8.5.5 Packet Tracer – Configure Named Standard IPv4 ACLs Answers Version
Topology
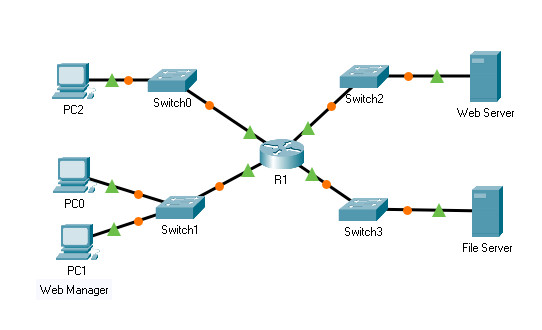
8.5.5 Packet Tracer – Configure Named Standard IPv4 ACLs
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | F0/0 | 192.168.10.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| F0/1 | 192.168.20.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| E0/0/0 | 192.168.100.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| E0/1/0 | 192.168.200.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| File Server | NIC | 192.168.200.100 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.200.1 |
| Web Server | NIC | 192.168.100.100 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.100.1 |
| PC0 | NIC | 192.168.20.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.20.1 |
| PC1 | NIC | 192.168.20.4 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.20.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 192.168.10.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.10.1 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Configure and Apply a Named Standard ACL
- Part 2: Verify the ACL Implementation
Background / Scenario
The senior network administrator has asked you to create a standard named ACL to prevent access to a file server. The file server contains the data base for the web applications. Only the Web Manager workstation PC1 and the Web Server need to access the File Server. All other traffic to the File Server should be denied.
Instructions
Part 1: Configure and Apply a Named Standard ACL
Step 1: Verify connectivity before the ACL is configured and applied.
All three workstations should be able to ping both the Web Server and File Server.
Step 2: Configure a named standard ACL.
a. Configure the following named ACL on R1.
R1(config)# ip access-list standard File_Server_Restrictions R1(config-std-nacl)# permit host 192.168.20.4 R1(config-std-nacl)# permit host 192.168.100.100 R1(config-std-nacl)# deny any
Note: For scoring purposes, the ACL name is case-sensitive, and the statements must be in the same order as shown.
b. Use the show access-lists command to verify the contents of the access list before applying it to an interface. Make sure you have not mistyped any IP addresses and that the statements are in the correct order.
R1# show access-lists Standard IP access list File_Server_Restrictions 10 permit host 192.168.20.4 20 permit host 192.168.100.100 30 deny any
Step 3: Apply the named ACL.
a. Apply the ACL outbound on the Fast Ethernet 0/1 interface.
Note: In an actual operational network, applying an access list to an active interface is not a good practice and should be avoided if possible.
R1(config-if)# ip access-group File_Server_Restrictions out
b. Save the configuration.
Part 2: Verify the ACL Implementation
Step 1: Verify the ACL configuration and application to the interface.
Use the show access-lists command to verify the ACL configuration. Use the show run or show ip interface fastethernet 0/1 command to verify that the ACL is applied correctly to the interface.
Step 2: Verify that the ACL is working properly.
All three workstations should be able to ping the Web Server, but only PC1 and the Web Server should be able to ping the File Server. Repeat the show access-lists command to see the number of packets that matched each statement.
R1# show access-lists Standard IP access list File_Server_Restrictions 10 permit host 192.168.20.4 (4 match(es)) 20 permit host 192.168.100.100 (4 match(es)) 30 deny any (8 match(es))
Answer Scripts
Router R1
enable configure terminal ip access-list standard File_Server_Restrictions permit host 192.168.20.4 permit host 192.168.100.100 deny any interface f0/1 ip access-group File_Server_Restrictions out
