6.4.1 Packet Tracer – Skills Integration Challenge Answers
Topology
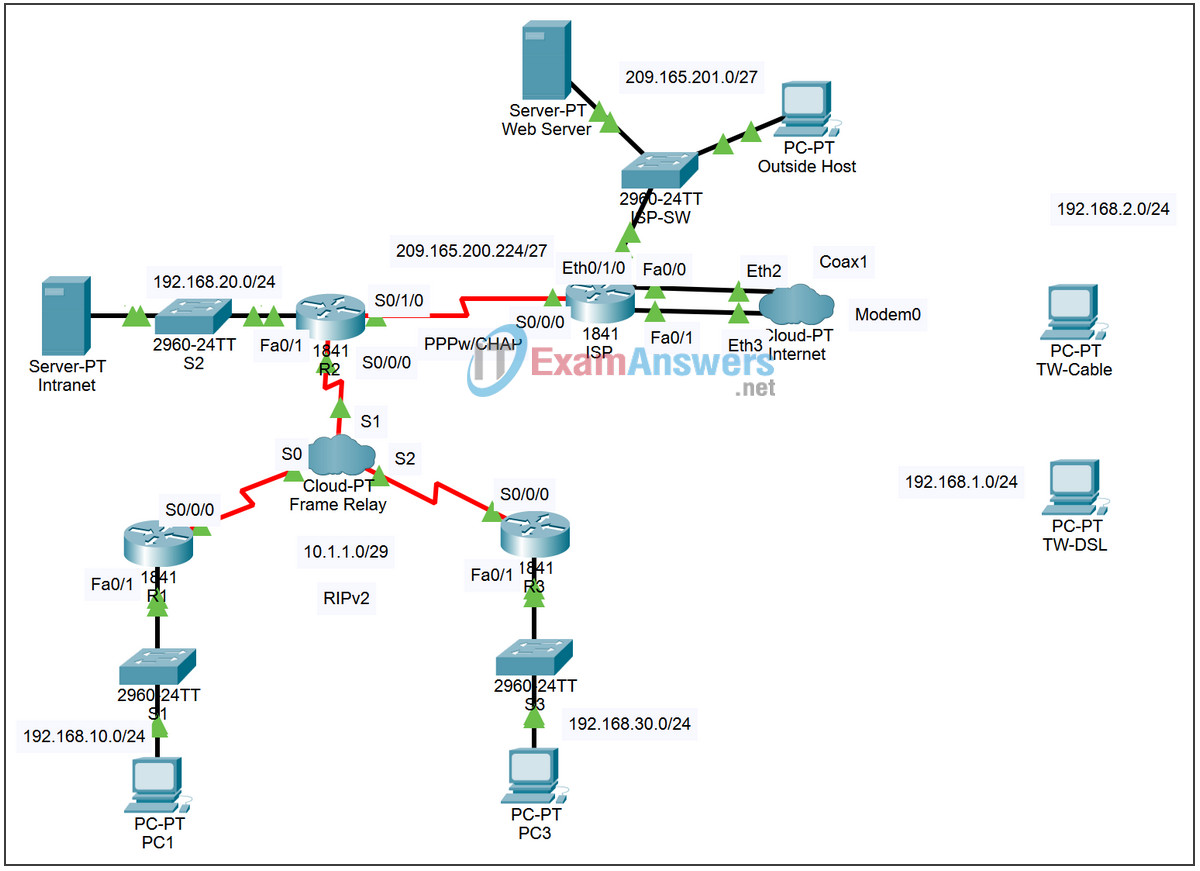
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Fa0/1 | 192.168.10.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
| S0/0/0 | 10.1.1.1 | 255.255.255.248 | |
| R2 | Fa0/1 | 192.168.20.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
| S0/0/0 | 10.1.1.2 | 255.255.255.248 | |
| S0/1/0 | 209.165.200.225 | 255.255.255.224 | |
| R3 | Fa0/1 | 192.168.30.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
| S0/0/0 | 10.1.1.3 | 255.255.255.248 | |
| ISP | S0/0/0 | 209.165.200.226 | 255.255.255.224 |
| Eth0/1/0 | 209.165.201.1 | 255.255.255.224 | |
| Fa0/0 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| Fa0/1 | 192.168.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| PC1 | NIC | 192.168.10.10 | 255.255.255.0 |
| PC3 | NIC | 192.168.30.10 | 255.255.255.0 |
| Intranet | NIC | 192.168.20.254 | 255.255.255.0 |
| TW-DSL | NIC | 192.168.1.10 | 255.255.255.0 |
| TW-Cable | NIC | 192.168.2.10 | 255.255.255.0 |
| Web Server | NIC | 209.165.201.30 | 255.255.255.224 |
| Outside Host | NIC | 209.165.201.10 | 255.255.255.224 |
Learning Objectives
- Apply basic router configurations
- Configure dynamic and default routing
- Establish teleworker services
- Test connectivity before ACL configuration
- Apply ACL policies
- Test connectivity after ACL configuration
Introduction
This activity requires you to configure a default route as well as dynamic routing using RIP version 2. You will also add broadband devices to the network. Finally, you will set up ACLs on two routers to control network traffic. Because Packet Tracer is very specific in how it grades ACLs, you will need to configure the ACL rules in the order given.
