CCNA Security 2.0 Study Material – Chapter 1: Modern Network Security Threats
1.0 Introduction
1.0.1 Welcome 1.0.1.1
1.0.1.1 Chapter 1: Modern Network Security Threats
Network security is now an integral part of computer networking. Network security involves protocols, technologies, devices, tools, and techniques to secure data and mitigate threats. Network security solutions emerged in the 1960s but did not mature into a comprehensive set of solutions for modern networks until the 2000s.
Network security is largely driven by the effort to stay one step ahead of ill-intentioned hackers. Just as medical doctors attempt to prevent new illness while treating existing problems, network security professionals attempt to prevent potential attacks while minimizing the effects of real-time attacks. Business continuity is another driver of network security.
Network security organizations have been created to establish formal communities of network security professionals. These organizations set standards, encourage collaboration, and provide workforce development opportunities for network security professionals. Network security professionals should be aware of the resources provided by these organizations.
The complexity of network security makes it difficult to master all it encompasses. Different organizations have created domains that subdivide the world of network security into more manageable pieces. This division allows professionals to focus on more precise areas of expertise in their training, research, and employment.
Network security policies are created by companies and government organizations to provide a framework for employees to follow during their day-to-day work. Network security professionals at the management level are responsible for creating and maintaining the network security policy. All network security practices relate to and are guided by the network security policy.
Network security is divided into domains of network security, and network attacks are organized into classifications so that it is easier to learn about them and address them appropriately. Viruses, worms, and Trojan horses are specific types of network attacks. More generally, network attacks are classified as reconnaissance, access, or denial of service (DoS) attacks.
Mitigating network attacks is the job of a network security professional. In this chapter, you will master the underlying theory of network security, which is essential before beginning an in-depth practice of network security. The methods of network attack mitigation are introduced here, and the implementation of these methods comprises the remainder of this course.
1.1 Securing Networks
1.1.1 Current State of Affairs
1.1.1.1 Networks Are Targets
Networks are routinely under attack. It is common to read in the news about yet another network that has been compromised. A quick Internet search for “network attacks” will reveal many articles regarding network attacks, including organizations which have been compromised, the latest threats to network security, tools to mitigate attacks, and more.
To help comprehend the gravity of the situation, a company called Norse Dark Intelligence maintains an interactive display of current network attacks on honeypot servers. These servers are decoys purposely deployed by organizations wishing to study how hackers compromise systems. The figure displays a sample screenshot of their web tool which is available here.

1.1.1.2 Reasons for Network Security
Network security relates directly to an organization’s business continuity. Network security breaches can disrupt e-commerce, cause the loss of business data, threaten people’s privacy, and compromise the integrity of information. These breaches can result in lost revenue for corporations, theft of intellectual property, lawsuits, and can even threaten public safety.
Maintaining a secure network ensures the safety of network users and protects commercial interests. To keep a network secure requires vigilance on the part of an organization’s network security professionals. They must constantly be aware of new and evolving threats and attacks to networks, and vulnerabilities of devices and applications.
One tool available to help network administrators adapt, develop, and implement mitigation techniques is provided by Cisco. The Cisco Security Intelligence Operations (SIO) provides alerts to network professionals regarding current network attacks. Figure 1 displays a sample of the Security Alerts for attacks and vulnerabilities discovered in February of 2015. This site updates information in real time and provides network administrators with information to help them identify threats and secure their networks. Several terms that are used in the alerts and among network security professionals are displayed in Figure 2. Figure 2 displays these terms and provides a brief explanation of each.
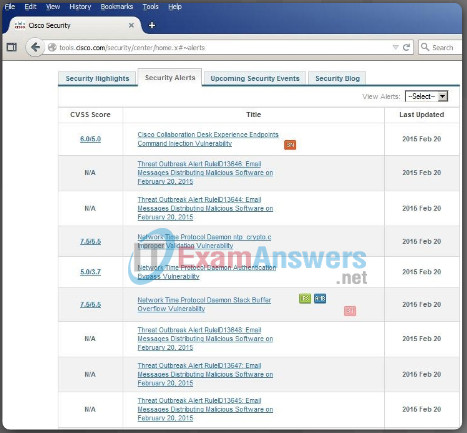
Figure 1: Cisco Security Alerts
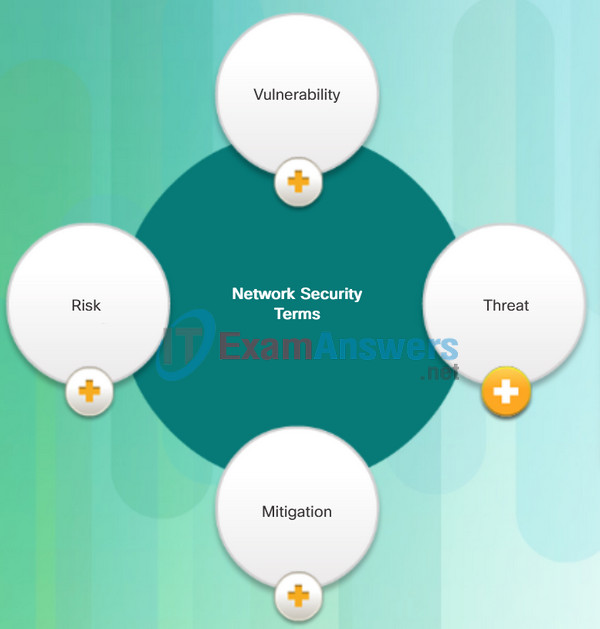
Figure 2: Common Network Security Terms
- Vulnerability: This is defined as a weakness or flaw in the network. The vulnerability can be exploited by an attacker to negatively impact a network, or to access confidential data within an organization. Sources of network vulnerabilities include weak and unsecure network protocols, configuration errors, or weak security policies.
- Threat: This is the potential for a vulnerability to turn into a network attack. Threats include malware, exploits, and more.
- Mitigation: This is the action of reducing the severity of the vulnerability. Network security involves multiple mitigation techniques.
- Risk: This is the potential of a threat to exploit the vulnerabilities of an asset in order to negatively affect an organization. Risk is measured using the probability of the occurence of an event and its consequence.
1.1.1.3 Vectors of Network Attacks
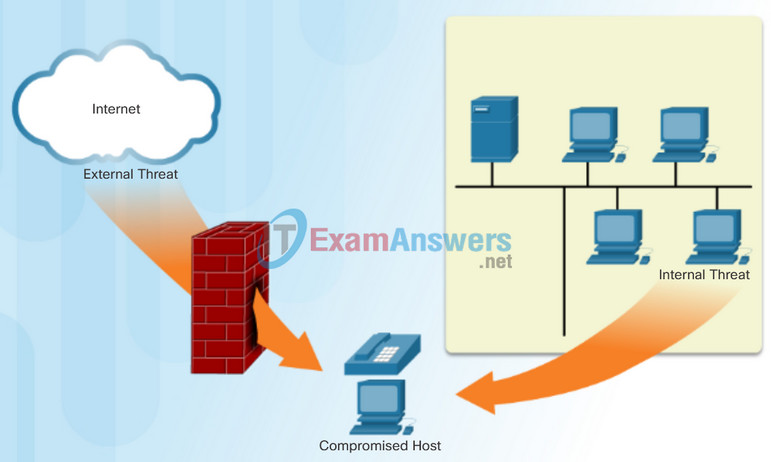
An attack vector is a path or other means by which an attacker can gain access to a server, host, or network. Many attack vectors originate from outside the corporate network. For example, attackers may target a network, through the Internet, in an attempt to disrupt network operations and create a denial of service (DoS) attack.
Note: A DoS attack occurs when a network is incapacitated and no longer capable of supporting requests from legitimate users.
Attack vectors can also originate from inside the network.
An internal user, such as an employee, can accidently or intentionally:
- Steal and copy confidential data to removable media, email, messaging software, and other media.
- Compromise internal servers or network infrastructure devices.
- Disconnect a critical network connection and cause a network outage.
- Connect an infected USB drive into a corporate computer system.
Internal threats also have the potential to cause greater damage than external threats because internal users have direct access to the building and its infrastructure devices. Employees also have knowledge of the corporate network, its resources, and its confidential data.
Network security professionals must implement tools and apply techniques for mitigating both external and internal threats.
1.1.1.4 Data Loss
Data is likely to be an organization’s most valuable asset. Organizational data can include research and development data, sales data, financial data, human resource and legal data, employee data, contractor data, and customer data.
Data loss or data exfiltration is when data is intentionally or unintentionally lost, stolen, or leaked to the outside world. The data loss can result in:
- Brand damage and loss of reputation
- Loss of competitive advantage
- Loss of customers
- Loss of revenue
- Litigation/legal action resulting in fines and civil penalties
- Significant cost and effort to notify affected parties and recover from the breach
Common data loss vectors are displayed in the figure.
Network security professionals must protect the organization’s data. Various Data Loss Prevention (DLP) controls must be implemented, that combine strategic, operational and tactical measures.
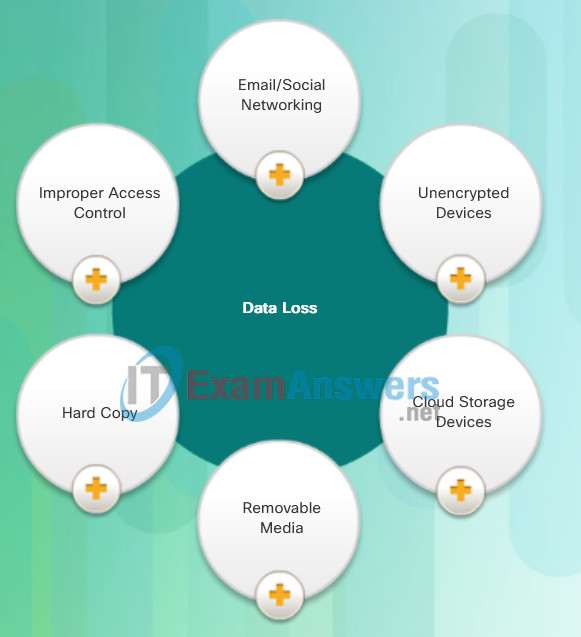
- Email/Social Networking: The most common vector for data loss includes instant messaging software and social media sites. For instance, intercepted email or IM messages could be captured and reveal confidential information.
- Unencrypted Devices: A stolen corporate laptop typically contains confidential organizational data. If the data is not stored using an encryption algorithm, then the thief can retrieve valuable confidential data.
- Cloud Storage Devices: Saving data to the cloud has many potential benefits. However, sensitive data can be lost if access to the cloud is compromised due to weak security settings.
- Removable Media: One risk is that an employee could perform an unauthorized transfer of data to a USB drive. Another risk is that a USB drive containing valuable corporate data could be lost.
- Hard Copy: Corporate data should be disposed of thoroughly. For example, confidential data should be shredded when no longer required. Otherwise, a thief could retrieve discarded reports and gain valuable information.
- Improper Access Control: Passwords are the first line of defense. Stolen passwords or weak passwords which have been compromised can provide an attacker easy access to corporate data.
1.1.2 Network Topology Overview
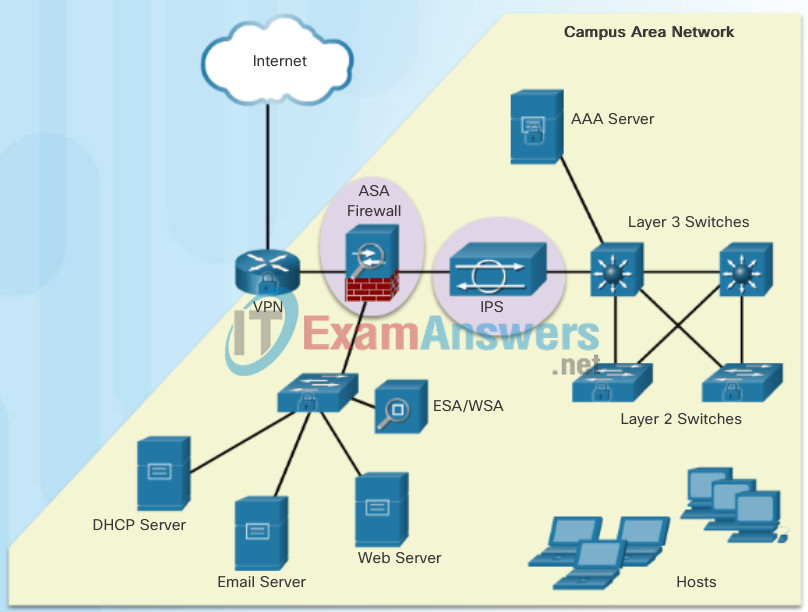
1.1.2.1 Campus Area Networks
All networks are targets. However, the main focus of this course is on securing Campus Area Networks (CANs). Campus Area Networks consists of interconnected LANs within a limited geographic area.
Network professionals must implement various network security techniques to protect the organizations’ assets from outside and inside threats. Connections to untrusted networks must be checked in-depth by multiple layers of defense before reaching enterprise resources.
The figure displays a sample CAN with a defense in-depth approach using various security features and security devices to secure it.
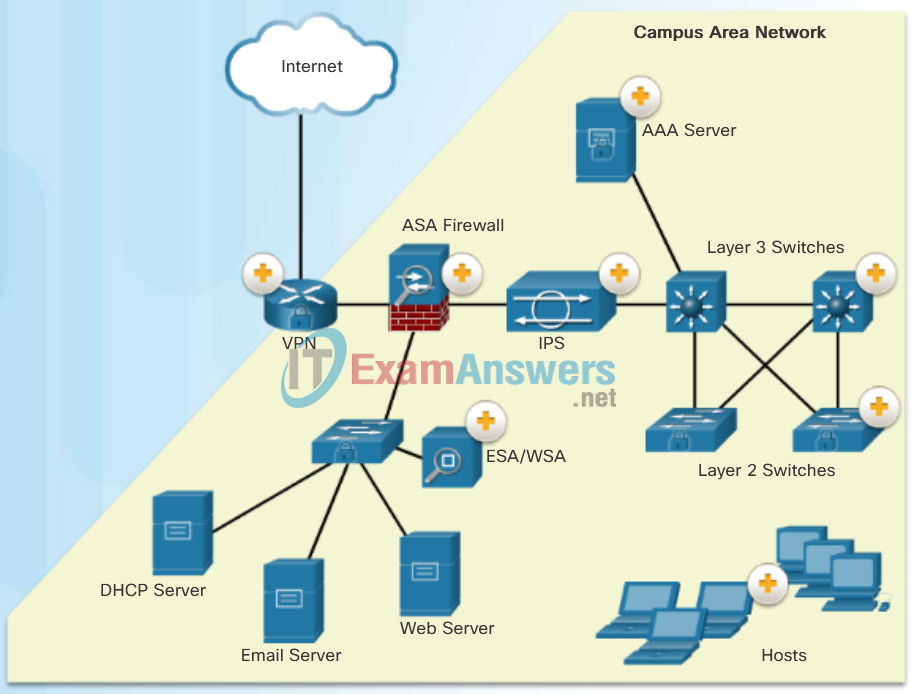
- AAA Server: An authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) server authenticates users, authorizes what they are allowed to do, and tracks what they are doing.
- ASA Firewall: A Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) firewall performs stateful packet filtering to filter return traffic from the outside network into the campus network.
- Layer 3 Switches: These distribution layer switches are secured and provide secure redundant trunk connections to the Layer 2 switches. Several different security features can be implemented, such as ACLs, DHCP snooping, Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI), and IP source guard.
- VPN: The Cisco ISR is secured. It protects data in motion that is flowing from the CAN to the outside world by establishing Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). VPNs ensure data confidentiality and integrity from authenticated sources.
- IPS: A Cisco Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) device continuously monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic for malicious activity. It logs information about the activity, and attempts to block and report it.
- ESA/WSA: A Cisco Email Security Appliance (ESA) and Web Security Appliance (WSA) provide advanced threat defense, application visibility and control, reporting, and secure mobility to secure and control email and web traffic.
- Layer 2 Switches: These access layer switches are secured and connect user-facing ports to the network. Several different security features can be implemented, such as port security, DHCP snooping, and 802.1X user authentication.
- Hosts: End points are secured using various features including antivirus and antimalware software, Host Intrusion Protection System features, and 802.1X authentication features.
1.1.2.2 Small Office and Home Office Networks
It is important that all types of networks, regardless of size, are protected. Attackers are also interested in home networks and small office and home office (SOHO) networks. They may want to use someone’s Internet connection for free, use the Internet connection for illegal activity, or view financial transactions, such as online purchases.
Home networks and SOHOs are typically protected using a consumer grade router, such as a Linksys home wireless router. These routers provide basic security features to adequately protect inside assets from the outside attackers.
The figure displays a sample SOHO using a consumer-grade wireless router to secure it.
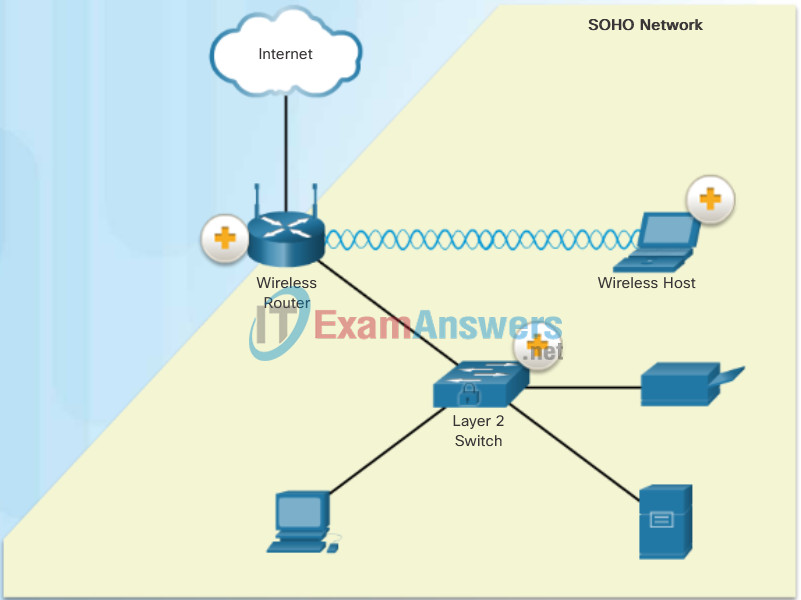
- Wireless Router: This consumer-grade wireless router provides integrated firewall features and secure wireless connections.
- Layer 2 Switch: This access layer switch is hardened and connects user-facing ports using port security to the SOHO network.
- Wireless Host: Wireless hosts connect to the wireless network using Wireless Protected Access 2 (WPA2) data encryption technology. Hosts typically have antivirus and antimalware software installed.
1.1.2.3 Wide Area Networks
Wide Area Networks (WANs) span a wide geographical area, often over the public Internet. Organizations must ensure secure transport for the data in motion as it travels between sites.
Network security professionals must use secure devices on the edge of the networks. In the figure, the main site is protected by an Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA), which provides stateful firewall features and establishes secure Virtual Private Network (VPN) tunnels to various destinations.
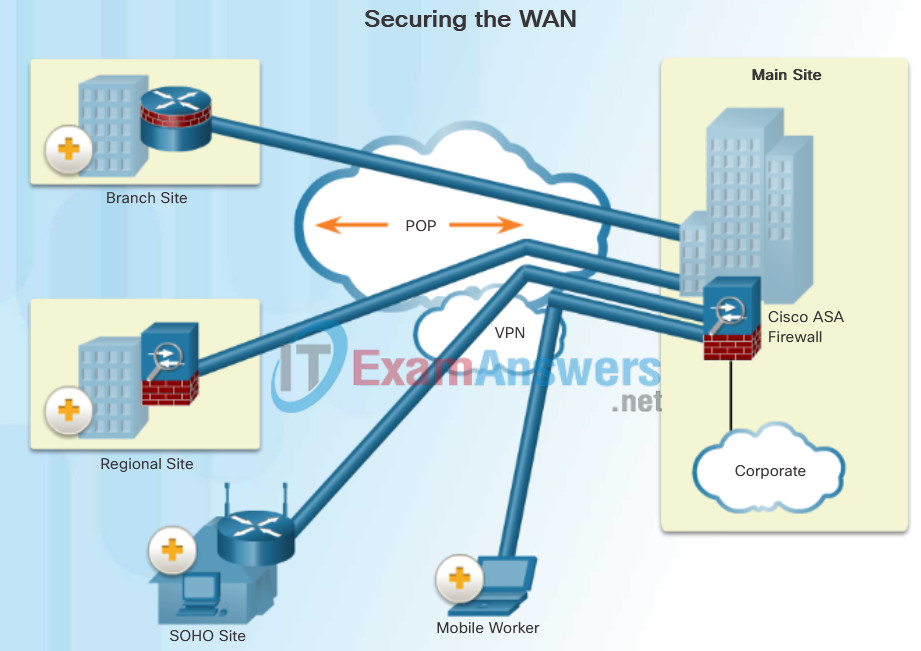
- Branch Site: This site connects to the corporate main site using a hardened ISR. The ISR can establish a permanent always-on VPN connection to the main site ASA.
- Regional Site: This is larger than a branch site and connects to the corporate main site using an ASA. The ASA can establish a permanent always-on VPN connection to the main site ASA.
- SOHO Site: This is a small branch site that connects to the corporate main site using a Cisco wireless router. The wireless router can establish a permanent always-on VPN connection to the main site ASA. Alternatively, the internal SOHO users could use the Cisco Anyconnect VPN client to establish a secure VPN connection to the main site ASA.
- Mobile Worker: This is a teleworker that can use the Cisco Anyconnect VPN client to establish a secure VPN connection to the main site ASA.
1.1.2.4 Data Center Networks
Data center networks are typically housed in an off-site facility to store sensitive or proprietary data. These sites are interconnected to corporate sites using VPN technology with ASA devices and integrated data center switches, such as a high-speed Nexus switches.
Today’s data centers store vast quantities of sensitive, business-critical information; therefore, physical security is critical to its operation. Physical security not only protects access to the premise but also protects people and equipment. For example, fire alarms, sprinklers, seismically-braced server racks, and redundant heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) and UPS systems are in place to protect people and equipment.
As highlighted in Figure 1, data center physical security can be divided into two areas:
- Outside perimeter security – This can include on-premise security officers, fences, gates, continuous video surveillance, and security breach alarms.
- Inside perimeter security – This can include continuous video surveillance, electronic motion detectors, security traps, and biometric access and exit sensors.
Security traps provide access to the data halls where data center data is stored. As shown in Figure 2, security traps are similar to an air lock. A person must first enter the security trap using their badge ID proximity card. After the person is inside the security trap, facial recognition, fingerprints, or other biometric verifications are used to open the second door. The user must repeat the process to exit the data hall.
Figure 3 displays the biometric requirements at the Cisco Allen Data Center, in Allen, Texas.
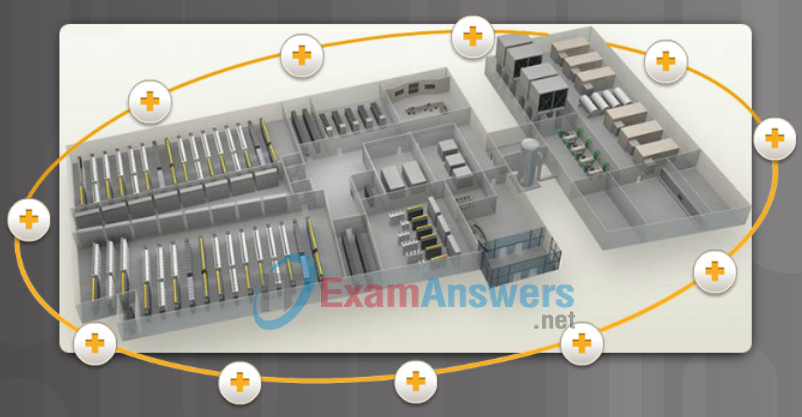
Figure 1 – Data Center Physical Security
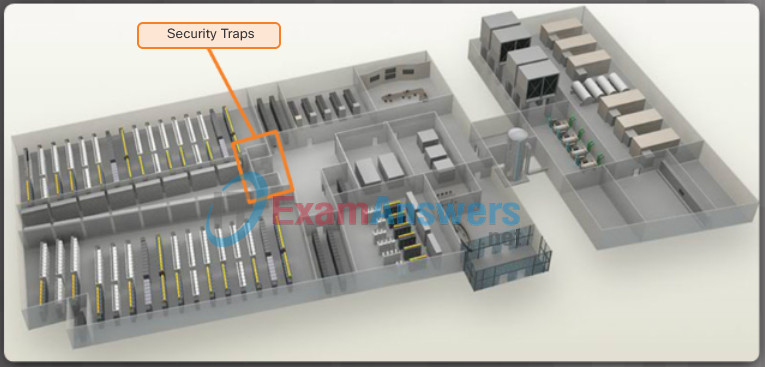
Figure 2 – Security Traps

