1. Which definition describes the term Internet?
- a group of PCs connected together on a LAN
- a group of PCs connected together by an ISP
- a network of networks that connects countries around the world
- a worldwide collection of networks controlled by a single organization
2. What type of connection point is a point of presence (POP)?
- between a client and a host
- between two local networks
- between a computer and a switch
- between an ISP and a home-based LAN
3. What is the term for the group of high-speed data links that interconnect ISPs?
- Internet LAN
- ISP backbone
- Internet gateways
- Internet providers
- Internet backbone
4. Which device can act as a router, switch, and wireless access point in one package?
- hub
- bridge
- modem
- repeater
- ISR
5. What are three characteristics of business class ISP service? (Choose three.)
- fast connections
- extra web space
- free Windows upgrade cheapest cost available to all users
- additional e-mail accounts
- replacement hardware at no cost
6. What is a major characteristic of asymmetric Internet service?
- Download speeds and upload speeds are equal.
- Download speeds are slower than upload speeds
- Upload speeds and download speeds are different.
- Upload speeds and download speeds are irrelevant.
7. Which three elements are required to successfully connect to the Internet? (Choose three.)
- an IP address
- file sharing enabled
- a network connection
- server services enabled
- access to an Internet service provider
- an address obtained directly from the RIR
8. What term describes each router through which a packet travels when moving between source and destination networks?
- NOC
- ISP
- hop
- segment
9. What does the tracert command test?
- NIC functionality
- the ISP bandwidth
- the network path to a destination
- the destination application functionality
10. What type of end-user connectivity requires that an ISP have a DSLAM device in their network?
- analog technology
- cable modem technology
- digital subscriber line technology
- wireless technology
11. Why would an ISP require a CMTS device on their network?
- to connect end users using cable technology
- to connect end users using analog technology
- to connect end users using wireless technology
- to connect end users using digital subscriber line technology
12. Refer to the graphic. What type of cabling is shown?

- STP
- UTP
- coax
- fiber
13. Refer to the graphic. What type of cabling is shown?

- STP
- UTP
- coax
- fiber
14. Which two places are most appropriate to use UTP cabling? (Choose two.)
- between buildings
- in a home office network
- where EMI is an issue in a cable TV network
- inside a school building
- in a manufacturing environment with hundreds of electrical devices
15. What does adherence to cabling standards ensure?
- data security
- no loss of signal
- no electromagnetic interference
- reliable data communications
16. Refer to the graphic. What type of cable is shown?
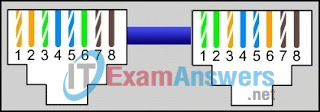
- crossover
- eight coax channels
- multimode fiber
- single-mode fiber
- straight-through
17. What connector is used to terminate Ethernet unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cabling?
- ST
- BNC
- RJ-11
- RJ-45
18. Which two characteristics describe copper patch panels? (Choose two.)
- uses RJ-11 jacks
- uses RJ-45 jacks
- supports only data transmissions
- allows quick rearrangements of network connections
- forwards transmissions based on MAC addresses
19. What are two advantages of cable management? (Choose two.)
- requires no preplanning
- aids in isolation of cabling problems
- protects cables from physical damage
- provides compliance with future standards
- provides a short-term solution for cable installation
20. What are two common causes of signal degradation when using UTP cabling? (Choose two.)
- installing cables in conduit
- having improper termination
- losing light over long distances
- installing low quality cable shielding
- using low quality cables or connectors
21. What are three commonly followed standards for constructing and installing cabling? (Choose three.)
- pinouts
- cable lengths
- connector color
- connector types
- cost per meter (foot)
- tensile strength of plastic insulator
