Packet Tracer – Configure IOS Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) Using the CLI
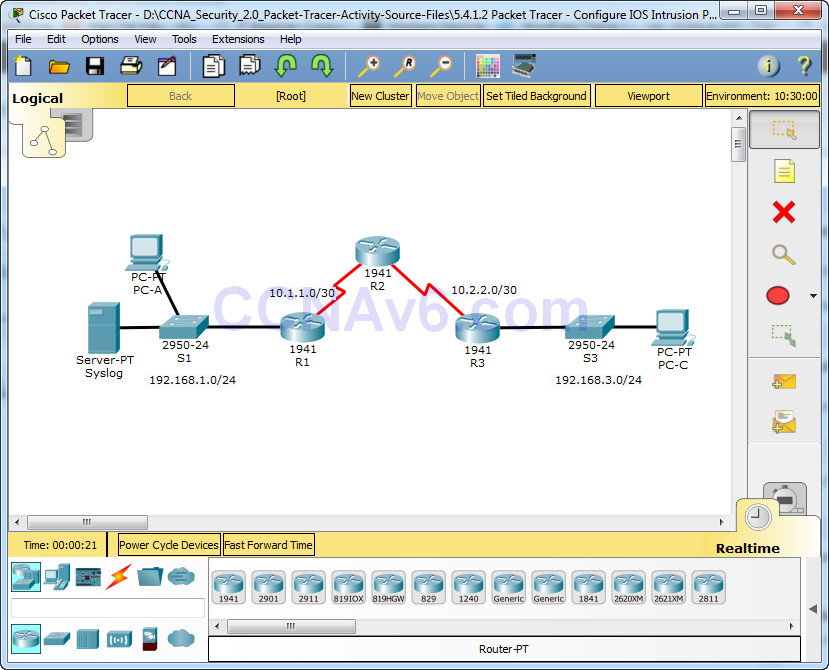
Topology
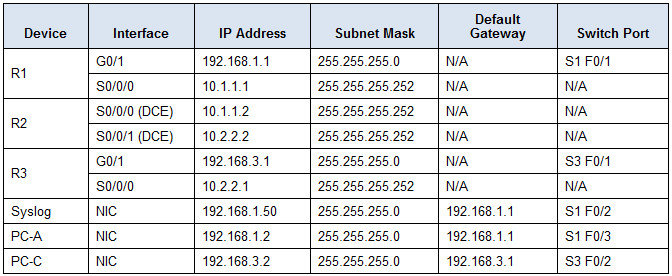
Addressing Table
Objectives
• Enable IOS IPS.
• Configure logging.
• Modify an IPS signature.
• Verify IPS.
Background / Scenario
Your task is to enable IPS on R1 to scan traffic entering the 192.168.1.0 network.
The server labeled Syslog is used to log IPS messages. You must configure the router to identify the syslog server to receive logging messages. Displaying the correct time and date in syslog messages is vital when using syslog to monitor the network. Set the clock and configure the timestamp service for logging on the routers. Finally, enable IPS to produce an alert and drop ICMP echo reply packets inline.
The server and PCs have been preconfigured. The routers have also been preconfigured with the following:
• Enable password: ciscoenpa55
• Console password: ciscoconpa55
• SSH username and password: SSHadmin / ciscosshpa55
• OSPF 101
Part 1: Enable IOS IPS
Note: Within Packet Tracer, the routers already have the signature files imported and in place. They are the default xml files in flash. For this reason, it is not necessary to configure the public crypto key and complete a manual import of the signature files.
Step 1: Enable the Security Technology package.
a. On R1, issue the show version command to view the Technology Package license information.
b. If the Security Technology package has not been enabled, use the following command to enable the package.
R1(config)# license boot module c1900 technology-package securityk9
c. Accept the end user license agreement.
d. Save the running-config and reload the router to enable the security license.
e. Verify that the Security Technology package has been enabled by using the show version command.
Step 2: Verify network connectivity.
a. Ping from PC-C to PC-A. The ping should be successful.
b. Ping from PC-A to PC-C. The ping should be successful.