Figure 3 – Biometrics Access
1.1.2.5 Cloud and Virtual Networks
The Cloud is playing an increasing role in enterprise networks. Cloud computing allows organizations to use services such as data storage or Cloud-based applications, to extend their capacity or capabilities without adding infrastructure. By its very nature, the Cloud is outside of the traditional network perimeter, allowing an organization to have a data center that may or may not reside behind the traditional firewall.
The terms “Cloud computing” and “virtualization” are often used interchangeably; however, they mean different things. Virtualization is the foundation of Cloud computing. Without it, Cloud computing, as it is most-widely implemented, would not be possible. Cloud computing separates the application from the hardware. Virtualization separates the OS from the hardware.
The actual Cloud network consists of physical and virtual servers which are commonly housed in data centers. However, data centers are increasingly using virtual machines (VM) to provide server services to their clients. Server virtualization takes advantage of idle resources and consolidates the number of required servers. This also allows for multiple operating systems to exist on a single hardware platform. However, VMs are also prone to specific targeted attacks as highlighted in Figure 1.

VM-Specific Threats
- Hyperjacking: An attacker could hijack a VM hypervisor (VM controlling software) and then use it as a launch point to attack other devices on the data center network.
- Instant On Activation: When a VM that has not been used for a period of time is brought online, it may have outdated security policies that deviate from the baseline security and can introduce security vulnerabilities.
- Antivirus Storms: This happens when all VMs attempt to download antivirus data files at the same time.
For security teams, an easy to implement yet comprehensive strategy that addresses business demands and defends the data center is a necessity. Cisco developed the Secure Data Center solution to operate in this unpredictable threat landscape. The Cisco Secure Data Center solution blocks internal and external threats at the data center edge.
As shown in Figure 2, the core components of the Cisco Secure Data Center solution provide:
- Secure Segmentation
- Threat Defense
- Visibility
For more information, click here to register with Cisco and then view a TechWise episode titled “How to Design the Secure Data Center.”
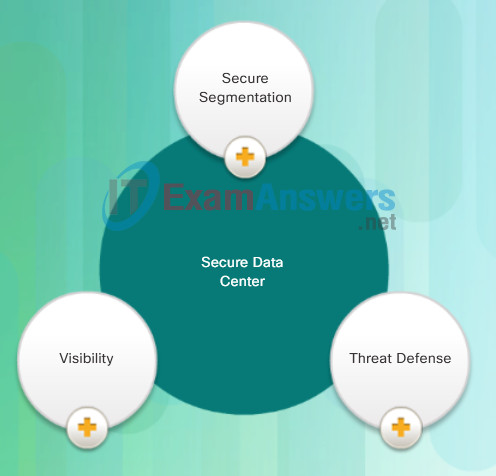
Components of a Secure Data Center Solution
- Secure Segmentation: ASA devices and a Virtual Security Gateway integrated into the Cisco Nexus Series switches are deployed in a data center network to provide secure segmentation. This provides granular inter-virtual-machine security.
- Threat Defense: ASAs and IPS devices in data center networks use threat intelligence, passive OS fingerprinting, and reputation and contextual analysis to provide threat defense.
- Visibility: Visibility solutions are provided using software such as the Cisco Security Manager which help simplify operations and compliance reporting.
1.1.2.6 The Evolving Network Border
In the past, employees and data resources remained within a predefined perimeter that was protected by firewall technology. Employees typically used company-issued computers connected to a corporate LAN that were continuously monitored and updated to meet security requirements.
Today, consumer endpoints, such as iPhones, smartphones, tablets, and thousands of other devices, are becoming powerful substitutes for, or complements to, the traditional PC. More and more people are using these devices to access enterprise information. This trend is known as Bring Your Own Device (BYOD).
To accommodate the BYOD trend, Cisco developed the Borderless Network. In a Borderless Network, access to resources can be initiated by users from many locations, on many types of endpoint devices, using various connectivity methods.
To support this blurred network edge, Cisco devices support Mobile Device Management (MDM) features. MDM features secure, monitor, and manage mobile devices, including corporate-owned devices and employee-owned devices. MDM-supported and managed devices include not only handheld devices, such as smartphones and tablets, but also laptop and desktop computing devices.
The figure highlights critical functions performed by MDM.

