6.2.7 Lab – Configure Automated Security Features Answers version
Topology
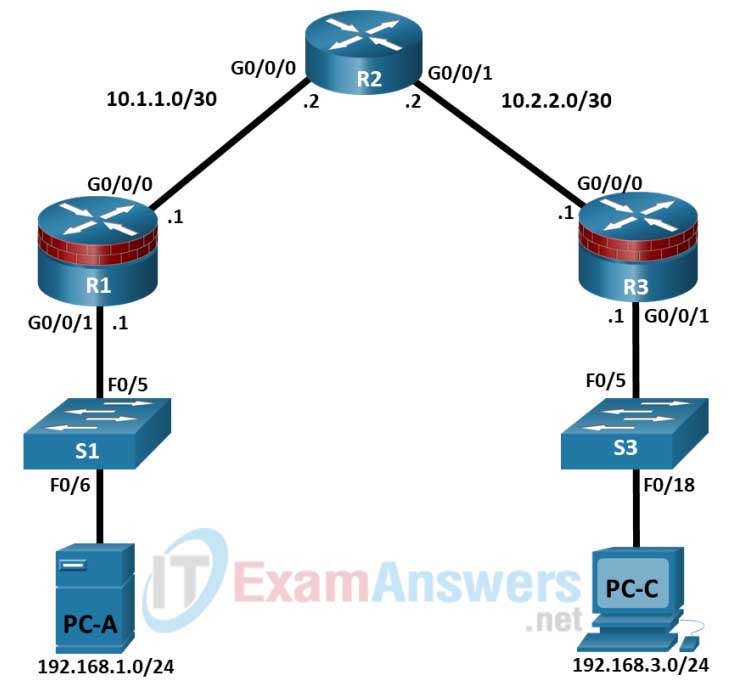
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway | Switch Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0/0 | 10.1.1.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | N/A |
| G0/0/1 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | S1 F0/5 | |
| R2 | G0/0/0 | 10.1.1.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | N/A |
| G0/0/1 | 10.2.2.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | N/A | |
| R3 | G0/0/0 | 10.2.2.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | N/A |
| G0/0/1 | 192.168.3.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | S3 F0/5 | |
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.1.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 | S1 F0/6 |
| PC-C | NIC | 192.168.3.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.3.1 | S3 F0/18 |
Objectives
Part 1: Configure Basic Device Settings
- Cable the network as shown in the topology.
- Configure basic IP addressing for routers and PCs.
- Configure OSPF routing.
- Configure PC hosts.
- Verify connectivity between hosts and routers.
Part 2: Configure Automated Security Features
- Lock down a router using AutoSecure and verify the configuration.
- Contrast using AutoSecure with manually securing a router using the command line.
Background / Scenario
The router is a critical component in any network. It controls the movement of data into and out of the network and between devices within the network. It is particularly important to protect network routers because the failure of a routing device could make sections of the network, or the entire network, inaccessible. Controlling access to routers and enabling reporting on routers is critical to network security and should be part of a comprehensive security policy.
In this lab, you will build a multi-router network and configure the routers and hosts. You will use automated security features on router R3.
Note: The routers used with hands-on labs are Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.6 (universalk9 image). The switches used in the labs are Cisco Catalyst 2960+ with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(7) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of the lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Before you begin, ensure that the routers and the switches have been erased and have no startup configurations.
Required Resources
- 3 Routers (Cisco 4221 with Cisco XE Release 16.9.6 universal image or comparable with a Security Technology Package license)
- 2 Switches (Cisco 2960+ with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(7) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 2 PCs (Windows OS with a terminal emulation program, such as PuTTY or Tera Term installed)
- Console cables to configure Cisco networking devices
- Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Instructions
Part 1: Configure Basic Device Settings
In this part, set up the network topology and configure basic settings, such as interface IP addresses.
Step 1: Cable the network.
Attach the devices, as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
Step 2: Configure basic settings for each router.
a. Console into the router and enable privileged EXEC mode.
Router> enable Router# configure terminal
Configure host names as shown in the topology.
R1(config)# hostname R1
Configure interface IP addresses as shown in the IP Addressing Table.
R1(config)# interface g0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config)# interface g0/0/1 R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# no shutdown
b. To prevent the router from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were host names, disable DNS lookup. R1 is shown here as an example.
R1(config)# no ip domain-lookup
Step 3: Configure OSPF routing on the routers.
a. Use the router ospf command in global configuration mode to enable OSPF on R1.
