Question:
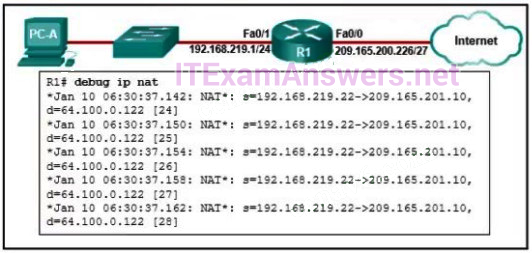
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to configure PAT on R1, but PC-A is unable to access the Internet. The administrator tries to ping a server on the Internet from PC-A and collects the debugs that are shown in the exhibit. Based on this output, what is most likely the cause of the problem?
- The inside and outside NAT interlaces have been configured backwards
- The inside global address is not on the same subnet as the ISP
- The address on Fa0/0 should be 64.100.0.1.
- The NAT source access list matches the wrong address range.
Explanation: The output of debug ip nat shows each packet that is translated by the router. The “s” is the source IP address of the packet and the “d” is the destination. The address after the arrow (“->”) shows the translated address. In this case, the translated address is on the 209.165.201.0 subnet but the ISP facing interface is in the 209.165.200.224/27 subnet. The ISP may drop the incoming packets, or might be unable to route the return packets back to the host because the address is in an unknown subnet.
Exam with this question: CCNA 3 v7 Course Final Exam Answers
Exam with this question: CCNA 2 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Practice Final Exam Answers
Exam with this question: CCNA 2 (v5.0.3 + v6.0) Final Exam Answers
Please login or Register to submit your answer