Step 3: Create an IOS IPS configuration directory in flash.
On R1, create a directory in flash using the mkdir command. Name the directory ipsdir.
R1# mkdir ipsdir Create directory filename [ipsdir]? <Enter> Created dir flash:ipsdir
Step 4: Configure the IPS signature storage location.
On R1, configure the IPS signature storage location to be the directory you just created.
R1(config)# ip ips config location flash:ipsdir
Step 5: Create an IPS rule.
On R1, create an IPS rule name using the ip ips name name command in global configuration mode. Name the IPS rule iosips.
R1(config)# ip ips name iosips
Step 6: Enable logging.
IOS IPS supports the use of syslog to send event notification. Syslog notification is enabled by default. If logging console is enabled, IPS syslog messages display.
a. Enable syslog if it is not enabled.
R1(config)# ip ips notify log
b. If necessary, use the clock set command from privileged EXEC mode to reset the clock.
R1# clock set 10:20:00 10 january 2014
c. Verify that the timestamp service for logging is enabled on the router using the show run command. Enable the timestamp service if it is not enabled.
R1(config)# service timestamps log datetime msec
d. Send log messages to the syslog server at IP address 192.168.1.50.
R1(config)# logging host 192.168.1.50
Step 7: Configure IOS IPS to use the signature categories.
Retire the all signature category with the retired true command (all signatures within the signature release). Unretire the IOS_IPS Basic category with the retired false command.
R1(config)# ip ips signature-category R1(config-ips-category)# category all R1(config-ips-category-action)# retired true R1(config-ips-category-action)# exit R1(config-ips-category)# category ios_ips basic R1(config-ips-category-action)# retired false R1(config-ips-category-action)# exit R1(config-ips-cateogry)# exit Do you want to accept these changes? [confirm] <Enter>
Step 8: Apply the IPS rule to an interface.
Apply the IPS rule to an interface with the ip ips name direction command in interface configuration mode. Apply the rule outbound on the G0/1 interface of R1. After you enable IPS, some log messages will be sent to the console line indicating that the IPS engines are being initialized.
Note: The direction in means that IPS inspects only traffic going into the interface. Similarly, out means that IPS inspects only traffic going out of the interface.
R1(config)# interface g0/1 R1(config-if)# ip ips iosips out
Part 2: Modify the Signature
Step 1: Change the event-action of a signature.
Un-retire the echo request signature (signature 2004, subsig ID 0), enable it, and change the signature action to alert and drop.
R1(config)# ip ips signature-definition R1(config-sigdef)# signature 2004 0 R1(config-sigdef-sig)# status R1(config-sigdef-sig-status)# retired false R1(config-sigdef-sig-status)# enabled true R1(config-sigdef-sig-status)# exit R1(config-sigdef-sig)# engine R1(config-sigdef-sig-engine)# event-action produce-alert R1(config-sigdef-sig-engine)# event-action deny-packet-inline R1(config-sigdef-sig-engine)# exit R1(config-sigdef-sig)# exit R1(config-sigdef)# exit Do you want to accept these changes? [confirm] <Enter>
Step 2: Use show commands to verify IPS.
Use the show ip ips all command to view the IPS configuration status summary.
To which interfaces and in which direction is the iosips rule applied?
G0/1 outbound.
Step 3: Verify that IPS is working properly.
a. From PC-C, attempt to ping PC-A. Were the pings successful? Explain.
The pings should fail. This is because the IPS rule for event-action of an echo request was set to “denypacket-inline”.
b. From PC-A, attempt to ping PC-C. Were the pings successful? Explain.
The ping should be successful. This is because the IPS rule does not cover echo reply. When PC-A pings PC-C, PC-C responds with an echo reply.
Step 4: View the syslog messages.
a. Click the Syslog server.
b. Select the Services tab.
c. In the left navigation menu, select SYSLOG to view the log file.
Step 5: Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 100%. Click Check Results to see feedback and verification of which required components have been completed.

Thanks this website for work.
Thanks