Task 1: Apply Basic Router Configurations
Step 1: Configure basic commands.
Using the information in the topology diagram and addressing table, configure the basic device configurations on R1, R2, and R3. Hostnames are configured for you.
Include the following:
- Console and vty lines.
- Banners.
- Disable domain name lookup.
- Interface descriptions.
Task 2: Configure Dynamic and Default Routing
Step 1. Configure default routing.
R2 needs a default route. Use the exit-interface argument in the default route configuration.
Step 2. Configure dynamic routing.
Configure RIPv2 on R1, R2, and R3 for all available networks. R2 needs to pass its default network configuration to the other routers. Also, be sure to use the passive-interface command on all active interfaces not used for routing.
Step 3. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 59%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 3: Establish Teleworker Services
Step 1. Add WAN devices.
Add one DSL and one cable modem according to the topology diagram.
Step 2. Name the WAN devices.
Use the Config tab to change the display name of each WAN device to Cable and DSL, respectively.
Step 3. Connect the WAN devices.
Connect the WAN devices to their PCs and the Internet using the appropriate cables and interfaces.
Step 4. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 86%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 4: Test Connectivity Before ACL Configuration
At this point, all branches of the topology should have connectivity. Switching between Simulation mode and Realtime mode can speed up convergence.
Task 5: Apply ACL Policies
Step 1. Create and apply security policy number 1.
Implement the following ACL rules using ACL number 101:
- Allow hosts on the 192.168.30.0/24 network web access to any destination.
- Allow hosts on the 192.168.30.0/24 network ping access to any destination.
- Deny any other access originating from the network.
Step 2. Create and apply security policy number 2.
Because ISP represents connectivity to the Internet, configure a named ACL called FIREWALL in the following order:
- Allow TW-DSL web access to the Intranet server.
- Allow TW-Cable web access to the Intranet server.
- Allow only inbound ping replies from ISP and any source beyond ISP.
- Allow only established TCP sessions from ISP and any source beyond ISP.
- Explicitly block all other inbound access from ISP and any source beyond ISP.
Step 3. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 100%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 6: Test Connectivity After ACL Configuration
Teleworkers should not be able to ping the Intranet Server, but should be able to access its HTTP server via the web browser. Included in the activity are three PDUs, two of which should fail and one should succeed. Check the Connectivity Tests in the Check Results menu to be sure that the completion results are 100%.

Task 1: Apply Basic Router Configurations
Step 1: Configure basic commands.
Using the information in the topology diagram and addressing table, configure the basic device configurations on R1, R2, and R3. Hostnames are configured for you.