Critical MDM Functions for a BYOD Network
- Data Encryption: Most devices have built-in encryption capabilities, both at the device and file level. MDM features can ensure that only devices that support data encryption and have it enabled can access the network and corporate content.
- PIN Enforcement: Enforcing a PIN lock is the first and most effective step in preventing unauthorized access to a device. Furthermore, strong password policies can also be enforced by an MDM, reducing the likelihood of brute-force attacks.
- Data Wipe: Lost or stolen devices can be remotely fully- or partially-wiped, either by the user or by an administrator via the MDM.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): While data protection functions (like PIN locking, data encryption and remote data wiping) prevent unauthorized users from accessing data, DLP prevents authorized users from doing careless or malicious things with critical data.
- Jailbreak/Root Detection: Jailbreaking (on Apple iOS devices) and rooting (on Android devices) are a means to bypass the management of a device. MDM features can detect such bypasses and immediately restrict a device’s access to the network or other corporate assets.
1.2 Network Threats
1.2.1 Who is Attacking Our Network?
1.2.1.1 The Hacker
Hacker is a common term used to describe a network attacker. In this course, the terms attacker and hacker are often used interchangeably. However, the term “hacker” has a variety of meanings:
- A clever programmer capable of developing new programs and coding changes to existing programs to make them more efficient.
- A network professional that uses sophisticated programming skills to ensure that networks are not vulnerable to attack.
- A person who tries to gain unauthorized access to devices on the Internet.
- Individuals who run programs to prevent or slow network access to a large number of users, or corrupt or wipe out data on servers.
As shown in the figure, the terms white hat hacker, black hat hacker, and grey hat hacker are often used to describe hackers.
Good or bad, hacking is an import aspect of network security.

White, Black, and Grey Hat Hackers
- White Hat Hackers: These are ethical hackers who use their programming skills for good, ethical, and legal purposes. White hat hackers may perform network penetration tests in an attempt to compromise networks and systems by using their knowledge of computer security systems to discover network vulnerabilities. Security vulnerabilities are reported to developers for them to fix before the vulnerabilities can be exploited. Some organizations award prizes or bounties to white hat hackers when they inform them of a vulnerability.
- Grey Hat Hackers: These are individuals who commit crimes and do arguably unethical things, but not for personal gain or to cause damage. An example would be someone who compromises a network without permission and then discloses the vulnerability publicly. Grey hat hackers may disclose a vulnerability to the affected organization after having compromised their network. This allows the organization to fix the problem.
- Black Hat Hackers: These are unethical criminals who violate computer and network security for personal gain, or for malicious reasons, such as attacking networks. Black hat hackers exploit vulnerabilities to compromise computer and network systems.
1.2.1.2 Evolution of Hackers
Hacking started in the 1960s with phone freaking, or phreaking, which refers to using various audio frequencies to manipulate phone systems. At that time, telephone switches used various tones, or tone dialing, to indicate different functions. Early hackers realized that by mimicking a tone using a whistle, they could exploit the phone switches to make free long-distance calls.
In the mid-1980s, computer dial-up modems were used to connect computers to networks. Hackers wrote “war dialing” programs which dialed each telephone number in a given area in search of computers, bulletin board systems, and fax machines. When a phone number was found, password-cracking programs were used to gain access.
Since then, general hacker profiles and motives have changed quite a bit. The figure displays modern hacking terms and a brief description of each.
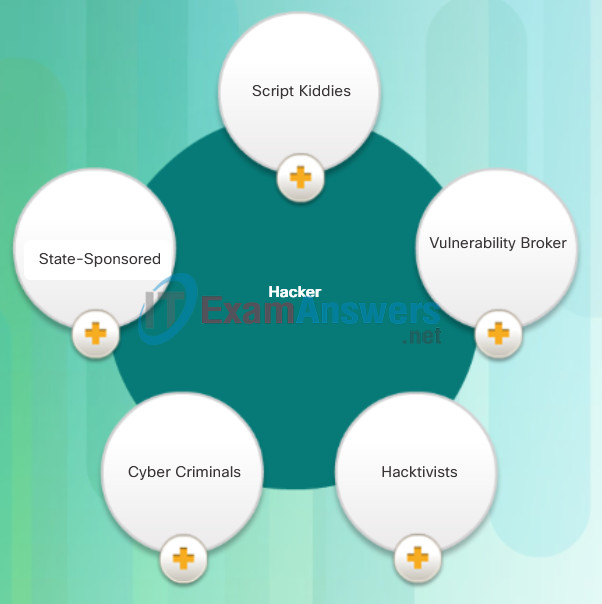
Modern Hacking Titles
- Script Kiddies: The term emerged in the 1990s and refers to teenagers or inexperienced hackers running existing scripts, tools, and exploits, to cause harm, but typically not for profit.
- Vulnerability Broker: These are usually grey hat hackers who attempt to discover exploits and report them to vendors, sometimes for prizes or rewards.
- Hacktivists: These are grey hat hackers who rally and protest against different political and social ideas. Hacktivists publicly protest against organizations or governments by posting articles, videos, leaking sensitive information, and performing distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks.
- Cyber Criminals: These are black hat hackers who are either self-employed or working for large cybercrime organizations. Each year, cyber criminals are responsible for stealing billions of dollars from consumers and businesses.
- State-Sponsored: Depending on a person’s perspective, these are either white hat or black hat hackers who steal government secrets, gather intelligence, and sabotage networks. Their targets are foreign governments, terrorist groups, and corporations. Most countries in the world participate to some degree in state-sponsored hacking.
1.2.1.3 Cyber Criminals
Cyber criminals are black hat hackers with the motive to make money using any means necessary. While sometimes these are lone wolves working independently, they are more often financed and sponsored by criminal organizations. It is estimated that globally, cyber criminals steal billions of dollars from consumers and businesses.
Cyber criminals operate in an underground economy where they buy, sell, and trade attack toolkits, zero day exploit code, botnet services, banking Trojans, keyloggers, and much more. They also buy and sell the private information and intellectual property they steal from victims. Cyber criminals target small businesses and consumers, as well as large enterprises and industry verticals.

1.2.1.4 Hacktivists
Hacktivists do not hack for profit, they hack for attention. They are usually politically or socially motivated cyber attackers who use the power of the Internet to promote their message.
Two examples of hacktivist groups are Anonymous and the Syrian Electronic Army. Although most hacktivist groups are not extremely organized, they can cause significant problems for governments and businesses. Hacktivists tend to rely on fairly basic, freely available tools.

Anonymous Hacktivist Group
1.2.1.5 State-Sponsored Hackers
State-sponsored cyber hackers are the newest type of hacker. These are government-funded and guided attackers, ordered to launch operations that vary from cyber espionage to intellectual property theft. Many countries sponsor these hackers but very few will publically admit they exist. Nations hire the best talent to create the most advanced and stealthy threats.
State-sponsored hackers create advanced, customized attack code, often using previously undiscovered software vulnerabilities.
An example of a state-sponsored attack involves the Stuxnet malware that was created to damage Iran’s nuclear enrichment capabilities.

1.2.2 Hacker Tools
1.2.2.1 Introduction of Attack Tools
To exploit vulnerability, an attacker must have a technique or tool that can be used. Over the years, attack tools have become more sophisticated, and highly automated, requiring less technical knowledge to use them than in the past.
In the figure, drag the white circle across the timeline to view the relationship between the sophistication of attack tools versus the technical knowledge required to use them.
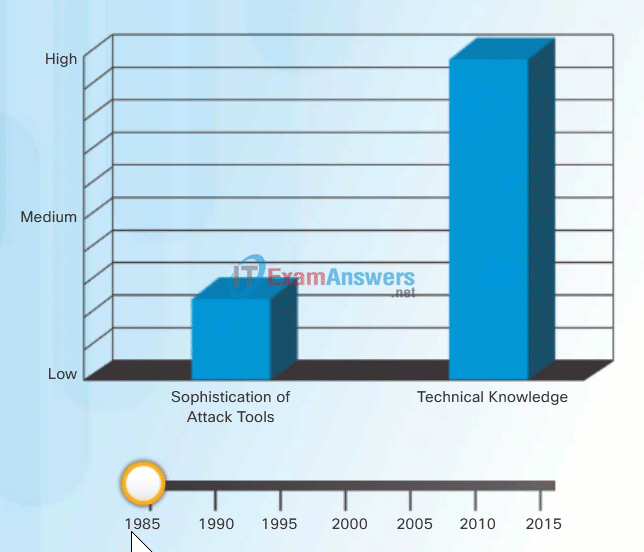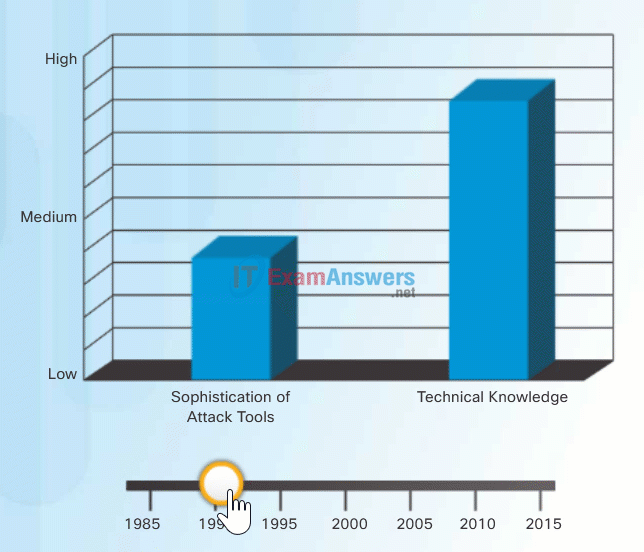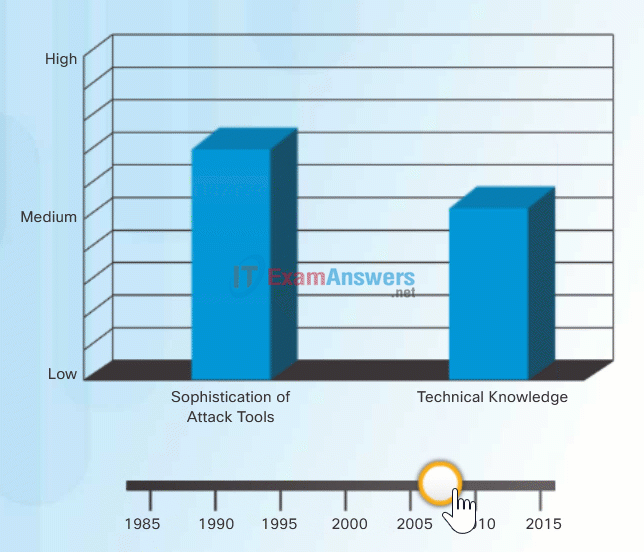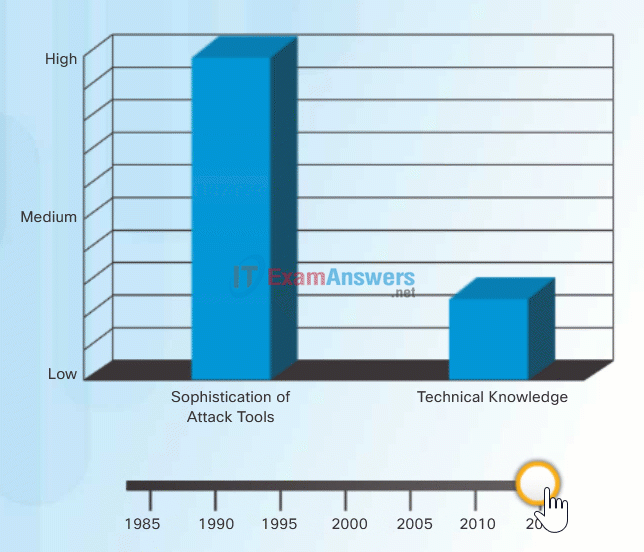
Sophistication of Attack Tools vs. Technical Knowledge
1.2.2.2 Evolution of Security Tools
Ethical hacking involves many different types of tools to test and keep the network and its data secure. To validate the security of a network and its systems, many network penetration testing tools have been developed. However, many of these tools can also be used by black hat hackers for exploitation.
Black hat hackers have also created various hacking tools. These tools are explicitly written for nefarious reasons. White hat hackers must also know how to use these tools when performing network penetration tests.
Figures 1 and 2 highlight categories of common penetration testing tools. Notice how some tools are used by white hats and black hats. Keep in mind that the list is not exhaustive as new tools are continually being developed.
Note: Many of these tools are UNIX or Linux based; therefore, a security professional should have a strong UNIX and Linux background.
Penetration Testing Tools

- Password Crackers: Passwords are the most vulnerable security threat. Password cracking tools are often referred to as password recovery tools and can be used to crack or recover the password. This is accomplished either by removing the original password, after bypassing the data encryption, or by outright discovery of the password. Password crackers repeatedly make guesses in order to crack the password and access the system. Examples of password cracking tools include John the Ripper, Ophcrack, L0phtCrack, THC Hydra, RainbowCrack, and Medusa.
- Wireless Hacking Tools: Wireless networks are more susceptible to network security threats. Wireless hacking tools are used to intentionally hack into a wireless network to detect security vulnerabilities. Examples of wireless hacking tools include Aircrack-ng, Kismet, InSSIDer, KisMAC, Firesheep, and NetStumbler.
- Network Scanning and Hacking Tools: Network scanning tools are used to probe network devices, servers, and hosts for open TCP or UDP ports. Examples of scanning tools include Nmap, SuperScan, Angry IP Scanner, and NetScanTools.
- Packet Crafting Tools: These tools are used to probe and test a firewall’s robustness using specially crafted forged packets. Examples of such tools include Hping, Scapy, Socat, Yersinia, Netcat, Nping, and Nemesis.
- Packet Sniffers: These tools are used to capture and analyze packets within traditional Ethernet LANs or WLANs. Tools include Wireshark, Tcpdump, Ettercap, Dsniff, EtherApe, Paros, Fiddler, Ratproxy, and SSLstrip.
- Rootkit Detectors: This is a directory and file integrity checker used by white hats to detect installed root kits. Example tools include AIDE, Netfilter, and PF: OpenBSD Packet Filter.
- Fuzzers to Search Vulnerabilities: Fuzzers are tools used by hackers when attempting to discover a computer system’s security vulnerabilities. Examples of fuzzers include Skipfish, Wapiti, and W3af.
Penetration Testing Tools (Cont.)

