8.5.6 Packet Tracer – Configure Numbered Standard IPv4 ACLs Answers Version
Topology
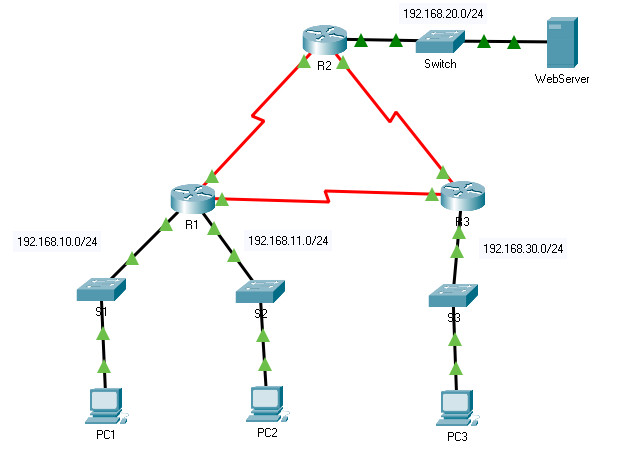
8.5.6 Packet Tracer – Configure Numbered Standard IPv4 ACLs
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0 | 192.168.10.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| G0/1 | 192.168.11.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| S0/0/0 | 10.1.1.1 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 10.3.3.1 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| R2 | G0/0 | 192.168.20.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 10.1.1.2 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 10.2.2.1 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| R3 | G0/0 | 192.168.30.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 10.3.3.2 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 10.2.2.2 | 255.255.255.252 | ||
| PC1 | NIC | 192.168.10.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.10.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 192.168.11.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.11.1 |
| PC3 | NIC | 192.168.30.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.30.1 |
| WebServer | NIC | 192.168.20.254 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.20.1 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Plan an ACL Implementation
- Part 2: Configure, Apply, and Verify a Standard ACL
Background / Scenario
Standard access control lists (ACLs) are router configuration scripts that control whether a router permits or denies packets based on the source address. This activity focuses on defining filtering criteria, configuring standard ACLs, applying ACLs to router interfaces, and verifying and testing the ACL implementation. The routers are already configured, including IP addresses and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) routing.
Instructions
Part 1: Plan an ACL Implementation
Step 1: Investigate the current network configuration.
Before applying any ACLs to a network, it is important to confirm that you have full connectivity. Verify that the network has full connectivity by choosing a PC and pinging other devices on the network. You should be able to successfully ping every device.
Step 2: Evaluate two network policies and plan ACL implementations.
a. The following network policies are implemented on R2:
- The 192.168.11.0/24 network is not allowed access to the WebServer on the 192.168.20.0/24 network.
- All other access is permitted.
To restrict access from the 192.168.11.0/24 network to the WebServer at 192.168.20.254 without interfering with other traffic, an ACL must be created on R2. The access list must be placed on the outbound interface to the WebServer. A second rule must be created on R2 to permit all other traffic.
b. The following network policies are implemented on R3:
- The 192.168.10.0/24 network is not allowed to communicate with the 192.168.30.0/24 network.
- All other access is permitted.
To restrict access from the 192.168.10.0/24 network to the 192.168.30/24 network without interfering with other traffic, an access list will need to be created on R3. The ACL must be placed on the outbound interface to PC3. A second rule must be created on R3 to permit all other traffic.
Part 2: Configure, Apply, and Verify a Standard ACL
Step 1: Configure and apply a numbered standard ACL on R2.
a. Create an ACL using the number 1 on R2 with a statement that denies access to the 192.168.20.0/24 network from the 192.168.11.0/24 network.
R2(config)# access-list 1 deny 192.168.11.0 0.0.0.255
b. By default, an access list denies all traffic that does not match any rules. To permit all other traffic, configure the following statement:
R2(config)# access-list 1 permit any
c. Before applying an access list to an interface to filter traffic, it is a best practice to review the contents of the access list, in order to verify that it will filter traffic as expected.
R2# show access-lists
Standard IP access list 1
10 deny 192.168.11.0 0.0.0.255
20 permit any
d. For the ACL to actually filter traffic, it must be applied to some router operation. Apply the ACL by placing it for outbound traffic on the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface. Note: In an actual operational network, it is not a good practice to apply an untested access list to an active interface.
R2(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0 R2(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out
Step 2: Configure and apply a numbered standard ACL on R3.
a. Create an ACL using the number 1 on R3 with a statement that denies access to the 192.168.30.0/24 network from the PC1 (192.168.10.0/24) network.
R3(config)# access-list 1 deny 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
b. By default, an ACL denies all traffic that does not match any rules. To permit all other traffic, create a second rule for ACL 1.
R3(config)# access-list 1 permit any
c. Verify that the access list is configured correctly.
R3# show access-lists
Standard IP access list 1
10 deny 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255
20 permit any
d. Apply the ACL by placing it for outbound traffic on the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface.
R3(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/0 R3(config-if)# ip access-group 1 out
Step 3: Verify ACL configuration and functionality.
a. Enter the show run or show ip interface gigabitethernet 0/0 command to verify the ACL placements.
b. With the two ACLs in place, network traffic is restricted according to the policies detailed in Part 1. Use the following tests to verify the ACL implementations:
- A ping from 192.168.10.10 to 192.168.11.10 succeeds.
- A ping from 192.168.10.10 to 192.168.20.254 succeeds.
- A ping from 192.168.11.10 to 192.168.20.254 fails.
- A ping from 192.168.10.10 to 192.168.30.10 fails.
- A ping from 192.168.11.10 to 192.168.30.10 succeeds.
- A ping from 192.168.30.10 to 192.168.20.254 succeeds.
c. Issue the show access-lists command again on routers R2 and R3. You should see output that indicates the number of packets that have matched each line of the access list. Note: The number of matches shown for your routers may be different, due to the number of pings that are sent and received.
R2# show access-lists
Standard IP access list 1
10 deny 192.168.11.0 0.0.0.255 (4 match(es))
20 permit any (8 match(es))
R3# show access-lists
Standard IP access list 1
10 deny 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 (4 match(es))
20 permit any (8 match(es))
Answer Configurations
Router R2
enable configure terminal interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip access-group 1 out access-list 1 deny 192.168.11.0 0.0.0.255 access-list 1 permit any end
Router R3
enable configure terminal interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip access-group 1 out access-list 1 deny 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 access-list 1 permit any end
