1. Refer to the exhibit. Which type of cipher method is depicted?
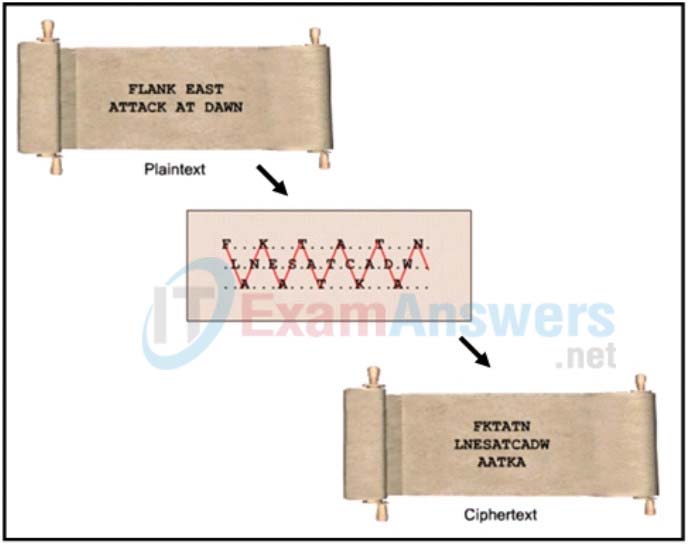
- stream cipher
- substitution cipher
- transposition cipher
- Caesar cipher
Explanation: There are many cipher methods developed for message encryptions. In transposition ciphers, no letters are replaced; they are simply rearranged. An example of this type of cipher is known as the rail fence cipher. In this transposition, the words are spelled out as if they were a rail fence, meaning some are in front and some in back across several parallel lines.
2. What are two objectives of ensuring data integrity? (Choose two.)
- Access to the data is authenticated.
- Data is unaltered during transit.
- Data is available all the time.
- Data is encrypted while in transit and when stored on disks.
- Data is not changed by unauthorized entities.
Explanation: The objectives for data integrity include data not being altered during transit and not being changed by unauthorized entities. Authentication and encryption are methods to ensure confidentiality. Data being available all the time is the goal of availability.
3. A network security specialist is tasked to implement a security measure that monitors the status of critical files in the data center and sends an immediate alert if any file is modified. Which aspect of secure communications is addressed by this security measure?
- data integrity
- data confidentiality
- origin authentication
- nonrepudiation
Explanation: Secure communications consists of four elements:
- Data confidentiality – guarantees that only authorized users can read the message
- Data integrity – guarantees that the message was not altered
- Origin authentication – guarantees that the message is not a forgery and does actually come from whom it states
- Data nonrepudiation – guarantees that the sender cannot repudiate, or refute, the validity of a message sent
4. Which type of attack allows an attacker to use a brute force approach?

- password cracking
- denial of service
- social engineering
- packet sniffing
Explanation: Common ways used to crack Wi-Fi passwords include social engineering, brute-force attacks, and network sniffing.
5. Why would HMAC be used to help secure the data as it travels across various links?
- It is an asymmetric encryption algorithm used when the two communicating parties have not previously shared a secret key.
- It is a hashing algorithm used to guarantee that the message is not a forgery and actually comes from the authentic source.
- It is a hashing algorithm used to encrypt the message and guarantee that no one intercepted the message and altered it.
- It is a popular symmetric encryption algorithm used when each communicating party needs to know the pre-shared key.
Explanation: MD5 is a hashing algorithm that guarantees that no one intercepted the message and altered it. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a popular symmetric encryption algorithm where each communicating party needs to know the pre-shared key. Public key infrastructure (PKI) is an asymmetric encryption algorithm based on the assumption that the two communicating parties have not previously shared a secret key. HMAC is a hash message authentication code that guarantees that the message is not a forgery and actually comes from the authentic source.
6. What is the focus of cryptanalysis?
- developing secret codes
- breaking encrypted codes
- implementing encrypted codes
- hiding secret codes
Explanation: Cryptology is the science of making and breaking secret codes. There are two separate disciplines in cryptology, cryptography and cryptanalysis. Cryptography is the development and use of codes. Cryptanalysis is the breaking of those secret (encrypted) codes.
7. What is cryptology?
- the science of making and breaking secret codes
- the science of creating transposition and substitution ciphers
- the science of guaranteeing that a message is not a forgery and comes from the authentic source
- the science of cracking the code without access to the shared secret key
Explanation: Cryptography is the science of creating transposition and substitution ciphers. Cryptanalysis is the science of cracking the code without access to the shared secret key. Cryptology is the science of making and breaking secret codes. Cryptology combines cryptography and cryptanalysis.
8. Which objective of secure communications is achieved by encrypting data?
- integrity
- confidentiality
- availability
- authentication
Explanation: When data is encrypted, it is scrambled to keep the data private and confidential so that only authorized recipients can read the message. A hash function is another way of providing confidentiality.
9. What is the purpose of a nonrepudiation service in secure communications?
- to provide the highest encryption level possible
- to ensure that the source of the communications is confirmed
- to confirm the identity of the recipient of the communications
- to ensure that encrypted secure communications cannot be decoded
Explanation: Nonrepudiation uses the unique characteristics of the sender of a message to confirm that the reputed sender is in fact the actual sender.
10. What is an example of the transposition cipher?
- Caesar
- RC4
- Vigenère
- rail fence
Explanation: RC4 is an example of the one-time pad cipher, and it is widely used on the Internet. The Caesar cipher is a simple substitution cipher, and the Vigenère cipher is based on the Caesar cipher. An example of the transposition cipher is the rail fence cipher.
11. A web server administrator is configuring access settings to require users to authenticate first before accessing certain web pages. Which requirement of information security is addressed through the configuration?
- confidentiality
- scalability
- integrity
- availability
Explanation: Confidentiality ensures that data is accessed only by authorized individuals. Authentication will help verify the identity of the individuals.
12. As data is being stored on a local hard disk, which method would secure the data from unauthorized access?
- data encryption
- deletion of sensitive files
- two factor authentication
- a duplicate hard drive copy
Explanation: Data encryption is the process of converting data into a form where only a trusted, authorized person with a secret key or password can decrypt the data and access the original form.