- Forensic Tools: These tools are used by white hat hackers to sniff out any trace of evidence existing in a particular computer system. Example of tools include Sleuth Kit, Helix, Maltego, and Encase.
- Debuggers: These tools are used by black hats to reverse engineer binary files when writing exploits. They are also used by white hats when analyzing malware. Debugging tools include GDB, WinDbg, IDA Pro, and Immunity Debugger.
- Hacking Operating Systems: These are specially designed operating systems preloaded with tools and technologies optimized for hacking. Examples of specially designed hacking operating systems include Kali Linux, SELinux, Knoppix, BackBox Linux.
- Encryption Tools: These tools safeguard the contents of an organization’s data at rest and data in motion. Encryption tools use algorithm schemes to encode the data to prevent unauthorized access to the encrypted data. Examples of these tools include VeraCrypt, CipherShed, OpenSHH, OpenSSL, Tor, OpenVPN, and Stunnel.
- Vulnerability Exploitation Tools: These tools identify whether a remote host is vulnerable to a security attack. Examples of vulnerability exploitation tools include Metasploit, Core Impact, Sqlmap, Social Engineer Toolkit, and Netsparker.
- Vulnerability Scanners: These tools scan a network or system to identify open ports. They can also be used to scan for known vulnerabilities and scan VMs, BYOD devices, and client databases. Examples of tools include Nipper, Secunia PSI, Core Impact, Nessus v6, SAINT, and Open VAS.
1.2.2.3 Categories of Attack Tools
Hackers can use the previously mentioned attack tools or a combination of tools to create various attacks. The figure displays common types of hacking attacks. However, the list of attacks is not exhaustive as new attack vulnerabilities are continually discovered.
It is important to understand that hackers use a variety of security tools to carry out these attacks.
Network Hacking Attacks

- Eavesdropping Attack: This is when a hacker captures and “listens” to network traffic. This attack is also referred to as sniffing or snooping.
- Data Modification Attack: If hackers have captured enterprise traffic, they can alter the data in the packet without the knowledge of the sender or receiver.
- IP Address Spoofing Attack: A hacker constructs an IP packet that appears to originate from a valid address inside the corporate intranet.
- Password-Based Attacks: If hackers discover a valid user account, the attackers have the same rights as the real user. Hackers could use that valid account to obtain lists of other users and network information. They could also change server and network configurations, modify, reroute, or delete data.
- Denial-of-Service Attack: A DoS attack prevents normal use of a computer or network by valid users. After gaining access to your network, a DoS attack can crash applications or network services. A DoS attack can also flood a computer or the entire network with traffic until a shutdown occurs because of the overload. A DoS attack can also block traffic, which results in a loss of access to network resources by authorized users.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attack: This attack occurs when hackers have positioned themselves between a source and destination. They can now actively monitor, capture, and control the communication transparently.
- Compromised-Key Attack: If a hacker obtains a secret key, that key is referred to as a compromised key. A compromised key can be used to gain access to a secured communication without the sender or receiver being aware of the attack.
- Sniffer Attack: A sniffer is an application or device that can read, monitor, and capture network data exchanges and read network packets. If the packets are not encrypted, a sniffer provides a full view of the data inside the packet. Even encapsulated (tunneled) packets can be broken open and read unless they are encrypted and the attacker does not have access to the key.
1.2.3 Malware
1.2.3.1 Various Types of Malware
The focus of this topic is on threats for end devices. Specifically, end devices are prone to malware attacks. It is important to know about malware because hackers and online criminals rely on users to install malware or help exploit the security gaps.
Click Play to view an animation of the three most common types of malware.

Types of Malware
1.2.3.2 Viruses
A virus is malicious code that is attached to executable files which are often legitimate programs. Most viruses require end user activation and can lay dormant for an extended period and then activate at a specific time or date.
A simple virus may install itself at the first line of code on an executable file. When activated, the virus might check the disk for other executables so that it can infect all the files it has not yet infected. Viruses can be harmless, such as those that display a picture on the screen, or they can be destructive, such as those that modify or delete files on the hard drive. Viruses can also be programmed to mutate to avoid detection.
Most viruses are now spread by USB memory drives, CDs, DVDs, network shares, and email. Email viruses are now the most common type of virus.

1.2.3.3 Trojan Horses
The term Trojan horse originated from Greek mythology. Greek warriors offered the people of Troy (Trojans) a giant hollow horse as a gift, as shown in the figure. The Trojans brought the giant horse into their walled city, unaware that it contained many Greek warriors. At night, after most Trojans were asleep, the warriors burst out of the horse and overtook the city.
A Trojan horse is malware that carries out malicious operations under the guise of a desired function. A Trojan horse comes with malicious code hidden inside of it. This malicious code exploits the privileges of the user that runs it. Often, Trojans are found attached to online games.
While playing the game, the user will not notice a problem. In the background, the Trojan horse has been installed on the user’s system. The malicious code from the Trojan horse continues operating even after the game has been closed.
The Trojan horse concept is flexible. It can cause immediate damage, provide remote access to the system, or access through a back door. It can also perform actions as instructed remotely, such as “send me the password file once per week.”
Custom-written Trojan horses, such as those with a specific target, are difficult to detect.
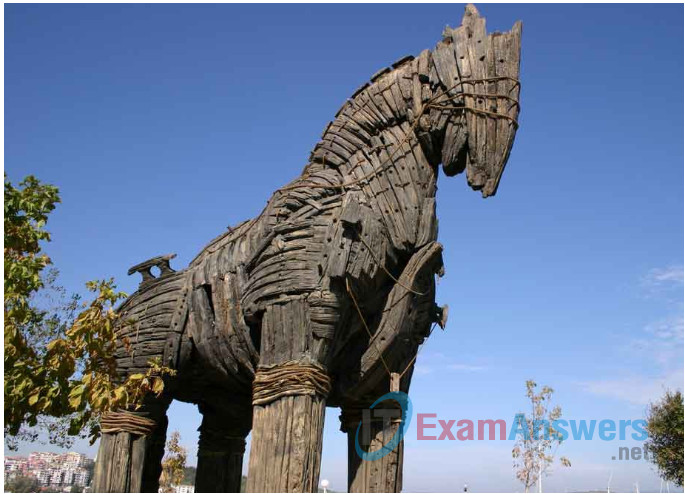

