1.1.7 Packet Tracer – Basic Switch Configuration – Physical Mode Answers
Topology

1.1.7 Packet Tracer – Basic Switch Configuration – Physical Mode
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address / Prefix |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | VLAN 99 | 192.168.1.2 /24 |
| 2001:db8:acad:1::2 /64 | ||
| fe80::2 | ||
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.1.10 /24 |
| 2001:db8:acad:1::10 /64 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Cable the Network and Verify the Default Switch Configuration
- Part 2: Configure Basic Network Device Settings
- Part 3: Verify and Test Network Connectivity
Background / Scenario
Cisco switches can be configured with a special IP address known as the switch virtual interface (SVI). The SVI, or management address, can be used for remote access to the switch to display or configure settings. If the VLAN 1 SVI is assigned an IP address, by default, all ports on VLAN 1 have access to the SVI IP address.
In this activity, you will build a simple topology using Ethernet LAN cabling to access a Cisco switch using the console and remote access methods. You will examine default switch configurations before configuring basic switch settings. These basic switch settings include device name, interface description, local passwords, message of the day (MOTD) banner, IP addressing, and static MAC address. You will also use a management IP address for remote switch management. The topology consists of one switch and two hosts using only Ethernet and console ports. You will verify network connectivity and manage a MAC address table using two end devices.
Instructions
Part 1: Cable the Network and Verify the Default Switch Configuration
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and verify default switch settings.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
a. From the shelf, click and drag switch S1 and place it on the left side of the table.
b. From the shelf, click and drag the device PC-A and place it on the right side of the table. Power on PC-A.
c. Connect a console cable from device PC-A to switch S1, as shown in the topology. Do not connect the device PC-A Ethernet cable at this time.
d. From the Desktop tab of PC-A, use Terminal to connect to the switch.
Why must you use a console connection to initially configure the switch? Why is it not possible to connect to the switch via Telnet or SSH?
No IP addressing parameters are configured yet. A Cisco 3650 switch first placed into service has no networking configured.
Step 2: Verify the default switch configuration.
In this step, you will examine the default switch settings, such as current switch configuration, IOS information, interface properties, VLAN information, and flash memory.
You can access all of the switch IOS commands in privileged EXEC mode. Access to privileged EXEC mode should be restricted by password protection to prevent unauthorized use because it provides direct access to global configuration mode and commands used to configure operating parameters. You will set passwords later in this activity.
The privileged EXEC mode command set includes those commands contained in user EXEC mode, as well as the configure command through which the access to the remaining command modes is gained. Use the enable command to enter privileged EXEC mode.
a. Assuming the switch had no configuration file stored in nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM), a console connection using Terminal will place you at the user EXEC mode prompt on the switch with a prompt of Switch>. Use the enable command to enter privileged EXEC mode.
Switch> enable Switch#
Notice that the prompt changed in the configuration to reflect privileged EXEC mode.
b. Verify that there is a clean default configuration file on the switch by issuing the show running-config privileged EXEC mode command. Examine the current running configuration file.
Switch# show running-config
How many GigabitEthernet interfaces does the switch have?
28
What is the range of values shown for the vty lines?
0-4 and 5-15
c. Examine the startup configuration file in NVRAM.
Switch# show startup-config startup-config is not present
Why does this message appear?
No configurations have been saved to NVRAM.
d. Examine the characteristics of the SVI for VLAN 1.
Switch# show interface vlan1
Is there an IP address assigned to VLAN 1?
No
What is the MAC address of this SVI? Answers will vary.
Answers will vary. In this activity the MAC address is 0060.2fde.172d.
Is this interface up?
Cisco switches have the shutdown command configured by default on VLAN 1, and VLAN 1 will not reach the up/up state until a port is assigned to it and this port is also up. If there is no port in the up state in VLAN 1, then the VLAN 1 interface will be up, line protocol down. By default, all ports are initially assigned to VLAN 1.
e. Examine the IP properties of the SVI VLAN 1.
Switch# show ip interface vlan1
What output do you see?
Vlan1 is administratively down, line protocol is down. The internet protocol processing is disabled.
f. Connect an Ethernet cable from PC-A to GigabitEthernet1/0/6 on the switch. Allow time for the switch and PC to negotiate duplex and speed parameters. Examine the IP properties of the SVI VLAN 1.
What output do you see?
