ENetwork Chapter 9 – CCNA Exploration: Network Fundamentals (Version 4.0)
1. Refer to the exhibit. Host_A is attempting to contact Server_B. Which statements correctly describe the addressing Host_A will generate in the process? (Choose two.)
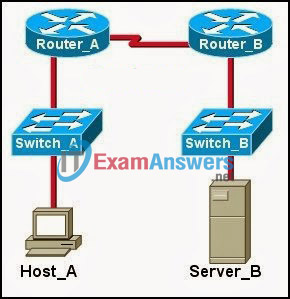
- A packet with the destination IP of Router_B.
- A frame with the destination MAC address of Switch_A.
- A packet with the destination IP of Router_A.
- A frame with the destination MAC address of Router_A.
- A packet with the destination IP of Server_B.
- A frame with the destination MAC address of Server_B.
2. Ethernet operates at which layers of the OSI model? (Choose two.)
- Network layer
- Transport layer
- Physical layer
- Application layer
- Session layer
- Data-link layer
3. Which of the following describe interframe spacing? (Choose two.)
- the minimum interval, measured in bit-times, that any station must wait before sending another frame
- the maximum interval, measured in bit-times, that any station must wait before sending another frame
- the 96-bit payload padding inserted into a frame to achieve a legal frame size
the 96-bit frame padding transmitted between frames to achieve proper synchronization - the time allowed for slow stations to process a frame and prepare for the next frame
- the maximum interval within which a station must send another frame to avoid being considered unreachable
4. What three primary functions does data link layer encapsulation provide? (Choose three.)
- addressing
- error detection
- frame delimiting
- port identification
- path determination
- IP address resolution
5. When a collision occurs in a network using CSMA/CD, how do hosts with data to transmit respond after the backoff period has expired?
- The hosts return to a listen-before-transmit mode.
- The hosts creating the collision have priority to send data.
- The hosts creating the collision retransmit the last 16 frames.
- The hosts extend their delay period to allow for rapid transmission.
6. What are three functions of the upper data link sublayer in the OSI model? (Choose three.)
- recognizes streams of bits
- identifies the network layer protocol
- makes the connection with the upper layers
- identifies the source and destination applications
- insulates network layer protocols from changes in physical equipment
- determines the source of a transmission when multiple devices are transmitting
7. What does the IEEE 802.2 standard represent in Ethernet technologies?
- MAC sublayer
- Physical layer
- Logical Link
- Control sublayer
- Network layer
8. Why do hosts on an Ethernet segment that experience a collision use a random delay before attempting to transmit a frame?
- A random delay is used to ensure a collision-free link.
- A random delay value for each device is assigned by the manufacturer.
- A standard delay value could not be agreed upon among networking device vendors.
- A random delay helps prevent the stations from experiencing another collision during the transmission.
9. Refer to the exhibit. Which option correctly identifies content that the frame data field may contain?
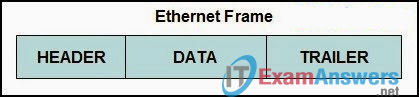
- preamble and stop frame
- network layer packet
- physical addressing
- FCS and SoF
10. Host A has an IP address of 172.16.225.93 and a mask of 255.255.248.0. Host A needs to communicate with a new host whose IP is 172.16.231.78. Host A performs the ANDing operation on the destination address. What two things will occur? (Choose two.)
- Host A will change the destination IP to the IP of the nearest router and forward the packet.
- Host A will broadcast an ARP request for the MAC of its default gateway.
- A result of 172.16.225.0 will be obtained.
- Host A will broadcast an ARP request for the MAC of the destination host.
- A result of 172.16.224.0 will be obtained.
- A result of 172.16.225.255 will be obtained.
11. Which of the following is a drawback of the CSMA/CD access method?
- Collisions can decrease network performance.
- It is more complex than non-deterministic protocols.
- Deterministic media access protocols slow network performance.
- CSMA/CD LAN technologies are only available at slower speeds than other LAN technologies.
12. Ethernet operates at which layer of the TCP/IP network model?
- application
- physical
- transport
- internet
- data link
- network access
13. What is the primary purpose of ARP?
- translate URLs to IP addresses
- resolve IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses
- provide dynamic IP configuration to network devices
- convert internal private addresses to external public addresses
14. Refer to the exhibit. The switch and workstation are administratively configured for full-duplex operation. Which statement accurately reflects the operation of this link?

- No collisions will occur on this link.
- Only one of the devices can transmit at a time.
- The switch will have priority for transmitting data.
- The devices will default back to half duplex if excessive collisions occur.
15. Which statements correctly describe MAC addresses? (Choose three.)
- dynamically assigned
- copied into RAM during system startup
- layer 3 address
- contains a 3 byte OUI
- 6 bytes long
- 32 bits long
16. Which two features make switches preferable to hubs in Ethernet-based networks? (Choose two.)
- reduction in cross-talk
- minimizing of collisions
- support for UTP cabling
- division into broadcast domains
- increase in the throughput of communications
17. What are the two most commonly used media types in Ethernet networks today? (Choose two.)
- coaxial thicknet
- copper UTP
- coaxial thinnet
- optical fiber
- shielded twisted pair
18. Convert the binary number 10111010 into its hexadecimal equivalent. Select the correct answer from the list below.
- 85
- 90
- BA
- A1
- B3
- 1C
19. After an Ethernet collision, when the backoff algorithm is invoked, which device has priority to transmit data?
- the device involved in the collision with the lowest MAC address
- the device involved in the collision with the lowest IP address
- any device in the collision domain whose backoff timer expires first
- those that began transmitting at the same time
20. Refer to the exhibit. What command was executed on a host computer to produce the results shown?
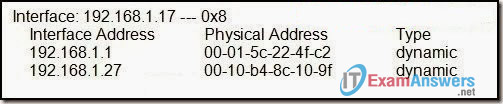
- route PRINT
- arp –a
- arp –d
- netstat
- telnet
21. Host A has an IP address of 172.16.225.93, a mask of 255.255.248.0, and a default gateway of 172.16.224.1. Host A needs to send a packet to a new host whose IP is 172.16.231.78. Host A performs the ANDing operation on its address and subnet mask. What two things will occur? (Choose two.)
- Host A will get a result of 172.16.224.0 from the AND process.
- Host A will send on to the media a broadcast frame that contains the packet.
- Host A will broadcast an ARP request for the MAC of the host 172.16.231.78.
- Host A will change the destination IP of the packet to 172.16.224.1 and forward the packet.
- Host A will encapsulate the packet in a frame with a destination MAC that is the MAC address associated with 172.16.224.1.
22. In the graphic, Host A has reached 50% completion in sending a 1 KB Ethernet frame to Host D when Host B wishes to transmit its own frame to Host C. What must Host B do?
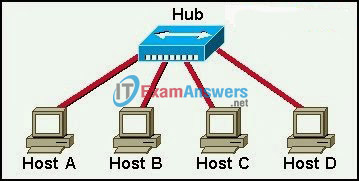
- Host B can transmit immediately since it is connected on its own cable segment.
- Host B must wait to receive a CSMA transmission from the hub, to signal its turn.
- Host B must send a request signal to Host A by transmitting an interframe gap.
- Host B must wait until it is certain that Host A has completed sending its frame.