1.2.3.4 Trojan Horse Classification
Trojan horses are usually classified according to the damage that they cause or the manner in which they breach a system, as shown in the figure:
- Remote-access Trojan horse – This enables unauthorized remote access.
- Data-sending Trojan horse – This provides the attacker with sensitive data, such as passwords.
- Destructive Trojan horse – This corrupts or deletes files.
- Proxy Trojan horse – This will use the victim’s computer as the source device to launch attacks and perform other illegal activities.
- FTP Trojan horse -This enables unauthorized file transfer services on end devices.
- Security software disabler Trojan horse – This stops antivirus programs or firewalls from functioning.
- DoS Trojan horse – This slows or halts network activity.
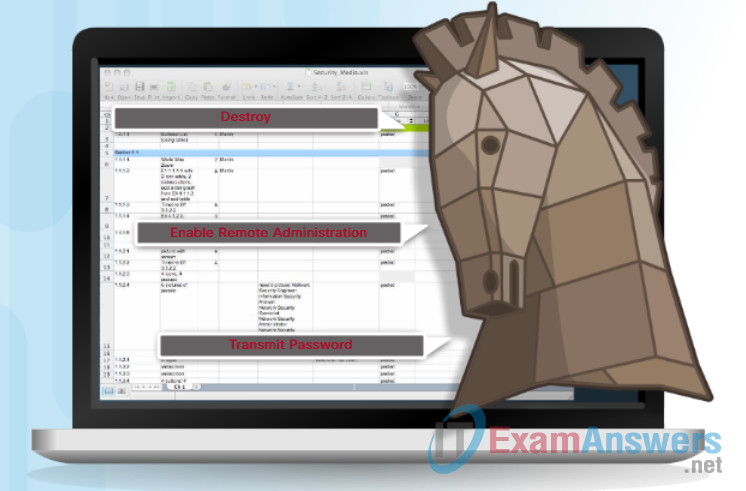
Types of Trojan Horses
1.2.3.5 Worms
Worms replicate themselves by independently exploiting vulnerabilities in networks. Worms usually slow down networks.
Whereas a virus requires a host program to run, worms can run by themselves. Other than the initial infection, they no longer require user participation. After a host is infected, the worm is able to spread very quickly over the network.
Worms are responsible for some of the most devastating attacks on the Internet. As shown in Figure 1, in 2001 the Code Red worm had infected 658 servers. Within 19 hours, the worm had infected over 300,000 servers as shown in Figure 2.
The initial infection of the SQL Slammer worm, known as the worm that ate the Internet, is shown in Figure 3. SQL Slammer was a DoS attack that exploited a buffer overflow bug in Microsoft’s SQL Server. At its peak, it doubled in size every 8.5 seconds. This is why it was able to infect 250,000+ hosts within 30 minutes, as shown in Figure 4. When it was released on the weekend of January 25, 2003, it disrupted the Internet, financial institutions, ATM cash machines, and more. Ironically, a patch for this vulnerability had been released 6 months earlier. The infected servers did not have the updated patch applied. This was a wake-up call for many organizations to implement a security policy requiring that updates and patches be applied in a timely fashion.
In 2004, the MyDoom worm would be activated by an unsuspecting user (i.e., User1) by opening an attachment in an email. The attachment released the worm that was able to learn all available email addresses on the system. The worm would then send spam email to all the recipients it discovered. This affected the Internet dramatically. Other users (i.e., User2) would open the attachment from User 1 and the cycle would repeat.
In 2008, the Conficker worm was the next largest computer worm infection since SQL Slammer.
All of these worms share similar patterns. They all have an enabling vulnerability, a way to propagate themselves, and they all contain a payload.
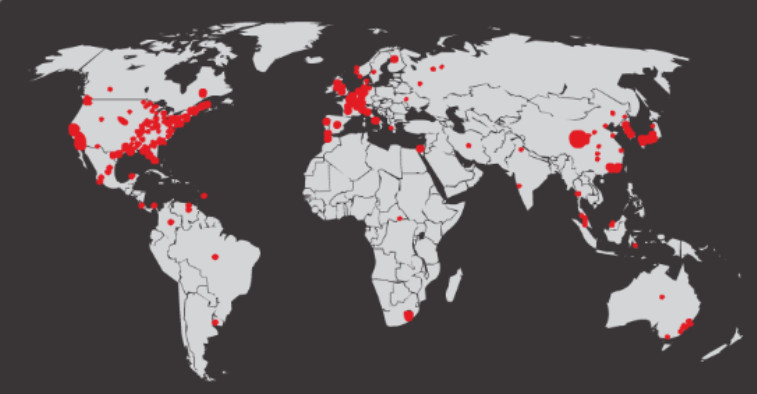
Figure 1: Initial Code Red Worm Infection
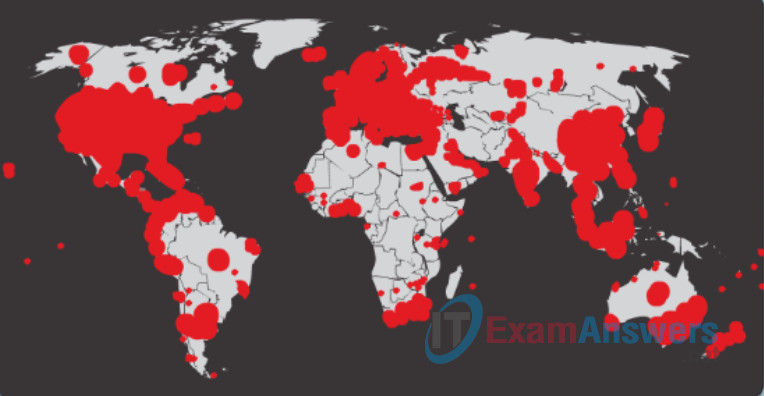
Figure 2: Code Red Worm Infection 19 Hours Later
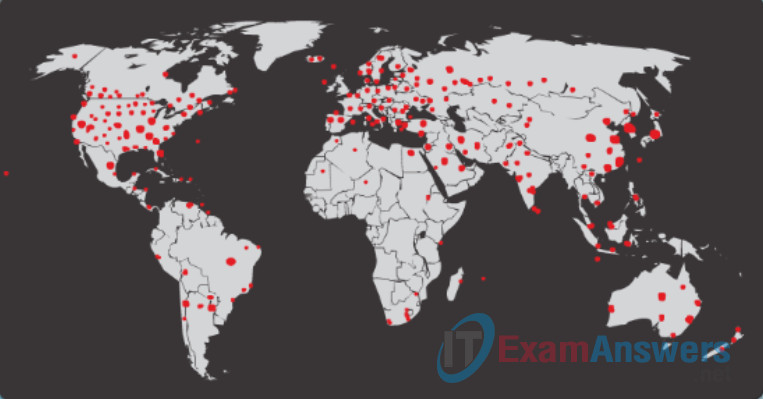
Figure 3: Initial SQL Slammer Worm Infection
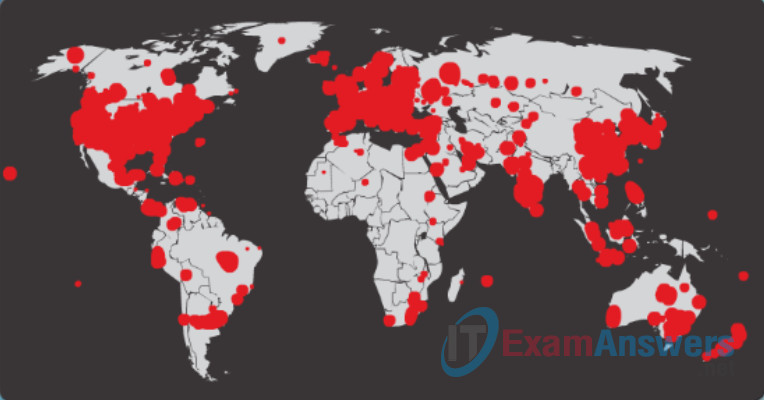
Figure 4: SQL Slammer Worm Infection 30 Minutes Later
1.2.3.6 Worm Components
Despite the mitigation techniques that have emerged over the years, worms have continued to evolve with the Internet and still pose a threat. While worms have become more sophisticated over time, they still tend to be based on exploiting weaknesses in software applications.
Most worm attacks consist of three components, as shown in Figure 1:
- Enabling vulnerability – A worm installs itself using an exploit mechanism, such as an email attachment, an executable file, or a Trojan horse, on a vulnerable system.
- Propagation mechanism – After gaining access to a device, the worm replicates itself and locates new targets.
- Payload – Any malicious code that results in some action is a payload. Most often this is used to create a backdoor to the infected host or create a DoS attack.
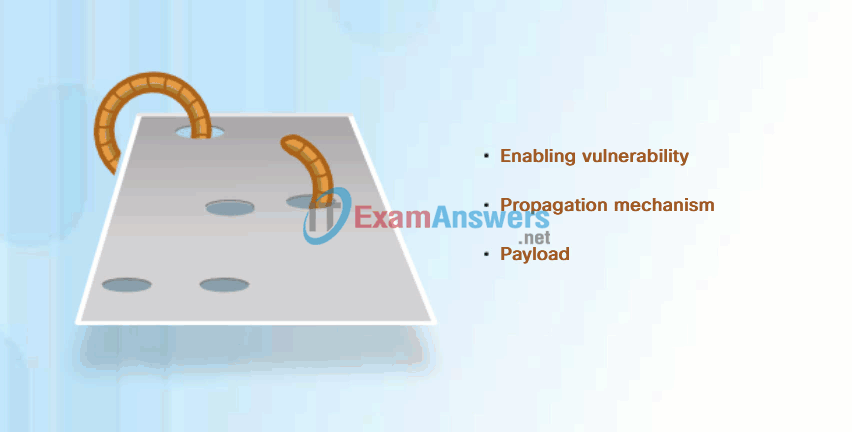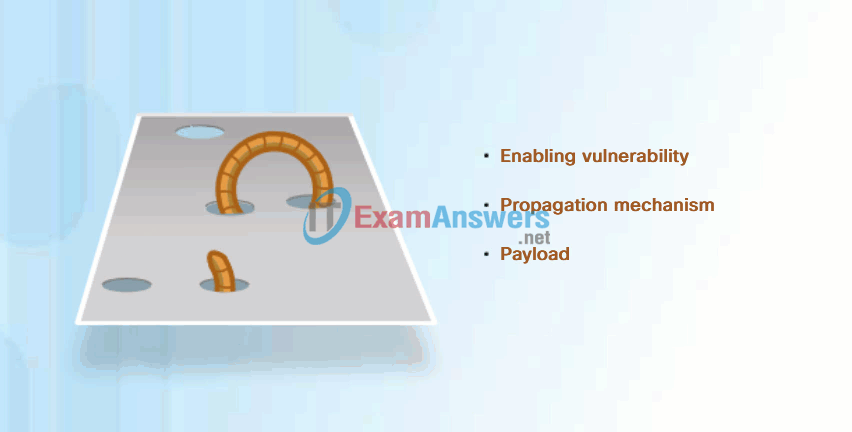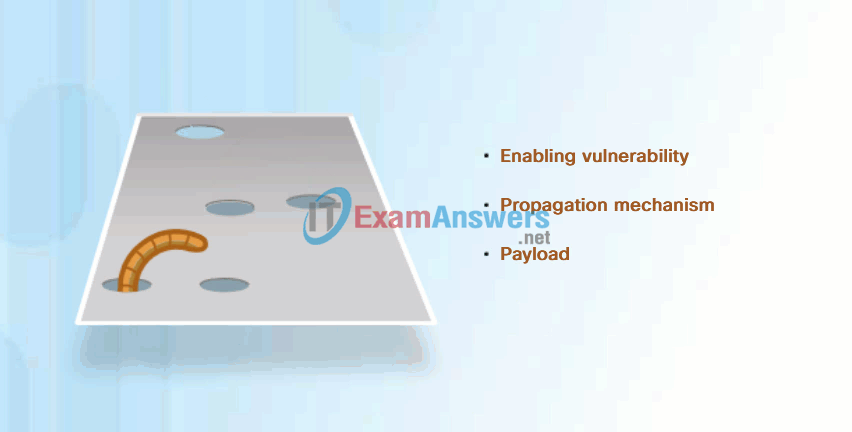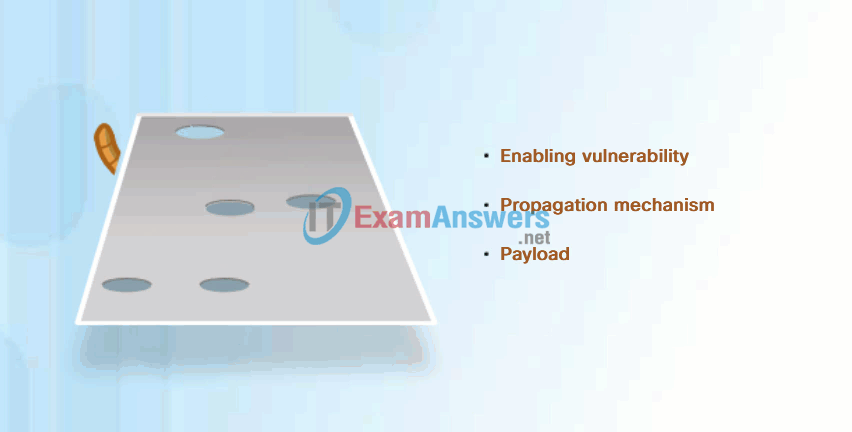
Common Worm Pattern
Worms are self-contained programs that attack a system to exploit a known vulnerability. Upon successful exploitation, the worm copies itself from the attacking host to the newly exploited system and the cycle begins again. Their propagation mechanisms are commonly deployed in a way that is difficult to detect.
Figure 2 displays the propagation technique used by the Code Red worm.
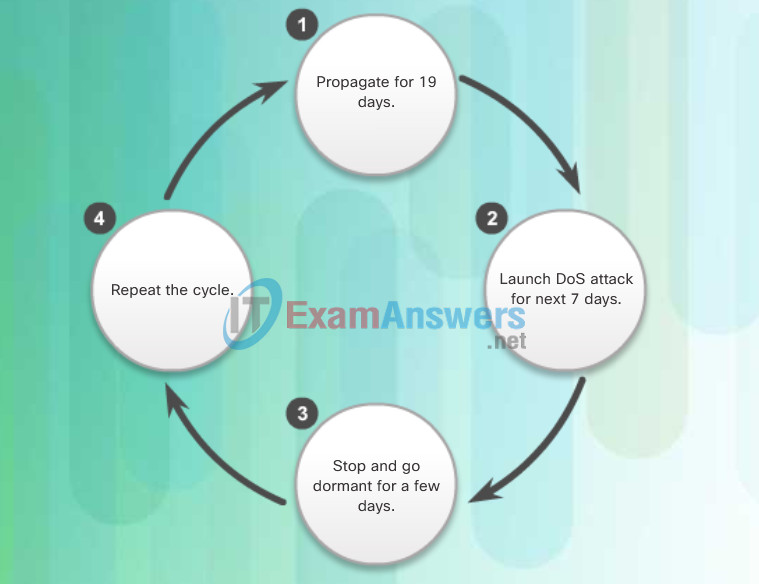
Code Red Worm Propagation
Note: Worms never really stop on the Internet. After they are released, they continue to propagate until all possible sources of infection are properly patched.
1.2.3.7 Other Malware
Hackers have used viruses, worms, and Trojan horses to carry their payloads and for other malicious reasons. Malware continues to evolve.
These are some examples of the variety of modern malware:
- Ransomware – This malware denies access to the infected computer system. The ransomware then demands a paid ransom for the restriction to be removed.
- Spyware – This malware is used to gather information about a user and send the information to another entity, without the user’s consent. Spyware can be classified as a system monitor, Trojan horse, Adware, Tracking cookies, and key loggers.
- Adware – This malware typically displays annoying pop-ups to generate revenue for its author. The malware may analyze user interests by tracking the websites visited. It can then send pop-up advertising pertinent to those sites.
- Scareware – This malware includes scam software which uses social engineering to shock or induce anxiety by creating the perception of a threat. It is generally directed at an unsuspecting user.
- Phishing – This malware attempts to convince people to divulge sensitive information. Examples include receiving an email from their bank asking users to divulge their account and PIN numbers.
- Rootkits – This malware is installed on a compromised system. After it is installed, it continues to hide its intrusion and maintain privileged access to the hacker.
This list will continue to grow as the Internet evolves. New malware will always be developed. A major goal of white hat hackers is to learn about new malware and how to promptly mitigate it.

1.2.4 Common Network Attacks
1.2.4.1 Types of Network Attacks
Malware is a means to get a payload delivered. When it is delivered and installed, the payload can be used to cause a variety of network related attacks.
Why do hackers attack networks? There are many motives including money, greed, revenge, or political, religious, or sociological beliefs. Network security professionals must understand the types of attacks used to counter these threats to ensure the security of the LAN.
Click Play to view different types of network and system attacks.
To mitigate attacks, it is useful to first categorize the various types of attacks. By categorizing network attacks, it is possible to address types of attacks rather than individual attacks. There is no standardized way of categorizing network attacks. The method used in this course classifies attacks in three major categories.
- Reconnaissance Attacks
- Access Attacks
- DoS Attacks
1.2.4.2 Reconnaissance Attacks
Reconnaissance is known as information gathering. It is analogous to a thief surveying a neighborhood by going door-to-door pretending to sell something. What the thief is actually doing is looking for vulnerable homes to break into such as unoccupied residences, residences with easy-to-open doors or windows, and those residences without security systems or security cameras.
Hackers use reconnaissance (or recon) attacks to do unauthorized discovery and mapping of systems, services, or vulnerabilities.
Recon attacks precede access attacks or DoS attacks and often employ the use of widely available tools.

Reconnaissance in a Neighborhood
1.2.4.3 Sample Reconnaissance Attack
These are some of the techniques used by malicious hackers conducting reconnaissance attacks:
- Perform an information query of a target – The hacker is looking for initial information about a target. Various tools exist, including the Google search, organizations website, whois, and more.
- Initiate a ping sweep of the target network – The information query usually reveals the target’s network address. The hacker can now initiate a ping sweep to determine which IP addresses are active.
- Initiate a port scan of active IP addresses – This is to determine which ports or services are available. Examples of port scanners include Nmap, SuperScan, Angry IP Scanner, and NetScanTools.
- Run Vulnerability Scanners – This is to query the identified ports to determine the type and version of the application and operating system that is running on the target host. Examples of tools include Nipper, Secuna PSI, Core Impact, Nessus v6, SAINT, and Open VAS.
- Run Exploitation tools – The hacker now attempts to discover vulnerable services that can be exploited. A variety of vulnerability exploitation tools exist including Metasploit, Core Impact, Sqlmap, Social Engineer Toolkit, and Netsparker.
Click Play in Figure 1 to view an animation of a hacker using the whois command to find information about a target.
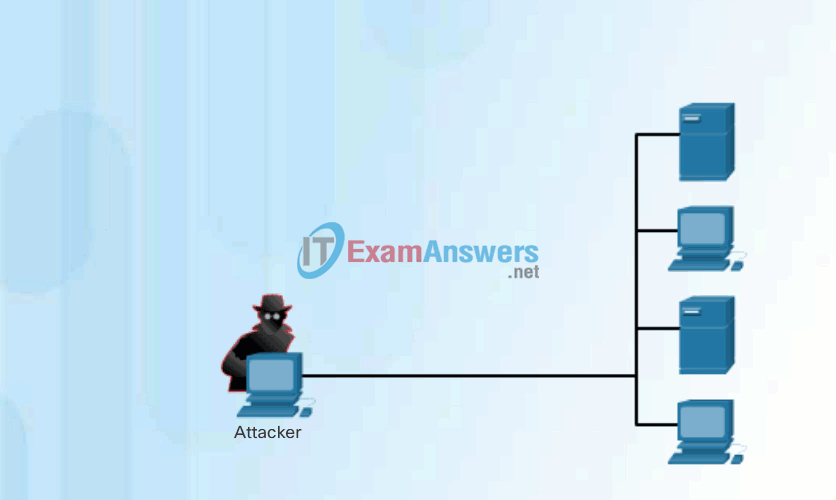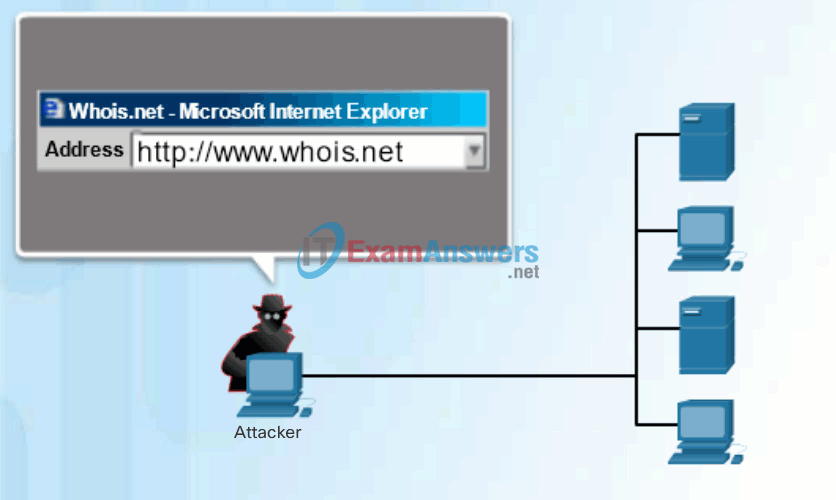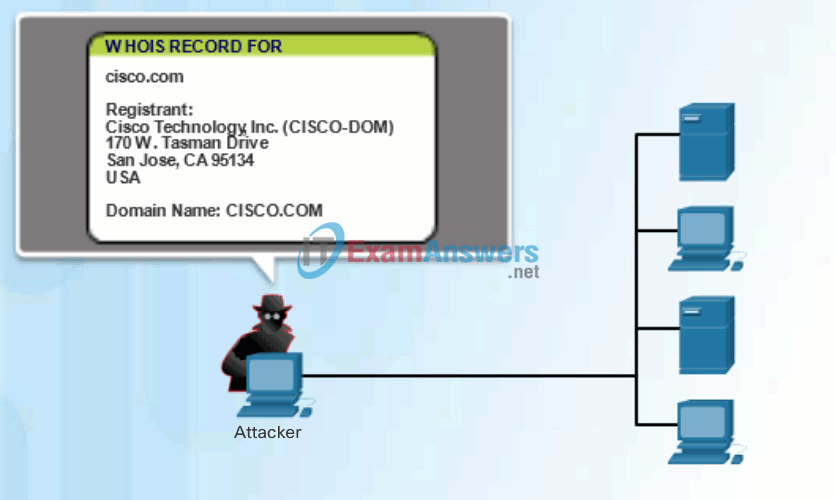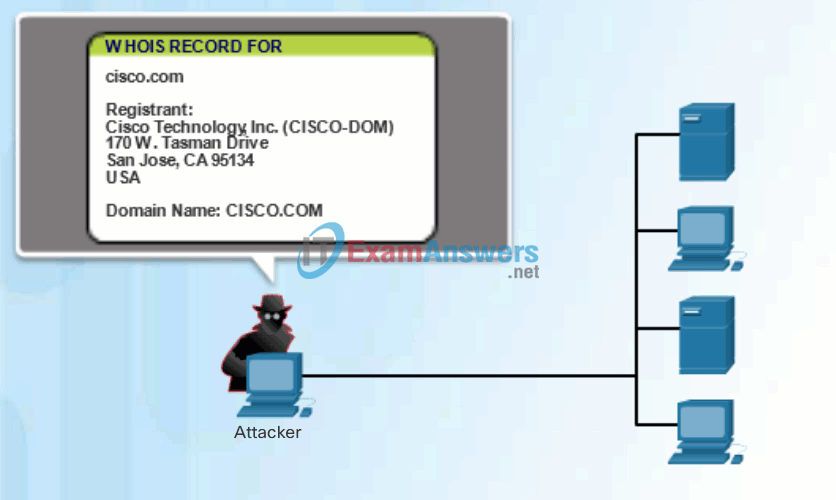
Internet Information Queries
Click Play in Figure 2 to view an animation of a hacker doing a ping sweep of the target’s network address to discover live and active IP addresses.