The vlan1 is administratively down, the line protocol is down, and the internet protocol processing is disabled.
g. Enter global configuration and enable the SVI VLAN 1 interface.
Switch# configure terminal Switch (config)# interface VLAN 1 Switch (config-if)# no shutdown
h. Examine the IP properties of the SVI VLAN 1.
Switch# show ip interface vlan1
What output do you see?
The vlan1 is up, and the line protocol is down.
Internet protocol processing disabled
i. Examine the Cisco IOS version information of the switch.
Switch# show version
What is the Cisco IOS version that the switch is running?
Answers may vary. In this activity the version is Version 16.3.2, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc4).
What is the system image filename?
Answers may vary. In this activity the image is cat3k_caa-universalk9.16.03.02.SPA.bin.
What is the base Ethernet MAC address of this switch?
Answers will vary. In this activity the base Ethernet MAC address is 00:60:2F:DE:17:2D
j. Examine the default properties of the GigabitEthernet1/0/6 interface used by PC-A.
Switch# show interface gig1/0/6
Is the interface up or down?
The interface is up.
What event would make an interface go down?
Removing the cable or enter the command ‘shutdown’ on the interface.
What is the MAC address of the interface?
Answers will vary. In this activity the address is 000c.8589.1806.
What is the speed and duplex setting of the interface?
Full-duplex, 100Mbps
k. Examine the default VLAN settings of the switch.
Switch# show vlan
What is the name of VLAN 1?
default
Which ports are in VLAN 1?
all ports; Gig1/0/1 – Gig1/0/24; Gig1/1/1 – Gig1/1/4
Is VLAN 1 active?
Yes
What type of VLAN is the default VLAN?
enet (Ethernet)
l. Examine flash memory.
Issue one of the following commands to examine the contents of the flash directory.
Switch# show flash: Switch# dir flash:
Files have a file extension, such as .bin, at the end of the filename. Directories do not have a file extension.
What is the filename of the Cisco IOS image?
Answers will vary. In this activity the image filename is cat3k_caa-universalk9.16.03.02.SPA.bin.
Part 2: Configure Basic Network Device Settings
In Part 2, you will configure basic settings for the switch and PC.
Step 1: Configure basic switch settings.
a. Copy the following basic configuration and paste it into S1 while in global configuration mode.
no ip domain-lookup hostname S1 service password-encryption enable secret class banner motd # Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited. #
b. Set the SVI IP address of the switch. This allows remote management of the switch.
Before you can manage S1 remotely from PC-A, you must assign the switch an IP address. The default configuration on the switch is to have the management of the switch controlled through VLAN 1. However, a best practice for basic switch configuration is to change the management VLAN to a VLAN other than VLAN 1.
For management purposes, use VLAN 99. The selection of VLAN 99 is arbitrary and in no way implies that you should always use VLAN 99.
First, create the new VLAN 99 on the switch. Next, set the IP address of the switch to 192.168.1.2 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 on the internal virtual interface VLAN 99. An IPv6 address can also be configured on the SVI interface. Use the IPv6 addresses listed in the Addressing Table.
S1# configure terminal S1(config)# vlan 99 S1(config-vlan)# exit S1(config)# interface vlan99 %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Vlan99, changed state to up S1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 S1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1::2/64 S1(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local S1(config-if)# no shutdown S1(config-if)# exit
Notice that the VLAN 99 interface is in the down state even though you entered the no shutdown command. The interface is currently down because no switch ports are assigned to VLAN 99.
c. Assign all user ports to VLAN 99.
S1(config)# interface range gig1/0/1-24
S1(config-if-range)# switchport access vlan 99
S1(config-if-range)# exit
S1(config)#
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Vlan99, changed state to up
To establish connectivity between the host and the switch, the ports used by the host must be in the same VLAN as the switch. After a few seconds, VLAN 99 comes up because at least one active port (Fa0/6 with PC-A attached) is now assigned to VLAN 99.
d. Issue the show vlan brief command to verify that all ports are in VLAN 99.
