Packet Tracer – Configuring a Zone-Based Policy Firewall (ZPF)
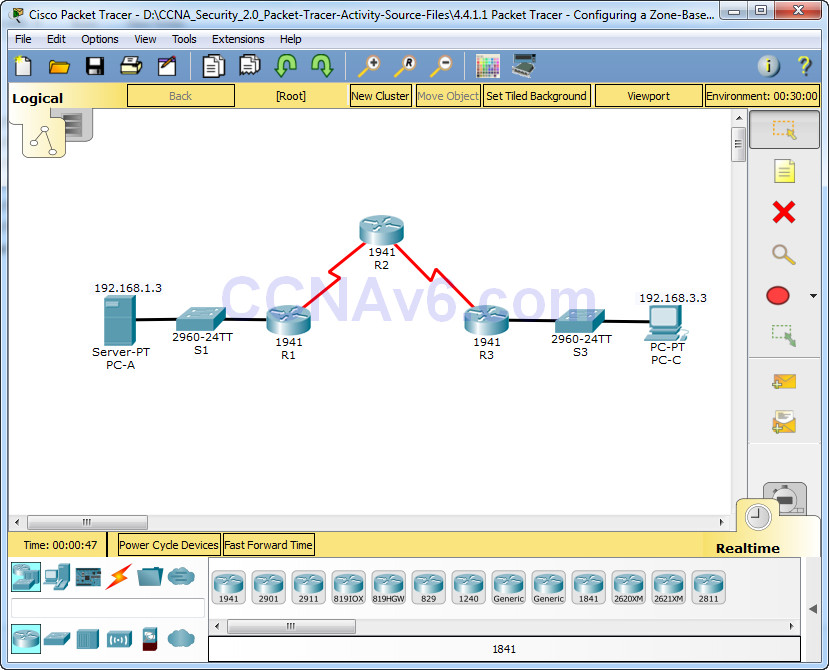
Topology
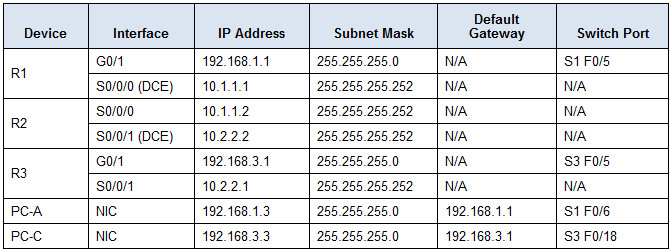
Addressing Table
Objectives
• Verify connectivity among devices before firewall configuration.
• Configure a zone-based policy (ZPF) firewall on R3.
• Verify ZPF firewall functionality using ping, SSH, and a web browser.
Background/Scenario
ZPFs are the latest development in the evolution of Cisco firewall technologies. In this activity, you will configure a basic ZPF on an edge router R3 that allows internal hosts access to external resources and blocks external hosts from accessing internal resources. You will then verify firewall functionality from internal and external hosts.
The routers have been pre-configured with the following:
• Console password: ciscoconpa55
• Password for vty lines: ciscovtypa55
• Enable password: ciscoenpa55
• Host names and IP addressing
• Local username and password: Admin / Adminpa55
• Static routing
Part 1: Verify Basic Network Connectivity
Verify network connectivity prior to configuring the zone-based policy firewall.
Step 1: From the PC-A command prompt, ping PC-C at 192.168.3.3.
Step 2: Access R2 using SSH.
a. From the PC-C command prompt, SSH to the S0/0/1 interface on R2 at 10.2.2.2. Use the username Admin and password Adminpa55 to log in.
PC> ssh -l Admin 10.2.2.2
b. Exit the SSH session.
Step 3: From PC-C, open a web browser to the PC-A server.
a. Click the Desktop tab and then click the Web Browser application. Enter the PC-A IP address 192.168.1.3 as the URL. The Packet Tracer welcome page from the web server should be displayed.
b. Close the browser on PC-C.
Part 2: Create the Firewall Zones on R3
Note: For all configuration tasks, be sure to use the exact names as specified.
Step 1: Enable the Security Technology package.
a. On R3, issue the show version command to view the Technology Package license information.
b. If the Security Technology package has not been enabled, use the following command to enable the package.
R3(config)# license boot module c1900 technology-package securityk9
c. Accept the end-user license agreement.
d. Save the running-config and reload the router to enable the security license.
e. Verify that the Security Technology package has been enabled by using the show version command.
Step 2: Create an internal zone.
Use the zone security command to create a zone named IN-ZONE.
R3(config)# zone security IN-ZONE R3(config-sec-zone) exit
Step 3: Create an external zone.
Use the zone security command to create a zone named OUT-ZONE.
R3(config-sec-zone)# zone security OUT-ZONE R3(config-sec-zone)# exit
Part 3: Identify Traffic Using a Class-Map
Step 1: Create an ACL that defines internal traffic.
Use the access-list command to create extended ACL 101 to permit all IP protocols from the 192.168.3.0/24 source network to any destination.
R3(config)# access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 any
Step 2: Create a class map referencing the internal traffic ACL.
Use the class-map type inspect command with the match-all option to create a class map named IN-NET-CLASS-MAP. Use the match access-group command to match ACL 101.
R3(config)# class-map type inspect match-all IN-NET-CLASS-MAP R3(config-cmap)# match access-group 101 R3(config-cmap)# exit
Part 4: Specify Firewall Policies
Step 1: Create a policy map to determine what to do with matched traffic.