R1(config)# router ospf 1
b. Configure the network statements for the networks on R1. Use an area ID of 0.
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)# network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
c. Configure OSPF on R2 and R3.
R2(config)# router ospf 1 R2(config-router)# network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R2(config-router)# network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R3(config)# router ospf 1 R3(config-router)# network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
d. Issue the passive-interface command to change the G0/0/1 interface on R1 and R3 to passive.
R1(config)# router ospf 1 R1(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0/1 R3(config)# router ospf 1 R3(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0/1
Step 4: Verify OSPF neighbors and routing information.
a. Issue the show ip ospf neighbor command to verify that each router lists the other routers in the network as neighbors.
R1# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 10.2.2.2 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:37 10.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/0/0
b. Issue the show ip route command to verify that all networks display in the routing table on all routers.
R1# show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.1.1.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
L 10.1.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
O 10.2.2.0/30 [110/2] via 10.1.1.2, 00:01:11, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
L 192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
O 192.168.3.0/24 [110/3] via 10.1.1.2, 00:01:07, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Step 5: Configure PC host IP settings.
Configure a static IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for PC-A and PC-C as shown in the IP Addressing Table.
Step 6: Verify connectivity between PC-A and PC-C.
a. Ping from R1 to R3.
If the pings are not successful, troubleshoot the basic device configurations before continuing.
b. Ping from PC-A, on the R1 LAN, to PC-C, on the R3 LAN.
If the pings are not successful, troubleshoot the basic device configurations before continuing.
Note: If you can ping from PC-A to PC-C you have demonstrated that OSPF routing is configured and functioning correctly. If you cannot ping but the device interfaces are up and IP addresses are correct, use the show run, show ip ospf neighbor, and show ip route commands to help identify routing protocol-related problems.
Part 2: Configure Basic Security Settings on R1
In this part, copy and paste the following commands into R1 to configure basic security settings.
enable configure terminal service password-encryption security passwords min-length 10 enable algorithm-type scrypt secret cisco12345 ip domain name netsec.com username user01 algorithm-type scrypt secret user01pass username admin privilege 15 algorithm-type scrypt secret adminpasswd banner motd " Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited! " line con 0 exec-timeout 5 0 login local logging synchronous line aux 0 exec-timeout 5 0 login local line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 5 0 privilege level 15 transport input ssh login local crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus 1024 ip ssh time-out 90 ip ssh authentication-retries 2 ip ssh version 2
Part 3: Configure Automated Security Features
In this part, you will do as follows:
- Use AutoSecure to secure R3.
- Review router security configurations with CLI.
By using a single command in CLI mode, the AutoSecure feature allows you to disable common IP services that can be exploited for network attacks. It can also enable IP services and features that can aid in the defense of a network when under attack. AutoSecure simplifies the security configuration of a router and hardens the router configuration.
Step 1: Use the AutoSecure Cisco IOS feature on R3.
a. Enter privileged EXEC mode using the enable command.
b. Issue the auto secure command on R3 to lock down the router. R2 represents an ISP router, so assume that R3 G0/0/0 is connected to the internet when prompted by the AutoSecure questions. Respond to the AutoSecure questions as shown in the following output. The responses are bolded.
R3# auto secure
--- AutoSecure Configuration ---
*** AutoSecure configuration enhances the security of
the router but it will not make router absolutely secure
from all security attacks ***
All the configuration done as part of AutoSecure will be
shown here. For more details of why and how this configuration
is useful, and any possible side effects, please refer to Cisco
documentation of AutoSecure.
At any prompt you may enter '?' for help.
Use ctrl-c to abort this session at any prompt.
If this device is being managed by a network management station,
AutoSecure configuration may block network management traffic.
Continue with AutoSecure? [no]: yes
Gathering information about the router for AutoSecure
Is this router connected to internet? [no]: yes
Enter the number of interfaces facing internet [1]:
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 10.2.2.1 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 192.168.3.1 YES manual up up
Serial0/1/0 unassigned YES unset up up
Serial0/1/1 unassigned YES unset up up
Enter the interface name that is facing internet: GigabitEthernet0/0/0
Securing Management plane services..
Disabling service finger
Disabling service pad
Disabling udp & tcp small servers
Enabling service password encryption
Enabling service tcp-keepalives-in
Enabling service tcp-keepalives-out
Disabling the cdp protocol
Disabling the bootp server
Disabling the http server
Disabling the finger service
Disabling source routing
Disabling gratuitous arp
Here is a sample Security Banner to be shown
at every access to device. Modify it to suit your
enterprise requirements.
