6.6.4 Packet Tracer – Configure and Verify NTP Answers Version
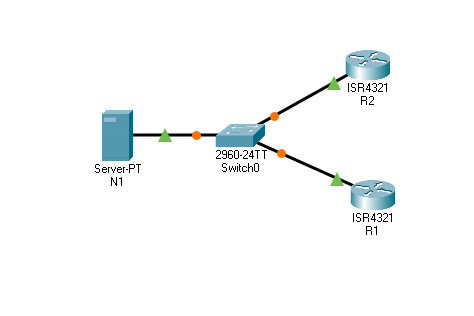
6.6.4 Packet Tracer – Configure and Verify NTP
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask |
|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | NIC | 209.165.200.225 | 255.255.255.0 |
| R1 | G0/0/0 | 209.165.200.226 | 255.255.255.0 |
| R2 | G0/0/0 | 209.165.200.227 | 255.255.255.0 |
Objectives
In this activity, you will configure NTP on R1 and R2 to allow time synchronization.
Background / Scenario
Network Time Protocol (NTP) synchronizes the time of day among a set of distributed time servers and clients. While there are a number of applications that require synchronized time, this lab will focus on correlating events that are listed in the system log and other time-specific events from multiple network devices. NTP uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) as its transport protocol. All NTP communications use Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
An NTP server usually receives its time from an authoritative time source, such as an atomic clock attached to a time server. The NTP server then distributes this time across the network. NTP is extremely efficient. No more than one packet per minute is necessary to synchronize two devices to within a millisecond of each other.
It is very important to network security monitoring that these timestamps be accurate and consistent. If a hacker is able to disrupt or distort the time information provided by NTP, it can greatly impact detection and remediation of network security breaches.
NTP authentication can protect the network from NTP attack by verifying the time source. NTP uses MD5 encoded keys to verify the timestamps from the trusted time sources.
Instructions
Part 1: NTP Server
a. Server N1 is already configured as the NTP Server for this topology. Verify its configuration under Services > NTP. Verify that key 1 and password NTPpa55 are configured for authentication.
b. From R1, ping N1 (209.165.200.225) to verify connectivity. The ping should be successful.
c. Repeat the ping to N1 from R2 to verify connectivity to N1.
Part 2: Configure the NTP Clients
Cisco devices can be configured to refer to an NTP server to use to synchronize their clocks. It is important to keep time consistent among all devices. Configure R1 and R2 as NTP clients so their clocks are synchronized. Both R1 and R2 will use N1 server as their NTP server.
a. Check the current NTP and clock settings as shown below. Verify the settings for R2.
R1# show ntp status %NTP is not enabled. R1# show clock detail *0:1:53.745 UTC Mon Mar 1 1993 Time source is hardware calendar
R2# show ntp status %NTP is not enabled. R2# show clock detail *0:1:53.745 UTC Mon Mar 1 1993 Time source is hardware calendar
b. Configure R1 and R2 as NTP Clients. Use the ntp server command to specify an NTP server, as shown below:
R1# conf t R1(config)# ntp server 209.165.200.225
c. Configure NTP authentication on R1 and R2 using key 1 and password NTPpa55.
R1(config)# ntp authenticate R1(config)# ntp trusted-key 1 R1(config)# ntp authentication-key 1 md5 NTPpa55
d. Repeat this configuration on R2.
R2# conf t R2(config)# ntp server 209.165.200.225 R2(config)# ntp authenticate R2(config)# ntp trusted-key 1 R2(config)# ntp authentication-key 1 md5 NTPpa55
Part 3: Verify NTP settings
a. Check the clocks on R1 and R2 again to verify that they are synchronized:
R1# show clock detail 12:7:18.451 UTC Wed Feb 3 2021 Time source is NTP
Note: When working on physical routers, allow a few minutes before R1 and R2 clocks are synchronized. With Packet Tracer, you can use the Fast Forward Time button to speed up synchronization.
Execute the same command on R2.
Question:
Are the clocks synchronized? Yes. R1 and R2 have the same time as N1.
b. Check the NTP status and NTP associations by using the following commands to verify NTP operation and configuration.
R1# show ntp status Clock is synchronized, stratum 2, reference is 209.165.200.225 <Output omitted> R1# show ntp associations address ref clock st when poll reach delay offset disp *~209.165.200.225127.127.1.1 1 13 64 377 1.00 -9.00 0.48 * sys.peer, # selected, + candidate, - outlyer, x falseticker, ~ configured
Answers Script
Router R1
enable configure terminal ntp server 209.165.200.225 ntp authenticate ntp trusted-key 1 ntp authentication-key 1 md5 NTPpa55 end
Router R2
enable configure terminal ntp server 209.165.200.225 ntp authenticate ntp trusted-key 1 ntp authentication-key 1 md5 NTPpa55 end