R1
R1>en
R1#conf t
R1(config)#line con 0
R1(config-line)#password cisco
R1(config-line)#login
R1(config-line)#exit
R1(config)#line vty 0 4
R1(config-line)#password cisco
R1(config-line)#login
R1(config-line)#exit
R1(config)#banner motd “Access to Router R1”
R1(config)#no ip domain-lookup
R1(config)#int s0/0/0
R1(config-if)#description line to cloud-PT
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int f0/0
R1(config-if)#desc
R1(config-if)#description fastethernet LAN
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config-if)#
R2
R2>en
R2#conf t
R2(config)#line con 0
R2(config-line)#password cisco
R2(config-line)#login
R2(config-line)#exit
R2(config)#line vty 0 4
R2(config-line)#password cisco
R2(config-line)#login
R2(config-line)#exit
R2(config)#banner motd “Access to Router R2”
R2(config)#no ip domain-lookup
R2(config)#int s0/0/0
R2(config-if)#description line to cloud-PT
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#int s0/1/0
R2(config-if)#description line to ISP
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#int f0/0
R2(config-if)#description line to LAN
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#
R3
R3>en
R3#conf t
R3(config)#line con 0
R3(config-line)#password cisco
R3(config-line)#login
R3(config-line)#exit
R3(config)#line vty 0 4
R3(config-line)#password cisco
R3(config-line)#login
R3(config-line)#exit
R3(config)#banner motd “Access to Router R3”
R3(config)#no ip domain-lookup
R3(config)#int s0/0/0
R3(config-if)#description line to cloud-PT
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#int f0/0
R3(config-if)#description line to LAN
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#
Task 2: Configure Dynamic and Default Routing
Step 1. Configure default routing.
R2 needs a default route. Use the exit-interface argument in the default route configuration.
R2(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/1/0
Step 2. Configure dynamic routing.
Configure RIPv2 on R1, R2, and R3 for all available networks. R2 needs to pass its default network configuration to the other routers. Also, be sure to use the passive-interface command on all active interfaces not used for routing.
R1
R1(config)#router rip
R1(config-router)#version 2
R1(config-router)#network 10.1.1.0
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.10.0
R1(config-router)#passive-interface f0/1
R1(config-router)#no auto-summary
R1(config-router)#exit
R1(config)#
R2
R2(config)#router rip
R2(config-router)#version 2
R2(config-router)#network 10.1.1.0
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.20.0
R2(config-router)#default-information originate
R2(config-router)#passive-interface s0/1/0
R2(config-router)#passive-interface f0/1
R2(config-router)#no auto-summary
R2(config-router)#exit
R2(config)#
R3
R3(config)#router rip
R3(config-router)#version 2
R3(config-router)#network 10.1.1.0
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.30.0
R3(config-router)#passive-interface f0/1
R3(config-router)#no auto-summary
R3(config-router)#exit
R3(config)#
Task 5: Apply ACL Policies
Step 1. Create and apply security policy number 1.
Implement the following ACL rules using ACL number 101:
Allow hosts on the 192.168.30.0/24 network web access to any destination.
Allow hosts on the 192.168.30.0/24 network ping access to any destination.
Deny any other access originating from the network.
R3
R3(config)#access-list 101 permit tcp 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255 any eq www
R3(config)#access-list 101 permit icmp 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255 any
R3(config)#access-list 101 deny ip any any
R3(config)#int fa0/1
R3(config-if)#ip access-group 101 in
R3(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#
Step 2. Create and apply security policy number 2.
Because ISP represents connectivity to the Internet, configure a named ACL called FIREWALL in the following order:
Allow TW-DSL web access to the Intranet server.
Allow TW-Cable web access to the Intranet server.
Allow only inbound ping replies from ISP and any source beyond ISP.
Allow only established TCP sessions from ISP and any source beyond ISP.
Explicitly block all other inbound access from ISP and any source beyond ISP.
R2
R2(config)#ip access-list extended FIREWALL
R2(config-ext-nacl)#permit tcp host 192.168.1.10 host 192.168.20.254 eq www
R2(config-ext-nacl)#permit tcp host 192.168.2.10 host 192.168.20.254 eq www
R2(config-ext-nacl)#permit icmp any any echo-reply
R2(config-ext-nacl)#permit tcp any any established
R2(config-ext-nacl)#deny ip any any
R2(config-ext-nacl)#int s0/1/0
R2(config-if)#ip access-group FIREWALL in
R2(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#