1. A technician is attempting to explain broadband technology to a customer. Which two descriptions or examples should be used to educate the customer? (Choose two.)
- includes dialup connections using POTS
- incompatible with multiplexing
- uses a wide band of frequencies
- offers sustained speeds of 128K or more
- requires line-of-sight connection with service provider
2. When accommodating a teleworker, which type of connection should be used when mobile access during traveling is required and broadband options are unavailable?
- residential cable
- DSL
- dialup
- satellite
3. When comparing DOCSIS and Euro-DOCSIS, what is the primary difference between the two specifications?
- flow control mechanisms
- maximum data rates
- access methods
- channel bandwidths
4. If asked to describe DSL technology, which three statements would help the user develop a better understanding of the technology? (Choose three.)
- DSL is available in any location that has a telephone.
- ADSL typically has a higher download bandwidth than available upload bandwidth.
- In home installations, a splitter separates the ADSL and voice signals at the NID, allowing multiple ADSL outlets in the house.
- DSL speeds can exceed the speeds available with a typical T1 line.
- Transfer rates vary by the length of the local loop.
- All varieties of DSL provide the same bandwidth, although they use different technologies to achieve upload and download.
5. In a DSL installation, which two devices are installed at the customer site? (Choose two.)
- CM
- DOCSIS
- DSLAM
- Microfilter
- DSL transceiver
6. Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the network topology shown, which devices or software applications provide encapsulation and encryption for the VPN traffic?
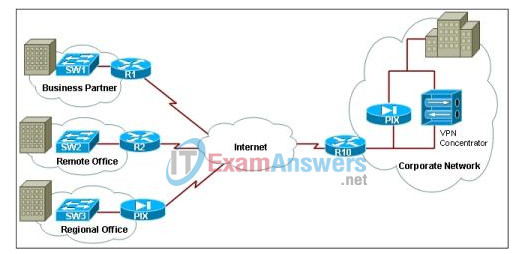
- VPN client software installed on the machines of the users at the Regional Office only
- PIX appliances at the Corporate Network and Regional Office only
- router and PIX appliance at the Corporate Network and the routers and PIX appliance at all remote locations
- LAN switches and routers at the remote locations only
- routers and PIX appliance at the remote locations only
7. Which two techniques can be used to secure the traffic sent over a VPN connection? (Choose two.)
- data labeling used to mark and separate the VPN traffic for different customers
- data encapsulation used to transmit data transparently from network to network through a shared network infrastructure
- data encryption used to code data into a different format using a secret key
- use of a second routing protocol to transport the traffic over the VPN tunnel
- use of a dedicated connection over the company private leased line
8. Match the description on the left with the corresponding VPN characteristic on the right.
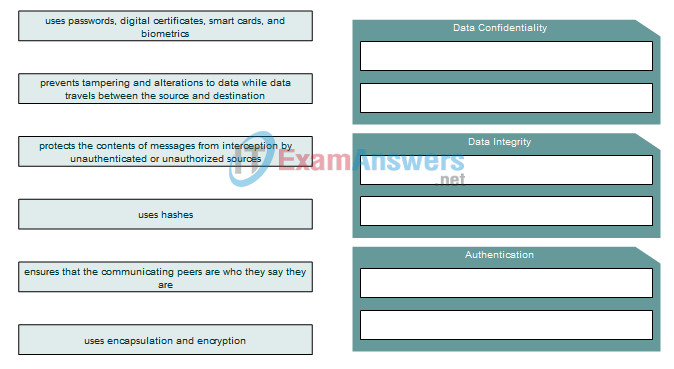
Answer
9. Which is an example of a tunneling protocol developed by Cisco?
- AES
- DES
- RSA
- ESP
- GRE
10. Drag the description on the left to the corresponding type of tunneling protocol on the right.
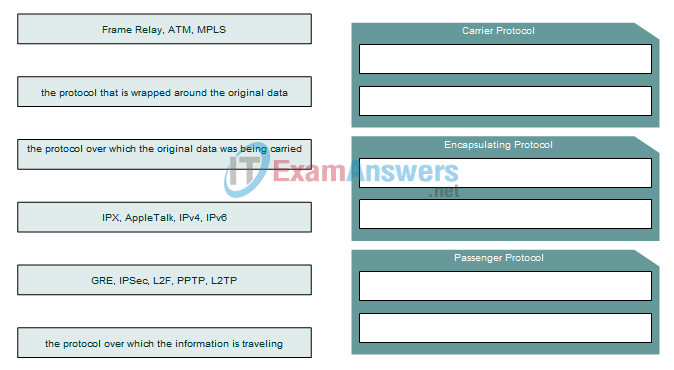
Answer
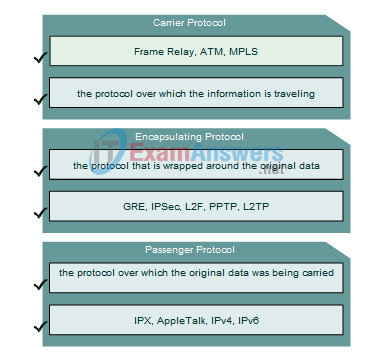
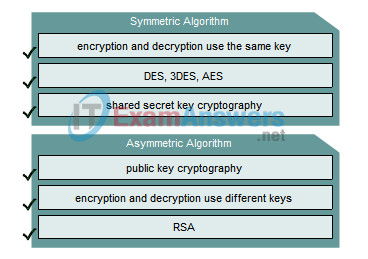
11. Drag the description on the left to the correct algorithm on the right.
Answer
12. What type of connection is the most cost effective to adequately support SOHO teleworker access to the Internet?
- direct T1 link to the Internet
- 56k dialup
- one-way multicast satellite Internet system
- DSL to an ISP
13. Which wireless standard operates in both licensed and unlicensed bands of the spectrum from 2 to 6 GHz and allows for transmission rates of 70 Mbps at a range of up to 50 kilometers?
- 802.11g
- 802.11n
- 802.11b
- 802.16
- 802.11e
14. What is typically deployed to support high-speed transmissions of data to SOHO cable modems?
- hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC)
- high speed dialup cable modems
- broadband copper coaxial
- 1000baseTX
