Packet Tracer – Configuring Extended ACLs – Scenario 2
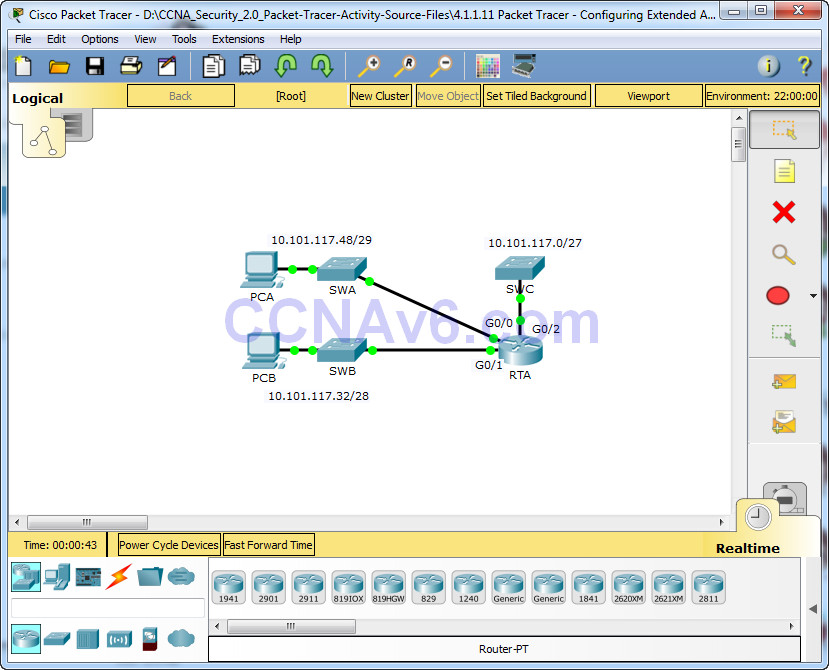
Topology
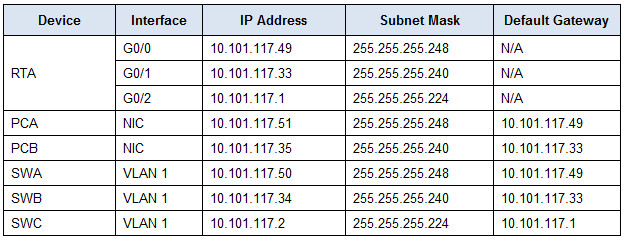
Addressing Table
Objectives
Part 1: Configure, Apply and Verify an Extended Numbered ACL
Part 2: Reflection Questions
Background / Scenario
In this scenario, devices on one LAN are allowed to remotely access devices in another LAN using the SSH protocol. Besides ICMP, all traffic from other networks is denied.
The switches and router have also been pre-configured with the following:
• Enable secret password: ciscoenpa55
• Console password: ciscoconpa55
• Local username and password: Admin / Adminpa55
Part 1: Configure, Apply and Verify an Extended Numbered ACL
Configure, apply and verify an ACL to satisfy the following policy:
• SSH traffic from devices on the 10.101.117.32/28 network is allowed to devices on the 10.101.117.0/27 networks.
• ICMP traffic is allowed from any source to any destination.
• All other traffic to 10.101.117.0/27 is blocked.
Step 1: Configure the extended ACL.
a. From the appropriate configuration mode on RTA, use the last valid extended access list number to configure the ACL. Use the following steps to construct the first ACL statement:
1) The last extended list number is 199.
2) The protocol is TCP.
3) The source network is 10.101.117.32.
4) The wildcard can be determined by subtracting 255.255.255.240 from 255.255.255.255.
5) The destination network is 10.101.117.0.
6) The wildcard can be determined by subtracting 255.255.255.224 from 255.255.255.255.
7) The protocol is SSH (port 22).
What is the first ACL statement?
access-list 199 permit tcp 10.101.117.32 0.0.0.15 10.101.117.0 0.0.0.31 eq 22
b. ICMP is allowed, and a second ACL statement is needed. Use the same access list number to permit all ICMP traffic, regardless of the source or destination address. What is the second ACL statement? (Hint: Use the any keywords)
access-list 199 permit icmp any any
c. All other IP traffic is denied, by default.
Step 2: Apply the extended ACL.
The general rule is to place extended ACLs close to the source. However, because access list 199 affects traffic originating from both networks 10.101.117.48/29 and 10.101.117.32/28, the best placement for this ACL might be on interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/2 in the outbound direction. What is the command to apply ACL 199 to the Gigabit Ethernet 0/2 interface?
ip access-group 199 out
Step 3: Verify the extended ACL implementation.
a. Ping from PCB to all of the other IP addresses in the network. If the pings are unsuccessful, verify the IP addresses before continuing.
b. SSH from PCB to SWC. The username is Admin, and the password is Adminpa55.
PC> ssh -l Admin 10.101.117.2
c. Exit the SSH session to SWC.
d. Ping from PCA to all of the other IP addresses in the network. If the pings are unsuccessful, verify the IP addresses before continuing.
e. SSH from PCA to SWC. The access list causes the router to reject the connection.
f. SSH from PCA to SWB. The access list is placed on G0/2 and does not affect this connection. The username is Admin, and the password is Adminpa55.
g. After logging into SWB, do not log out. SSH to SWC in privileged EXEC mode.
SWB# ssh -l Admin 10.101.117.2
Part 2: Reflection Questions
1. How was PCA able to bypass access list 199 and SSH to SWC?
Two steps were used: First, PCA used SSH to access SWB. From SWB, SSH was allowed to SWC.
2. What could have been done to prevent PCA from accessing SWC indirectly, while allowing PCB SSH access to SWC?
Because it was requested to block all traffic to 10.101.117.0/27 except SSH traffic originating from 10.101.117.32/28 the access list could be written as is. Instead of applying the ACL to G0/2 outbound apply the same ACL to both G0/0 and G0/1 inbound.
Suggested Scoring Rubric