7.4.7 Lab – Install the Virtual Machine Answers version
Objectives
- Part 1: Prepare a Personal Computer for Virtualization
- Part 2: Import a Virtual Machine into VirtualBox Inventory
Background / Scenario
Computing power and resources have increased tremendously over the last 10 years. A benefit of having multicore processors and large amounts of RAM is the ability to use virtualization. With virtualization, one or more virtual computers operate inside one physical computer. Virtual computers that run within physical computers are called virtual machines. Virtual machines are often called guests, and physical computers are often called hosts. Anyone with a modern computer and operating system can run virtual machines.
A virtual machine image file has been created for you to install on your computer. In this lab, you will download and import this image file into a desktop virtualization application, such as VirtualBox. When opened in the player software, this fille will permit you to run a Linux guest computer that can be accessed directly from your host operating system.
This virutal machine will be used later in the course.
Required Resources
- Host computer with a minimum of 8 GB of RAM and 20GB of free disk space
- High-speed internet access to download Oracle VirtualBox and the virtual machine image file
Instructions
Part 1: Prepare a Host Computer for Virtualization
In Part 1, you will download and install desktop virtualization software, and also download an image file that can be used to complete several of the labs throughout the course. For this lab, the virtual machine is running a Linux OS.
Step 1: Download and install VirtualBox.
VMware Player and Oracle VirtualBox are two virtualization programs that you can download and install to support the image file. In this lab, you will use VirtualBox.
a. Navigate to http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/server-storage/virtualbox/downloads/index.html.
b. Choose and download the appropriate installation file for your operating system.
c. When you have downloaded the VirtualBox installation file, run the installer and accept the default installation settings.
Step 2: Download the Virtual Machine image file.
The image file was created in accordance with the Open Virtualization Format (OVF). OVF is an open standard for packaging and distributing virtual appliances. An OVF package has several files placed into one directory. This directory is then distributed as an OVA package. This package contains all the OVF files necessary for the deployment of the virtual machine. The virtual machine used in this lab was exported in accordance with the OVF standard.
a. Navigate to the Network Security Virtual Machine (VM) page on netacad.com.
b. Download the security_workstation.ova image file and note the location of the downloaded VM file.
Note: Your browser may ask if you wish to open the file with the VirtualBox program. Select Save instead to follow the instructions in Part 2.
Part 2: Import the Virtual Machine into the VirtualBox Inventory
In Part 2, you will import the virtual machine image into VirtualBox and start the virtual machine.
Step 1: Import the virtual machine file into VirtualBox.
a. Open VirtualBox. Click File > Import Appliance… to import the virtual machine image.
b. In the Appliance to import window, specify the location of the .OVA file and click Next.
c. The Appliance window presents the settings suggested in the OVA archive. Review the default settings and change if necessary. Normally, the default settings are appropriate. Click Import to continue.
d. When the import process is complete, you will see the new Virtual Machine added to the VirtualBox inventory in the left panel. The virtual machine is now ready to use.
Step 2: Start the virtual machine and log in.
a. Click the Security Workstation virtual machine.
b. Click the green arrow Start button at the top portion of the VirtualBox application window. If you get the following error dialog box, click Change Network Settings and set your Bridged Adapter. Click the dropdown list next to the Name and choose your network adapter (this will vary for each computer).
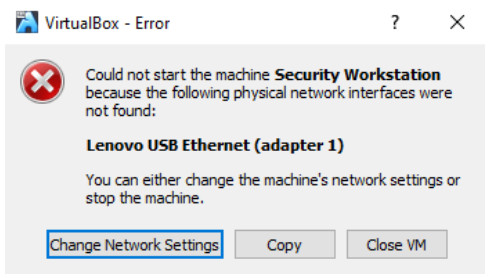
Note: If your network is not configured with DHCP services, click Change Network Settings and select NAT in the Attached to dropdown box. The network settings can also be accessed via Settings in the Oracle VirtualBox Manager or in the virtual machine menu by selecting Devices > Network > Network Settings. You may need to disable and enable the network adaptor for the change to take effect.
c. Click OK. A new window will appear and the virtual machine boot process will start.
d. When the boot process is complete, the virtual machine will ask for a username and password. Select sec_admin in the drop-down menu.
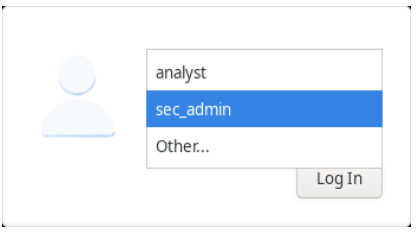
Use the following credentials to log in to the virtual machine:
Username: sec_admin
Password: net_secPW
You will be presented with a desktop environment with a launcher bar at the bottom, icons on the desktop, and an application menu at the top.