S1#show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Gig1/1/1, Gig1/1/2, Gig1/1/3, Gig1/1/4
99 VLAN0099 active Gig1/0/1, Gig1/0/2, Gig1/0/3, Gig1/0/4
Gig1/0/5, Gig1/0/6, Gig1/0/7, Gig1/0/8
Gig1/0/9, Gig1/0/10, Gig1/0/11, Gig1/0/12
Gig1/0/13, Gig1/0/14, Gig1/0/15, Gig1/0/16
Gig1/0/17, Gig1/0/18, Gig1/0/19, Gig1/0/20
Gig1/0/21, Gig1/0/22, Gig1/0/23, Gig1/0/24
1002 fddi-default active
1003 token-ring-default active
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trnet-default active
S1#
e. Configure the default gateway for S1. If no default gateway is set, the switch cannot be managed from a remote network that is more than one router away. Although this activity does not include an external IP gateway, assume that you will eventually connect the LAN to a router for external access. Assuming that the LAN interface on the router is 192.168.1.1, set the default gateway for the switch.
S1(config)# ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
f. Console port access should also be restricted with a password. Use cisco as the console login password in this activity. The default configuration is to allow all console connections with no password needed. To prevent console messages from interrupting commands, use the logging synchronous option.
S1(config)# line con 0 S1(config-line)# logging synchronous S1(config-line)# password cisco S1(config-line)# login S1(config-line)# exit
g. Configure the virtual terminal (vty) lines for the switch to allow Telnet access. If you do not configure a vty password, you will not be able to use Telnet to access the switch.
S1(config)# line vty 0 15 S1(config-line)# password cisco S1(config-line)# login S1(config-line)# end S1# *Mar1 00:06:11.590: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Why is the login command required?
Without the login command, the switch will not prompt you for a password.
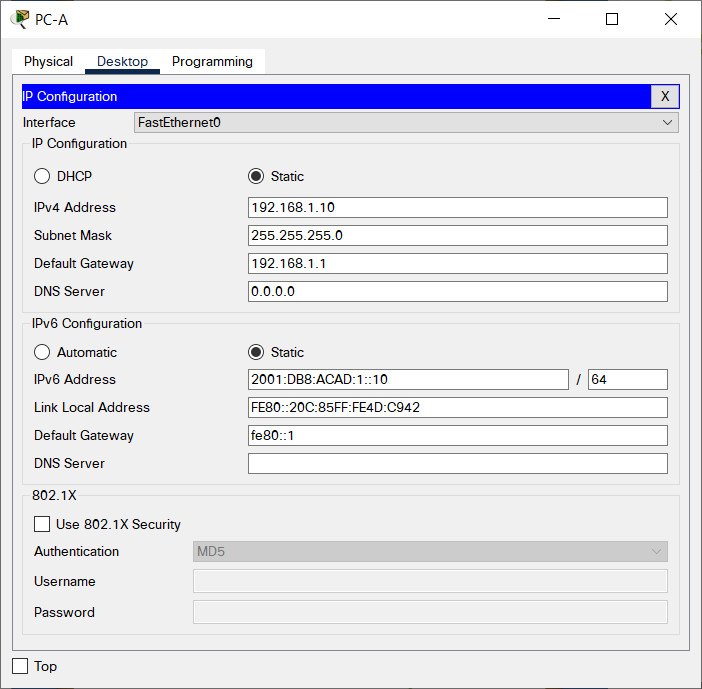
Step 2: Configure an IP address on PC-A.
Assign the IP address and subnet mask to the PC, as shown in the Addressing Table. An abbreviated version of the procedure is described here. A default gateway is not required for this topology to function; however, you should enter 192.168.1.1 and fe80::1 to simulate a router attached to S1.
a. Navigate to the Desktop tab.
b. Click IP Configuration.
c. Verify that the Static IP Configuration radial button is selected.
d. Enter the IPv4 address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
e. Verify that the Static IPv6 Configuration radial button is selected.
f. Enter the IPv6 address, prefix, and default gateway
g. Click the X to close the IP Configuration window.
Part 3: Verify and Test Network Connectivity
In Part 3, you will verify and document the switch configuration, test end-to-end connectivity between PC-A and S1, and test the remote management capability of the switch.
Step 1: Display the switch configuration.
Use the console connection on PC-A to display and verify the switch configuration. The show run command displays the entire running configuration, one page at a time. Use the spacebar to advance paging.
a. A sample configuration is shown here. The settings you configured are highlighted in yellow. The other configuration settings are IOS defaults.