Performing Ping Sweeps
Click Play in Figure 3 to view an animation of a hacker performing a port scan on the discovered active IP addresses using Nmap.
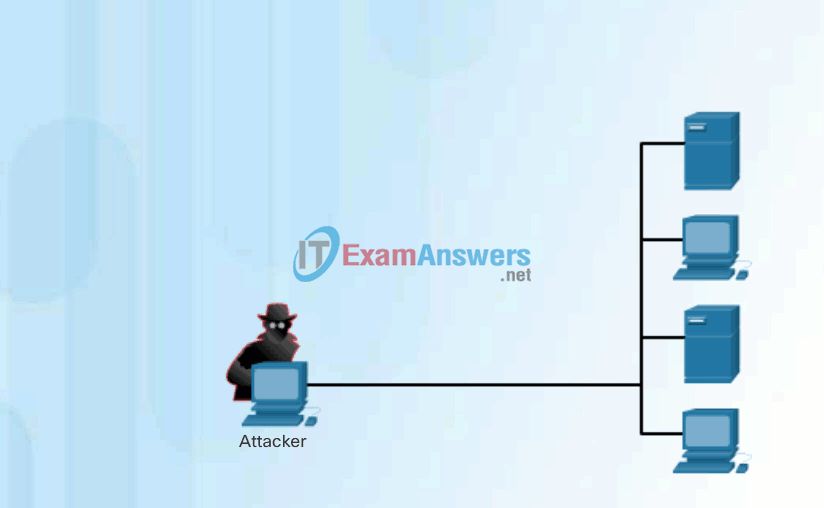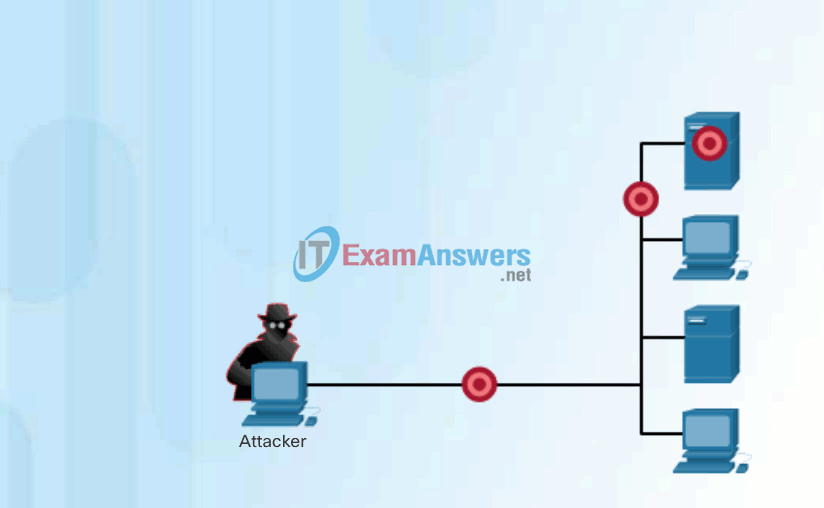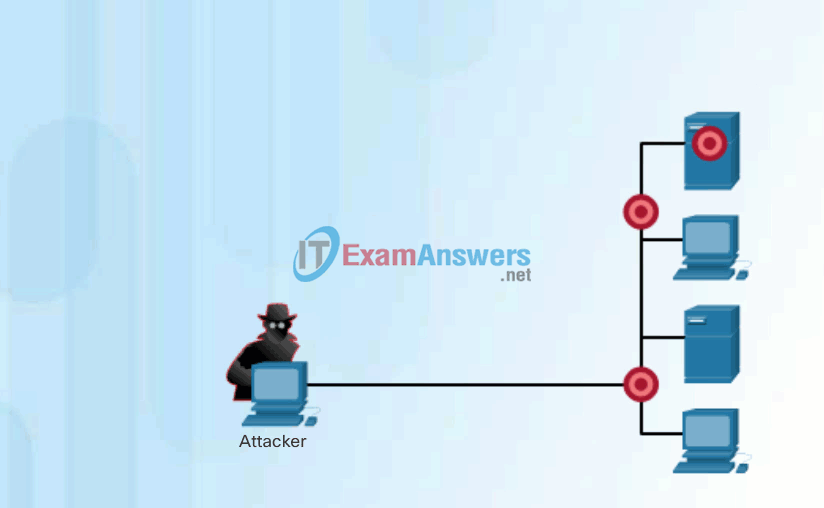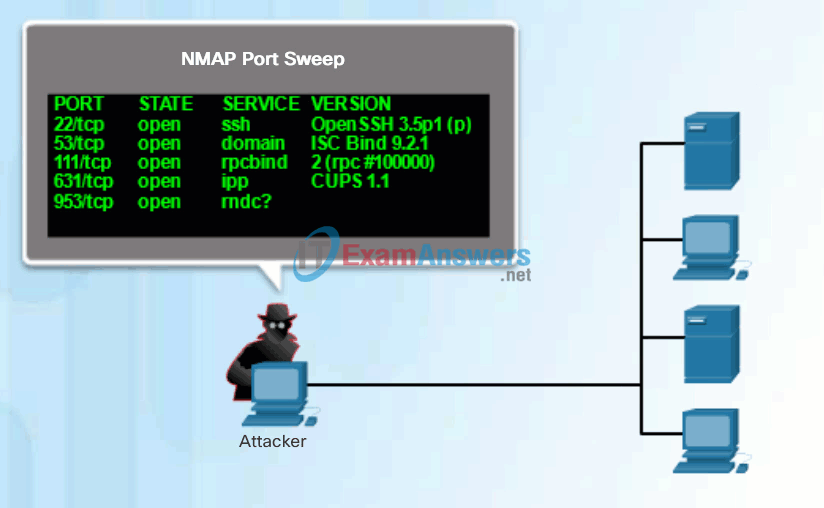
Performing Port Scans
1.2.4.4 Access Attacks
Access attacks exploit known vulnerabilities in authentication services, FTP services, and web services to gain entry to web accounts, confidential databases, and other sensitive information.
There are at least three reasons that hackers would use access attacks on networks or systems:
- To retrieve data
- To gain access
- To escalate access privileges
Click Play in the figure to view an animation of a hacker using an access attack to gain root privileges to an FTP server.
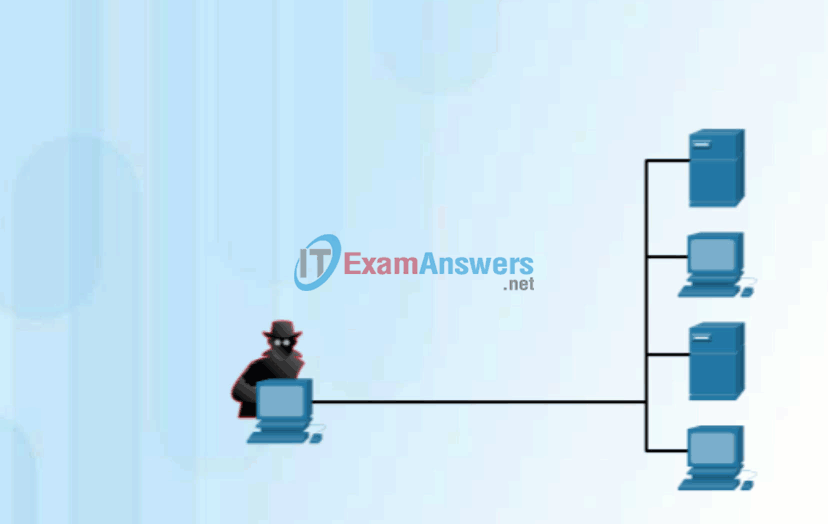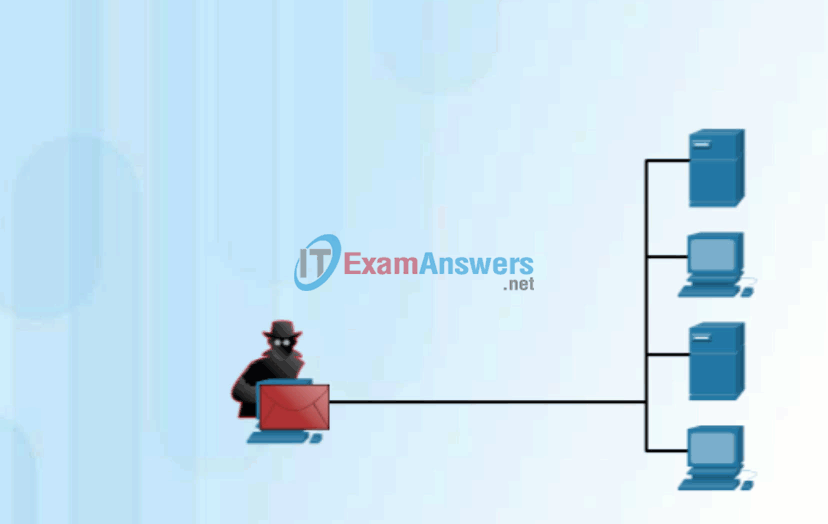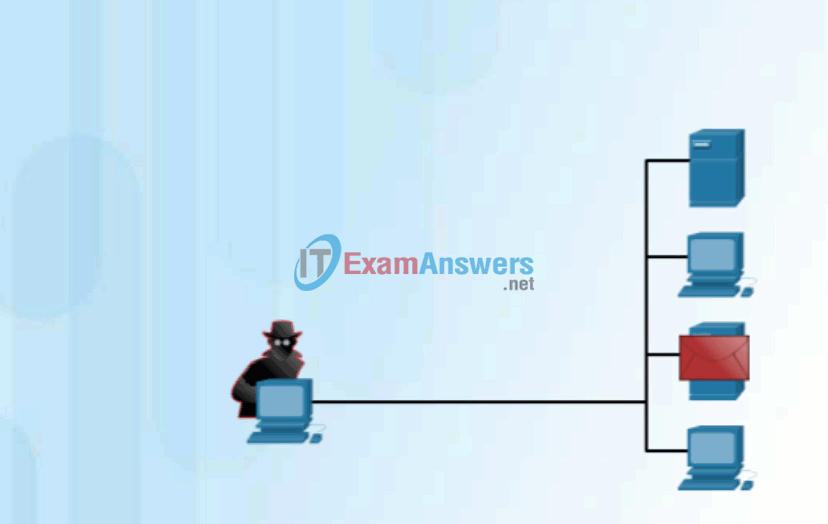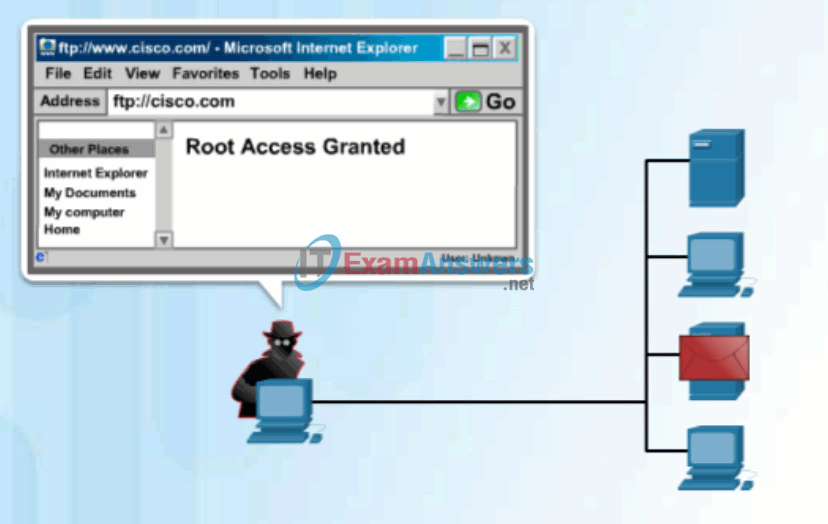
Access Attack on an FTP Server
1.2.4.5 Types of Access Attacks
There are five common types of access attacks:
- Password attack – Hackers attempt to discover critical system passwords using various methods, such as social engineering, dictionary attacks, brute-force attacks, or network sniffing. Brute-force password attacks involve repeated attempts using tools such as Ophcrack, L0phtCrack, THC Hydra, RainbowCrack, and Medusa.
- Trust exploitation – A hacker uses unauthorized privileges to gain access to a system, possibly compromising the target.
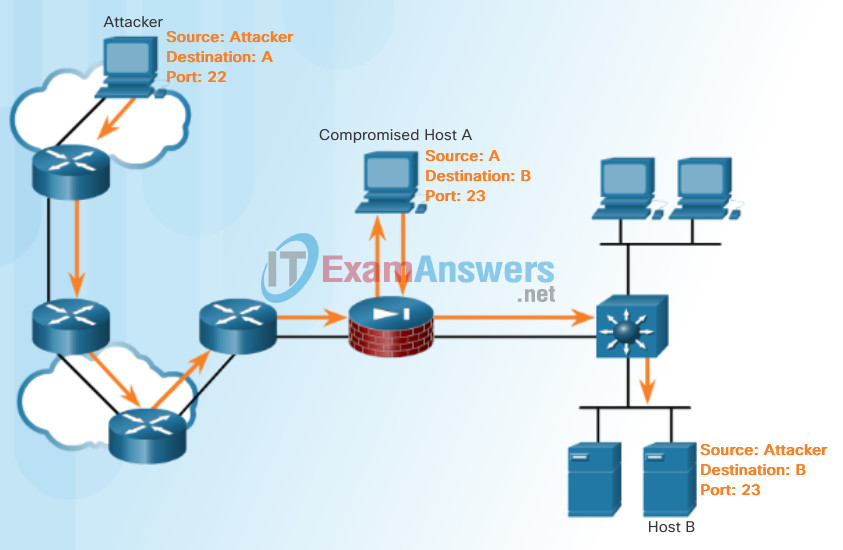
- Port redirection – This is when a hacker uses a compromised system as a base for attacks against other targets.
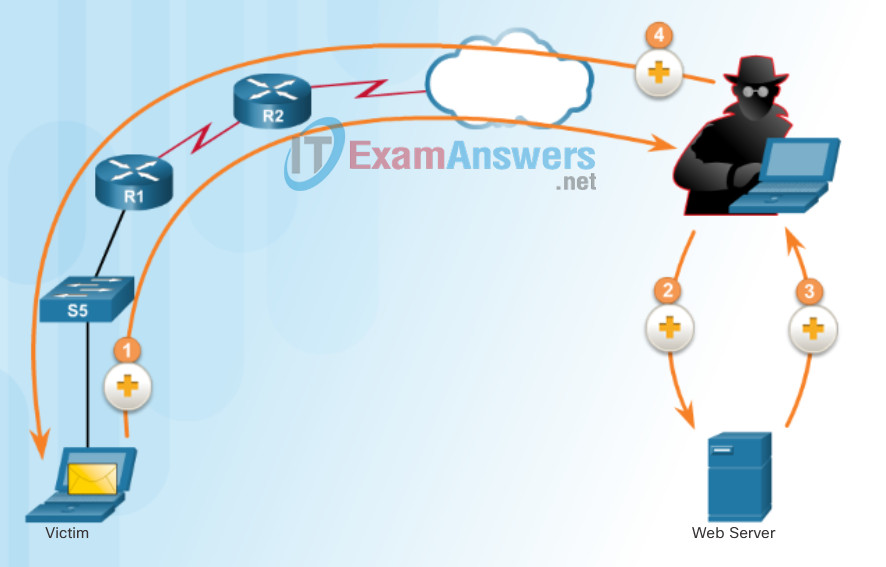
- Man-in-the-middle attack – The hacker is positioned in between two legitimate entities in order to read or modify the data that passes between the two parties.
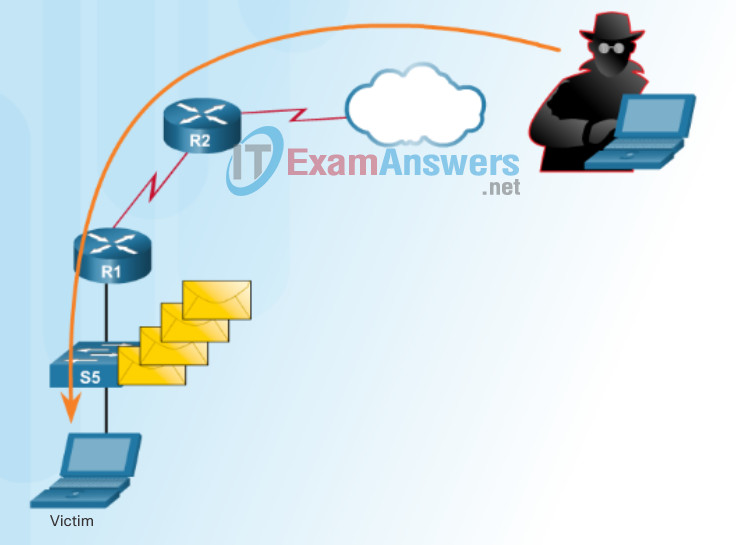
- Buffer overflow – This is when a hacker exploits the buffer memory and overwhelms it with unexpected values. This usually renders the system inoperable, creating a DoS attack. It is estimated that one third of malicious attacks are the result of buffer overflows.
- IP, MAC, DHCP Spoofing – Spoofing attacks are attacks in which one device attempts to pose as another by falsifying data. There are multiple types of spoofing attacks. For example, MAC address spoofing occurs when one computer accepts data packets based on the MAC address of another computer.
Click Play in the animation in Figure 1 to view an example of trust exploitation.
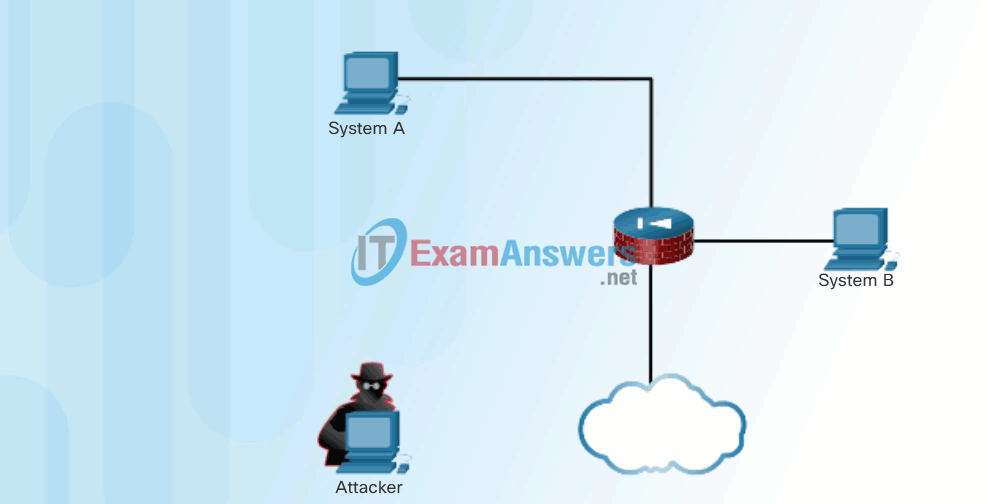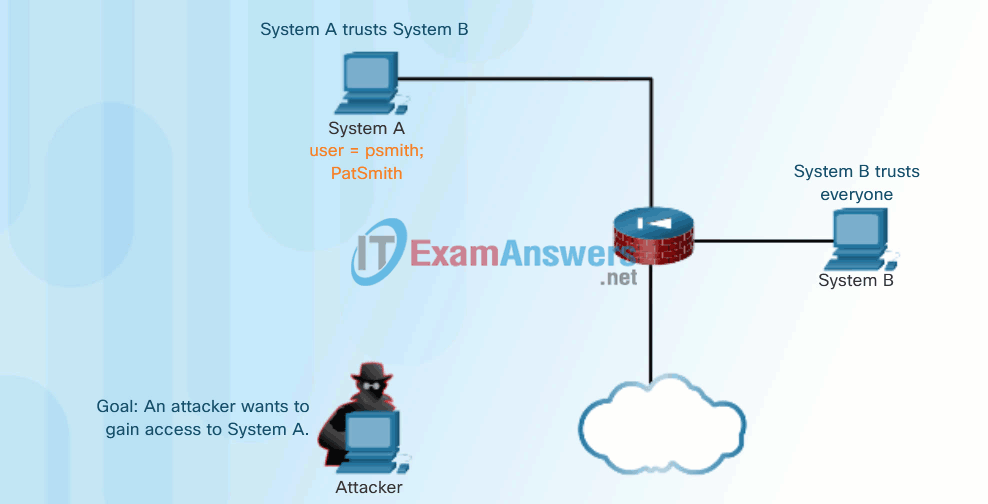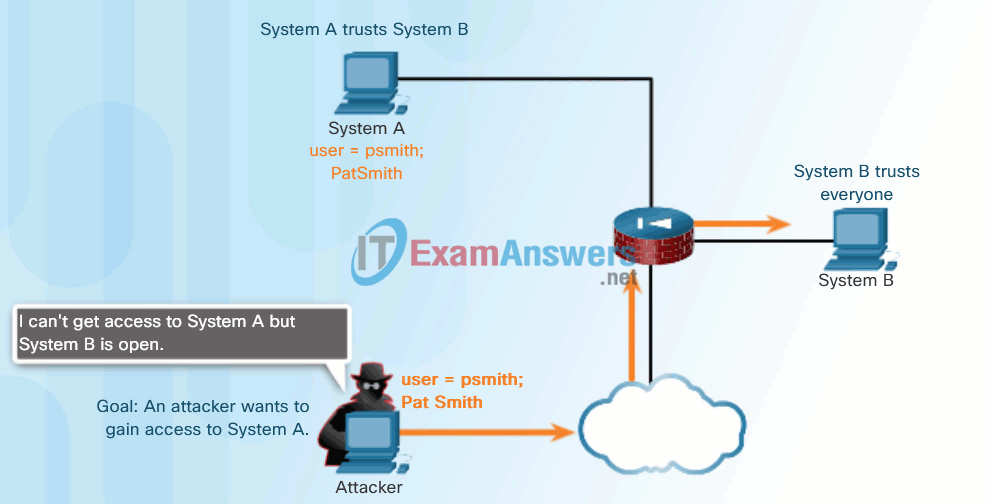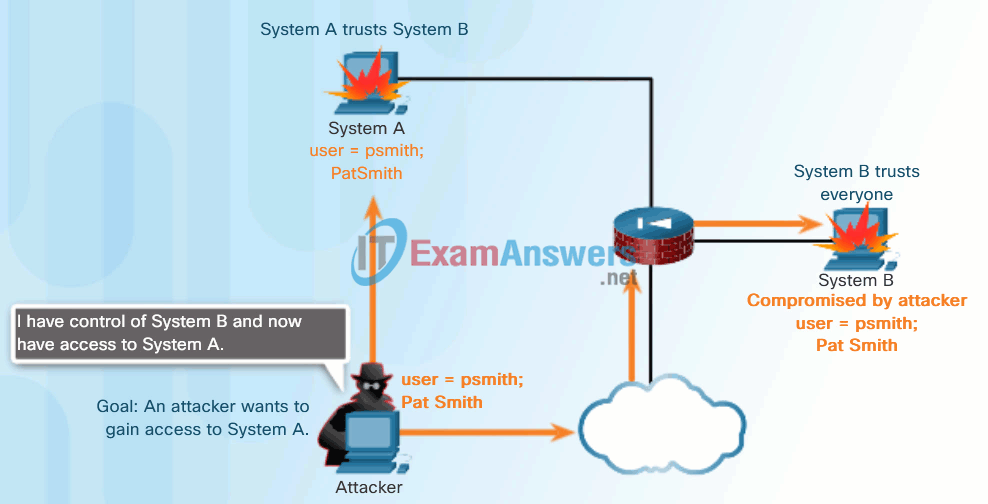