Use the policy-map type inspect command and create a policy map named IN-2-OUT-PMAP.
R3(config)# policy-map type inspect IN-2-OUT-PMAP
Step 2: Specify a class type of inspect and reference class map IN-NET-CLASS-MAP.
R3(config-pmap)# class type inspect IN-NET-CLASS-MAP
Step 3: Specify the action of inspect for this policy map.
The use of the inspect command invokes context-based access control (other options include pass and drop).
R3(config-pmap-c)# inspect %No specific protocol configured in class IN-NET-CLASS-MAP for inspection. All protocols will be inspected.
Issue the exit command twice to leave config-pmap-c mode and return to config mode.
R3(config-pmap-c)# exit R3(config-pmap)# exit
Part 5: Apply Firewall Policies
Step 1: Create a pair of zones.
Using the zone-pair security command, create a zone pair named IN-2-OUT-ZPAIR. Specify the source and destination zones that were created in Task 1.
R3(config)# zone-pair security IN-2-OUT-ZPAIR source IN-ZONE destination OUT-ZONE
Step 2: Specify the policy map for handling the traffic between the two zones.
Attach a policy-map and its associated actions to the zone pair using the service-policy type inspect command and reference the policy map previously created, IN-2-OUT-PMAP.
R3(config-sec-zone-pair)# service-policy type inspect IN-2-OUT-PMAP R3(config-sec-zone-pair)# exit R3(config)#
Step 3: Assign interfaces to the appropriate security zones.
Use the zone-member security command in interface configuration mode to assign G0/1 to IN-ZONE and S0/0/1 to OUT-ZONE.
R3(config)# interface g0/1 R3(config-if)# zone-member security IN-ZONE R3(config-if)# exit R3(config)# interface s0/0/1 R3(config-if)# zone-member security OUT-ZONE R3(config-if)# exit
Step 4: Copy the running configuration to the startup configuration.
Part 6: Test Firewall Functionality from IN-ZONE to OUT-ZONE
Verify that internal hosts can still access external resources after configuring the ZPF.
Step 1: From internal PC-C, ping the external PC-A server.
From the PC-C command prompt, ping PC-A at 192.168.1.3. The ping should succeed.
Step 2: From internal PC-C, SSH to the R2 S0/0/1 interface.
a. From the PC-C command prompt, SSH to R2 at 10.2.2.2. Use the username Admin and the password Adminpa55 to access R2. The SSH session should succeed.
b. While the SSH session is active, issue the command show policy-map type inspect zone-pair sessions on R3 to view established sessions.
R3# show policy-map type inspect zone-pair sessions policy exists on zp IN-2-OUT-ZPAIR Zone-pair: IN-2-OUT-ZPAIR Service-policy inspect : IN-2-OUT-PMAP Class-map: IN-NET-CLASS-MAP (match-all) Match: access-group 101 Inspect Number of Established Sessions = 1 Established Sessions Session 175216232 (192.168.3.3:1028)=>(10.2.2.2:22) tcp SIS_OPEN/TCP_ESTAB Created 00:00:25, Last heard 00:00:20 Bytes sent (initiator:responder) [1195:1256] Class-map: class-default (match-any) Match: any Drop (default action) 0 packets, 0 bytes
What is the source IP address and port number?
192.168.3.3:1028 (port 1028 is random)
What is the destination IP address and port number?
10.2.2.2:22 (SSH = port 22)
Step 3: From PC-C, exit the SSH session on R2 and close the command prompt window.
Step 4: From internal PC-C, open a web browser to the PC-A server web page.
Enter the server IP address 192.168.1.3 in the browser URL field, and click Go. The HTTP session should succeed. While the HTTP session is active, issue the command show policy-map type inspect zone-pair sessions on R3 to view established sessions.
Note: If the HTTP session times out before you execute the command on R3, you will have to click the Go button on PC-C to generate a session between PC-C and PC-A.
R3# show policy-map type inspect zone-pair sessions policy exists on zp IN-2-OUT-ZPAIR Zone-pair: IN-2-OUT-ZPAIR Service-policy inspect : IN-2-OUT-PMAP Class-map: IN-NET-CLASS-MAP (match-all) Match: access-group 101 Inspect Number of Established Sessions = 1 Established Sessions Session 565266624 (192.168.3.3:1031)=>(192.168.1.3:80) tcp SIS_OPEN/TCP_ESTAB Created 00:00:01, Last heard 00:00:01 Bytes sent (initiator:responder) [284:552] Class-map: class-default (match-any) Match: any Drop (default action) 0 packets, 0 bytes
What is the source IP address and port number?
192.168.3.3:1031 (port 1031 is random)
What is the destination IP address and port number?
192.168.1.3:80 (HTTP web = port 80)
Step 5: Close the browser on PC-C.
Part 7: Test Firewall Functionality from OUT-ZONE to IN-ZONE
Verify that external hosts CANNOT access internal resources after configuring the ZPF.
Step 1: From the PC-A server command prompt, ping PC-C.
From the PC-A command prompt, ping PC-C at 192.168.3.3. The ping should fail.
Step 2: From R2, ping PC-C.
From R2, ping PC-C at 192.168.3.3. The ping should fail.
Step 3: Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 100%. Click Check Results to see feedback and verification of which required components have been completed.