S1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2424 bytes ! version 16.3.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname S1 ! enable secret 5 $1$mERr$9cTjUIEqNGurQiFU.ZeCi1! no ip cef no ipv6 cef ! ! no ip domain-lookup ! <output omitted> ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6 switchport access vlan 99 ! <output omitted> ! interface GigabitEthernet1/0/24 switchport access vlan 99 ! <output omitted> ! interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown ! interface Vlan99 mac-address 00e0.f795.d201 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::2/64 ! ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1 ip classless ! banner motd ^C Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited. ^C ! line con 0 password 7 0822455D0A16 logging synchronous login line vty 0 4 password 7 0822455D0A16 login line vty 5 15 password 7 0822455D0A16 login ! end
b. Verify the management VLAN 99 settings.
S1# show interface vlan 99 Vlan99 is up, line protocol is down Hardware is CPU Interface, address is 0060.2fde.1701 (bia 0060.2fde.1701) Internet address is 192.168.1.2/24 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 100000 Kbit, DLY 1000000 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set ARP type: ARPA, ARP Timeout 04:00:00 Last input 21:40:21, output never, output hang never Last clearing of "show interface" counters never Input queue: 0/75/0/0 (size/max/drops/flushes); Total output drops: 0 Queueing strategy: fifo Output queue: 0/40 (size/max) 5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec 1682 packets input, 530955 bytes, 0 no buffer Received 0 broadcasts (0 IP multicast) 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles 0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored 563859 packets output, 0 bytes, 0 underruns 0 output errors, 23 interface resets 0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
What is the bandwidth on this interface?
100000 Kbps (100Mbps)
What is the VLAN 99 state?
Up
What is the line protocol state?
Up
Step 2: Test end-to-end connectivity with ping.
Verify that PC-A can ping the IPv4 and IPv6 address for S1.
C:\> ping 192.168.1.2 C:\> ping 2001:db8:acad:1::2
Because PC-A needs to resolve the MAC address of S1 through ARP, the first packet may time out. If ping results continue to be unsuccessful, troubleshoot the basic device configurations. Check both the physical cabling and logical addressing.
Step 3: Test and verify remote management of S1.
You will now use Telnet to remotely access the switch. In this activity, PC-A and S1 reside side by side. In a production network, the switch could be in a wiring closet on the top floor while your management PC is located on the ground floor. In this step, you will use Telnet to remotely access switch S1 using the SVI management address. Telnet is not a secure protocol; however, you will use it to test remote access. With Telnet, all information, including passwords and commands, are sent in plaintext. In subsequent activities, you will use SSH to remotely access network devices.
a. Open the Desktop tab on PC-A.
b. Scroll down in the listing of apps and click the Telnet/SSH Client.
c. Set the Connection Type to be Telnet.
d. Enter the SVI management address to connect to S1 and click Connect.
e. After entering the password cisco, you will be at the user EXEC mode prompt. Access privileged EXEC mode using the enable command and providing the secret password class.
f. Save the configuration.
g. Type exit to end the Telnet session. Click No to the pop-up.
Step 4: Deploy switch S1 on the production network.
You will now install switch S1 on the production network and disconnect the console cable. Telnet will be used to remotely access the switch and complete any additional configuration and verification. In subsequent activities, you will use SSH to remotely access network devices.
a. Move switch S1 to the Rack.
b. Right-click switch S1 and select Inspect Rear.
c. Click and drag the console cable to the peg board.
Reflection Questions
1. Why should you configure the vty password for the switch?
If you do not configure a vty password you will not be able to use Telnet to access the switch.
2. Why change the default VLAN 1 to a different VLAN number?
For improved security.
3. How can you prevent passwords from being sent in plaintext?
Issue the service password-encryption command.

no ip domain-lookup
hostname S1
service password-encryption
enable secret class
banner motd # Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited. #
vlan 99
exit
interface vlan99
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1::2/64
ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local
no shutdown
exit
interface range gig1/0/1-24
switchport access vlan 99
exit
ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1
line con 0
logging synchronous
password cisco
login
exit
line vty 0 15
password cisco
login
end
copy startup-config running-config
What is the bandwidth on this interface?
1000000 Kbps (1 Gbps)
I think this is (100Mbps)
Fixed it, thanks!
3. How can you prevent passwords from being sent in plaintext?
Using SSH Protocol instead of Telnet
I jumped into the CISCO Netwoking Academy CCNA2 instruction. Where did you find the S1, Routes, Ip Default-gateway information for 1.1.7 packet tracer lab?
no matter what I do this one says the ip default-gateway is wrong when I check results, even when I put 192.168.1.1 and my show run matches the example given IN THE PACKET TRACER, bugged I think
Same here. Most likely misconfigured pkt file.
switch cofiguretion