Trust Exploitation Example
The port redirection example in Figure 2 displays a hacker using SSH to connect to a compromised host A. Host A is trusted by Host B and, therefore, the hacker is allowed to use Telnet to access it.
Port Redirection Example
Figure 3 displays an example of a man-in-the-middle attack. Click each numbered “+” sign to learn more about that step in the man-in-the-middle attack.
Man-in-the-Middle Attack Example
Figure 4 displays an example of a buffer overflow attack.
Buffer Overflow Attack
1.2.4.6 Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering is an access attack that attempts to manipulate individuals into performing actions or divulging confidential information.
Social engineers often rely on people’s willingness to be helpful. They also prey on people’s weaknesses. For example, a hacker could call an authorized employee with an urgent problem that requires immediate network access. The hacker could appeal to the employee’s vanity, invoke authority using name-dropping techniques, or appeal to the employee’s greed.
There are many examples of social engineering tools available. Specific types of social engineering attacks include:
- Pretexting – This is when a hacker calls an individual and lies to them in an attempt to gain access to privileged data. An example involves an attacker who pretends to need personal or financial data in order to confirm the identity of the recipient.
- Phishing – Phishing is when a malicious party sends a fraudulent email disguised as being from a legitimate, trusted source. The message intends to trick the recipient into installing malware on their device, or into sharing personal or financial information.
- Spear phishing – This is a targeted phishing attack tailored for a specific individual or organization.
- Spam – Hackers may use spam email to trick a user to click an infected link or download an infected file.
- Tailgating – This is when a hacker quickly follows an authorized person into a secure location. The hacker then has access to a secure area.
- Something for Something (Quid pro quo) – This is when a hacker requests personal information from a party in exchange for something like a free gift.
- Baiting – This is when a hacker leaves a malware-infected physical device, such as a USB flash drive in a public location such as a corporate washroom. The finder finds the device and loads it onto their computer, unintentionally installing the malware.
The Social Engineering Toolkit (SET) was designed to help white hat hackers and other network security professionals create social engineering attacks to test their own networks.

