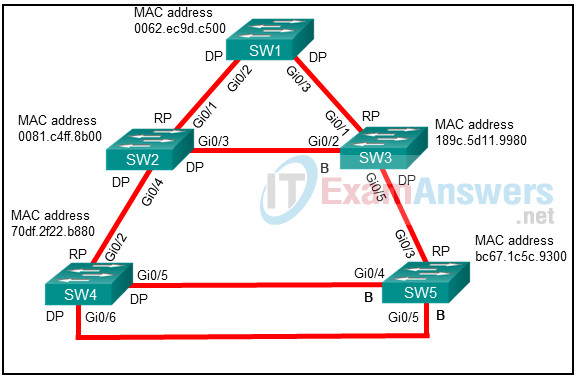
- SW5 Gi0/3 port toward SW3
- SW2 Gi0/4 port toward SW4
- SW3 Gi0/5 port toward SW5
- SW4 Gi0/6 port toward SW5
- SW4 Gi0/2 port toward SW2
Explanation: Root guard is an STP feature that is enabled on a port-by-port basis. It prevents a configured port from becoming a root port. Root guard prevents a downstream switch from becoming a root bridge in a topology. Root guard is placed on designated ports toward other switches that should never become root bridges. In order to prevent SW4 and SW5 from becoming root bridges, root guard has to be placed on SW2 Gi0/4 port toward SW4 and on SW3 Gi0/5 port toward SW5.
Exam with this question: CCNP ENCOR v8 Certification Practice Exam Answers
Please login or Register to submit your answer