Authorized Access only
This system is the property of So-&-So-Enterprise.
UNAUTHORIZED ACCESS TO THIS DEVICE IS PROHIBITED.
You must have explicit permission to access this
device. All activities performed on this device
are logged. Any violations of access policy will result
in disciplinary action.
Enter the security banner {Put the banner between
k and k, where k is any character}:
# Unauthorized Access Prohibited #
Enable secret is either not configured or
is the same as the enable password
Enter the new enable secret: cisco12345
Confirm the enable secret : cisco12345
Enter the new enable password: 12345cisco
Confirm the enable password: 12345cisco
Configuration of local user database
Enter the username: admin
Enter the password: adminpasswd
Confirm the password: adminpasswd
Configuring AAA local authentication
Configuring console, Aux and vty lines for
local authentication, exec-timeout, transport
Securing device against Login Attacks
Configure the following parameters
Blocking Period when Login Attack detected: 60
Maximum Login failures with the device: 2
Maximum time period for crossing the failed login attempts: 30
Configure SSH server? [yes]: [Enter]
Enter the domain-name: www.netsec.com
Configuring interface specific AutoSecure services
Disabling the following ip services on all interfaces:
no ip redirects
no ip proxy-arp
no ip unreachables
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip mask-reply
Securing Forwarding plane services..
Enabling unicast rpf on all interfaces connected
to internet
Configure CBAC Firewall feature? [yes/no]: no
This is the configuration generated:
no service finger
no service pad
no service udp-small-servers
no service tcp-small-servers
service password-encryption
service tcp-keepalives-in
service tcp-keepalives-out
no cdp run
no ip bootp server
no ip http server
no ip finger
no ip source-route
no ip gratuitous-arps
banner motd ^C Unauthorized Access Prohibited ^C
security passwords min-length 6
security authentication failure rate 10 log
enable secret 5 $1$lubv$Rdx4gHUcijbxV7p2z76/71
enable password 7 110A1016141D5D5B5C737B
username admin password 7 02050D4808095E731F1A5C
aaa new-model
aaa authentication login local_auth local
line console 0
login authentication local_auth
exec-timeout 5 0
transport output telnet
line aux 0
login authentication local_auth
exec-timeout 10 0
transport output telnet
line vty 0 4
login authentication local_auth
transport input telnet
line tty 1
login authentication local_auth
exec-timeout 15 0
login block-for 60 attempts 2 within 30
ip domain-name www.netsec.com
crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus 1024
ip ssh time-out 60
ip ssh authentication-retries 2
line vty 0 4
transport input ssh telnet
service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime show-timezone
service timestamps log datetime msec localtime show-timezone
logging facility local2
logging trap debugging
service sequence-numbers
logging console critical
logging buffered
int GigabitEthernet0/0/0
no ip redirects
no ip proxy-arp
no ip unreachables
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip mask-reply
int GigabitEthernet0/0/1
no ip redirects
no ip proxy-arp
no ip unreachables
no ip directed-broadcast
no ip mask-reply
ip access-list extended 100
permit udp any any eq bootpc
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx 100
!
end
Apply this configuration to running-config? [yes]: [Enter]
Applying the config generated to running-config
WARNING: Command has been added to the configuration using a type 5
password. However, type 5 passwords will soon be deprecated. Migrate to a
supported password type
WARNING: Command has been added to the configuration using a type 7
password. However, type 7 passwords will soon be deprecated. Migrate to a
supported password type
WARNING: Command has been added to the configuration using a type 7
password. However, type 7 passwords will soon be deprecated. Migrate to a
supported password typeThe name for the keys will be: R3.www.netsec.com
% The key modulus size is 1024 bits
% Generating 1024 bit RSA keys, keys will be non-exportable...
[OK] (elapsed time was 0 seconds)
R3#
Note: The questions asked and the output may vary depend on the features on the IOS image and device.
Step 2: Establish an SSH connection from PC-C to R3.
a. Start PuTTy or another SSH client, and log in with the admin account and password adminpasswd created when AutoSecure was run. Enter the IP address of the R3 G0/0/1 interface 192.168.3.1.
b. Because SSH was configured using AutoSecure on R3, you will receive a PuTTY security warning. Click Yes to connect anyway.
c. Enter privileged EXEC mode with password cisco12345, and verify the R3 configuration using the show run command.
Step 3: Contrast the AutoSecure-generated configuration of R3 with the manual configuration of R1.
1. What security-related configuration changes were performed on R3 by AutoSecure that were not performed in previous sections of the lab on R1?