Note: Notice the keyboard and mouse focus. When you click inside the virtual machine window, your mouse and keyboard will operate the guest operating system. Your host operating system will no longer detect keystrokes or mouse movements. Move your mouse outside of the VirtualBox window to control your host operating system. If you are unable to move the mouse out of the VirtualBox window, press the right CTRL key to return keyboard and mouse focus to the host operating system.
Step 3: Familiarize yourself with the Virtual Machine.
The virtual machine that you just installed will be used to complete several of the labs in this course. Familiarize yourself with the icons in the list below:
The launcher bar icons are (from left to right):
- Show the desktop
- Terminal emulator
- File manager application
- Web browser application (Firefox)
- File search tool
- Current user’s home directory
a. Open the Terminal Emulator application. Type ip address at the prompt to determine the IP address of your virtual machine.
[sec_admin@Workstation ~]$ ip address
What are the IP addresses assigned to your virtual machine?
Answer will vary. The loopback interface is assigned 127.0.0.1/8, and the Ethernet interface is assigned an IP address in the 10.0.2.0/24 network.
b. Locate and launch the web browser application.
Can you navigate to your favorite search engine?
Yes
Step 4: Run scripts.
In this step, you will run two scripts that were created for this course. A script is a plain text file that contains a set of commands that execute when the script filename is entered at the terminal prompt.
a. Open a terminal using the Terminal Emulator application.
b. Navigate to the scripts folder.
[sec_admin@Workstation ~]$ cd lab.support.files/scripts/ [sec_admin@Workstation scripts]$
c. You can list the files in the folder by entering ls at the promp.t
[sec_admin@Workstation scripts]$ ls configure_as_dhcp.sh configure_as_static.sh net_configuration_files
d. To run a script that changes the IP address to a static IP address of 192.168.1.11, enter ./configure_as_static.sh. Enter net_secPW as the password when prompted.
[sec_admin@Workstation scripts]$ ./configure_as_static.sh [sudo] password for sec_admin: Configuring the NIC as: IP: 192.168.1.11/24 GW: 192.168.1.1 IP Configuration successful.
e. Verify the static IP address by typing ip address at the terminal prompt.
[sec_admin@Workstation scripts]$ ip address
<output omitted>
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group
default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:8a:4b:dd brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.192.183/24 brd 192.168.192.255 scope global dynamic eth0
valid_lft 1774sec preferred_lft 1774sec
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe8a:4bdd/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
f. To return to using DHCP to get an IP address, enter ./configure_as_dhpc.sh at the prompt.
[sec_admin@Workstation scripts]$ ./configure_as_dhcp.sh [sudo] password for sec_admin: Configuring the NIC to request IP info via DHCP... Requesting IP information... IP Configuration successful.
Step 5: Shut down the VM.
When you are done with the VM, you can save the state of the VM for future use or shut down the VM.
Closing the VM using GUI:
From the VirtualBox File menu, choose Close…
Click the Save the machine state radio button and click OK. The next time you start the virtual machine, you will be able to resume working in the operating system in its current state.
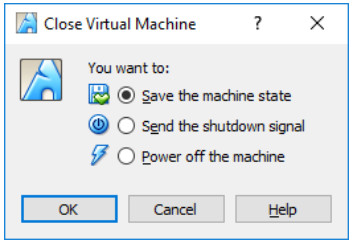
The other two options are:
Send the shutdown signal: simulates pressing the power button on a physical computer and selecting shut down
Power off the machine: simulates pulling the plug on a physical computer or holding down the power button until the computer turns off
Closing the VM using CLI:
To shut down the VM using the command line, you can use the menu options inside the VM or enter sudo shutdown -h now command in a terminal window and provide the password net_secPW when prompted.
Rebooting the VM:
If you want to reboot the VM, you can use the menu options inside the VM or enter sudo reboot command in a terminal and provide the password net_secPW when prompted.
Note: You can use the web browser in this virtual machine to research security issues. By using the virtual machine, you may prevent malware from being installed on your host computer.
Reflection
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a virtual machine?
With a virtual machine, you can test new applications or operating systems without affecting your host machine. You are also able to save the current machine state when you close the virtual machine. If you have any issues, you have the option to revert the virtual machine to a previously saved state. On the other hand, a virtual machine requires hardware resources from the host machine, such as hard drive space, RAM, and processing power.