Answers will vary but could include: AutoSecure enables AAA and creates a named authentication list (local_auth). Console, AUX, and vty logins are set up for local authentication. The security authentication failure rate 10 log command was added. The tcp intercept feature was enabled, ip http server was disabled, cdp was disabled, security passwords min-length is set to 6. Logging trap debugging was enabled. Other minor but potentially exploitable services were disabled. An enable password was created. Logging buffered and logging console critical were enabled.
2. What security-related configuration changes were performed in previous sections of the lab that were not performed by AutoSecure?
Answers will vary but could include: Telnet access was excluded from vty transport input. Additional accounts were created.
3. Identify at least five unneeded services that were locked down by AutoSecure and at least three security measures applied to each interface.
Note: Some of the services listed as being disabled in the AutoSecure output above might not appear in the show running-config output because they are already disabled by default for this router and Cisco IOS version.
Services disabled include:
no service pad no cdp run no ip bootp server no ip http server no ip source-route no ip gratuitous-arps no ip identd
For each interface, the following were disabled:
no ip redirects no ip proxy-arp no ip unreachables
4. What are some advantages to using AutoSecure?
This tool can catch security vulnerabilities that many network administrators might overlook or be unaware of. It can lock down a router much faster than entering one command at a time and the tools result in less potential for entry errors. Also, the tool avoids the need to use complex Cisco IOS commands and procedures.
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 4221 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 4300 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
Device Configs
Router R1
R1# show run Building configuration… Current configuration : 1932 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! security passwords min-length 10 enable secret 9 $9$608LjMVuvbEJZK$bG8hofgigO/nhdeamLoGOaHSBNqCt7DvjDQECDEbWrs ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ip domain name netsec.com ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! username user01 secret 9 $9$M.j0HXA.eYS.6a$fZzGLtwBmw7/MyYlkNO1J3tPKPZEnEdFeem7vgrfdQw username admin privilege 15 secret 9 $9$tsj8PFFTy1v294$1WywiLRIrkYnnjWn/6B4HnGRPDkFOMC/iGn5m6operU ! redundancy mode none ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 negotiation auto ! router ospf 1 passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ! ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server ip http secure-server ! ip ssh time-out 90 ip ssh authentication-retries 2 ip ssh version 2 ! control-plane ! banner motd ^C Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited! ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 5 0 logging synchronous login local transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 exec-timeout 5 0 login local stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 5 0 privilege level 15 login local transport input ssh end
Router R2
R2# show run Building configuration… Current configuration : 1138 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! redundancy mode none ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.252 negotiation auto ! router ospf 1 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 ! ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server ip http secure-server ! control-plane ! line con 0 logging synchronous transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 login ! end
Router R3
R3# show run Building configuration… Current configuration : 2604 bytes ! version 16.9 no service pad service tcp-keepalives-in service tcp-keepalives-out service timestamps debug datetime msec localtime show-timezone service timestamps log datetime msec localtime show-timezone service password-encryption service sequence-numbers platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R3 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! security authentication failure rate 10 log security passwords min-length 6 logging console critical enable secret 5 $1$KRNj$os8y9zWDfLjSVDb2Ol.eS1 enable password 7 091D1C5A4D50141B180F0B ! aaa new-model ! aaa authentication login local_auth local ! aaa session-id common no ip source-route no ip gratuitous-arps ! no ip bootp server no ip domain lookup ip domain name netsec.com ! ! login block-for 60 attempts 2 within 30 login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! username admin password 7 011202095205160E325F590D ! redundancy mode none ! no cdp run ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.252 no ip redirects no ip unreachables no ip proxy-arp ip verify unicast source reachable-via rx 100 negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects no ip unreachables no ip proxy-arp negotiation auto ! interface Serial0/1/0 no ip address no ip redirects no ip unreachables no ip proxy-arp ! interface Serial0/1/1 no ip address no ip redirects no ip unreachables no ip proxy-arp ! router ospf 1 passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ! ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server ip http secure-server ! ip ssh time-out 60 ip ssh authentication-retries 2 ! logging trap debugging logging facility local2 ip access-list extended 100 permit udp any any eq bootpc ! control-plane ! banner motd ^C Unauthorized Access Prohibited ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 5 0 logging synchronous login authentication local_auth transport input none transport output telnet stopbits 1 line aux 0 exec-timeout 15 0 login authentication local_auth transport output telnet stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 login authentication local_auth transport input telnet ssh ! end