Social Engineering
1.2.4.7 Denial of Service Attacks
Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks are highly publicized network attacks. A DoS attack results in some sort of interruption of service to users, devices, or applications.
There are two major sources of DoS attacks:
- Maliciously Formatted Packets – This is when a maliciously formatted packet is forwarded to a host or application and the receiver is unable to handle an unexpected condition. For example, a hacker forwards packets containing errors that cannot be identified by the application, or forwards improperly formatted packets. This causes the receiving device to crash or run very slowly.
- Overwhelming Quantity of Traffic – This is when a network, host, or application is unable to handle an enormous quantity of data, causing the system to crash or become extremely slow.
Click Play in the animation to view a simple animation of a DoS attack.
DoS attacks are considered a major risk because they can easily interrupt a business process and cause significant loss. These attacks are relatively simple to conduct, even by an unskilled attacker.
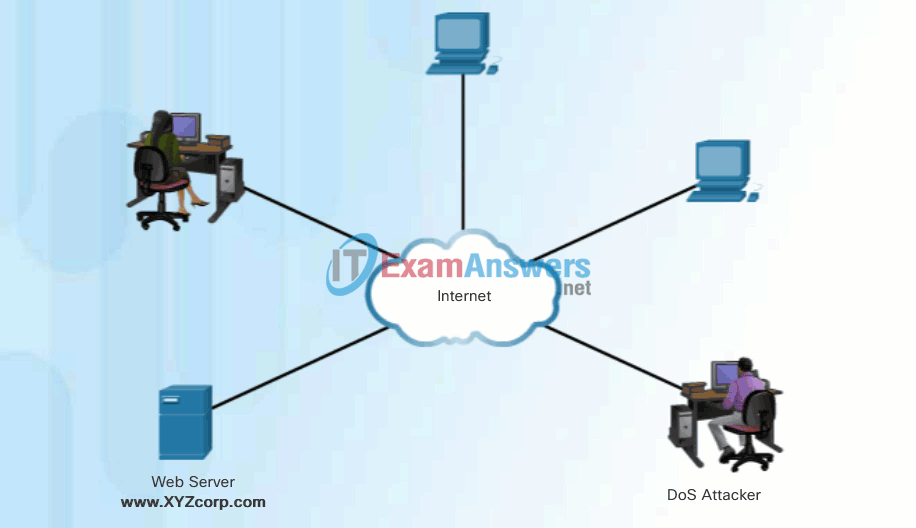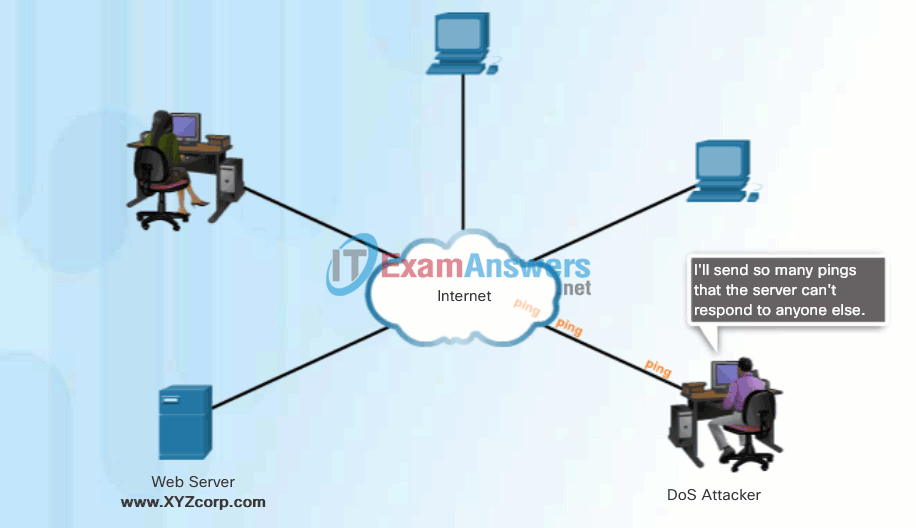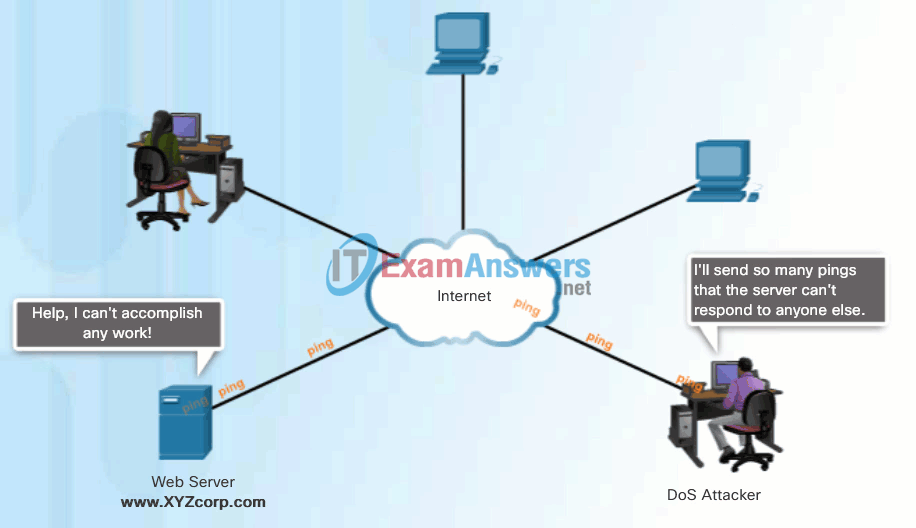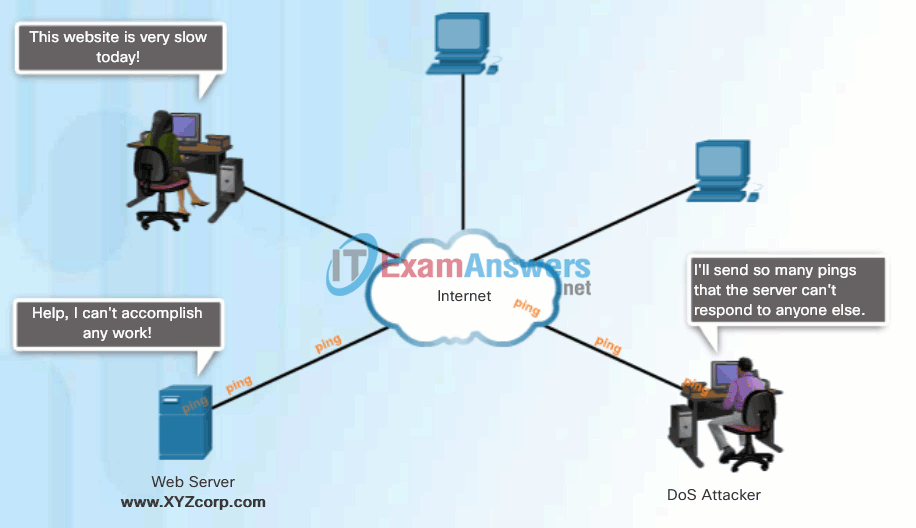
DoS Attack
1.2.4.8 Types of DoS Attacks
Although there are numerous methods of initiating a DoS attack, the following three attacks are introduced for historical reasons.
Three early DoS attacks include:
- Ping of Death – In this legacy attack, the attacker sent a ping of death which was an echo request in an IP packet larger than the maximum packet size of 65,535 bytes. The receiving host would not be able to handle a packet of that size and it would crash.
- Smurf Attack – In this legacy attack, a hacker sent a large number of ICMP requests to various recipients. Using multiple recipients amplified the attack. In addition, the packet source address contained a spoofed IP address of an intended target. This was a type of reflection attack because the echo replies would all be reflected back to the targeted host in an attempt to overwhelm it. Smurf attacks are mitigated with the no ip directed-broadcast command, which is a default interface setting, as of Cisco IOS version 12.0. The reflection and amplification technique continues to be used in newer forms of attacks. For example, click here to read about DNS-based reflection and amplification attacks.
- TCP SYN Flood Attack – In this type of attack, a hacker sends many TCP SYN session request packets with a spoofed source IP address to an intended target. The target device replies with a TCP SYN-ACK packet to the spoofed IP address and waits for a TCP ACK packet. However, the responses never arrive, and the target hosts are overwhelmed with TCP half-open connections.
The example in the figure illustrates a TCP SYN Flood attack.
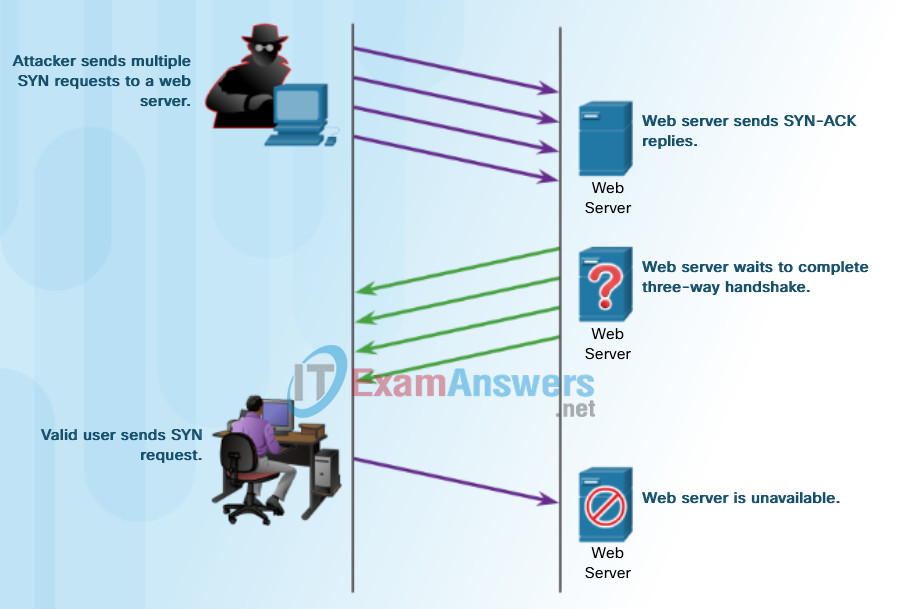
Sample TCP SYN Flood Attack
1.2.4.9 DDoS Attacks
A Distributed DoS Attack (DDoS) is similar in intent to a DoS attack, except that a DDoS attack increases in magnitude because it originates from multiple, coordinated sources. DDoS attacks also introduce new terms such as botnet, handler systems, and zombie computers.
As an example, a DDoS attack could proceed as follows:
- A hacker builds a network of infected machines. A network of infected hosts is called a botnet. The compromised computers are called zombie computers, and they are controlled by handler systems.
- The zombie computers continue to scan and infect more targets to create more zombies.
- When ready, the hacker instructs the handler systems to make the botnet of zombies carry out the DDoS attack.
Note: There is an underground economy where botnets can be bought (and sold) for a nominal fee providing hackers with an army of infected hosts ready to launch a DDoS attack.
Click Play in the figure to view the animations of a DDoS attack.
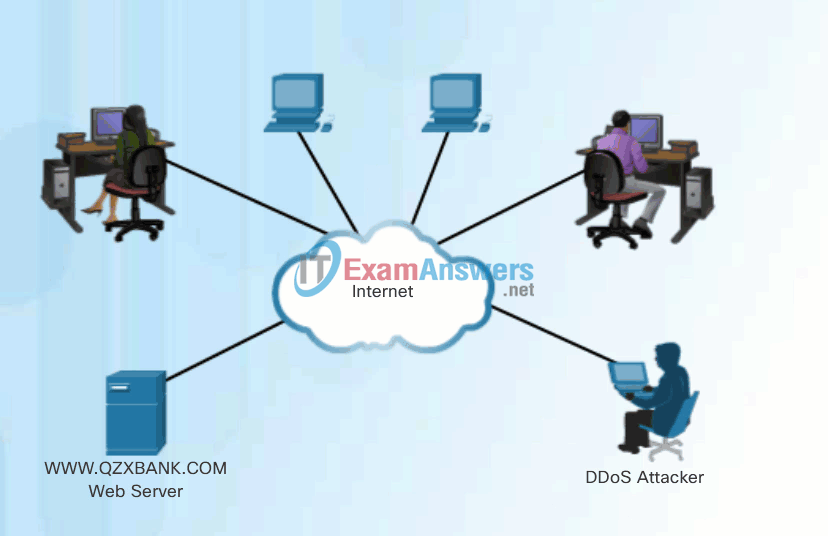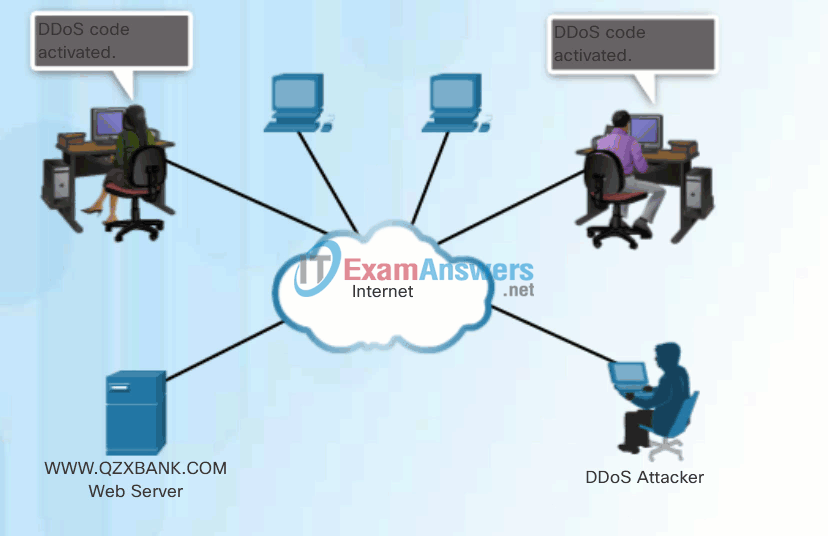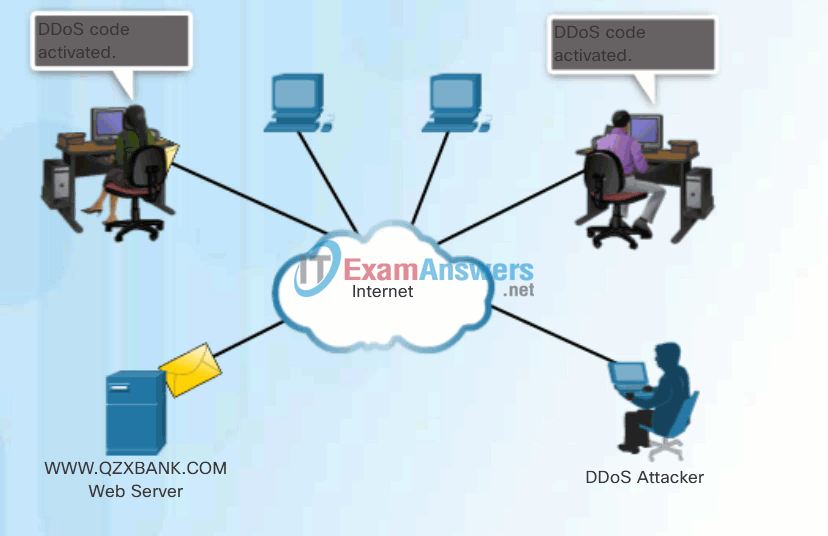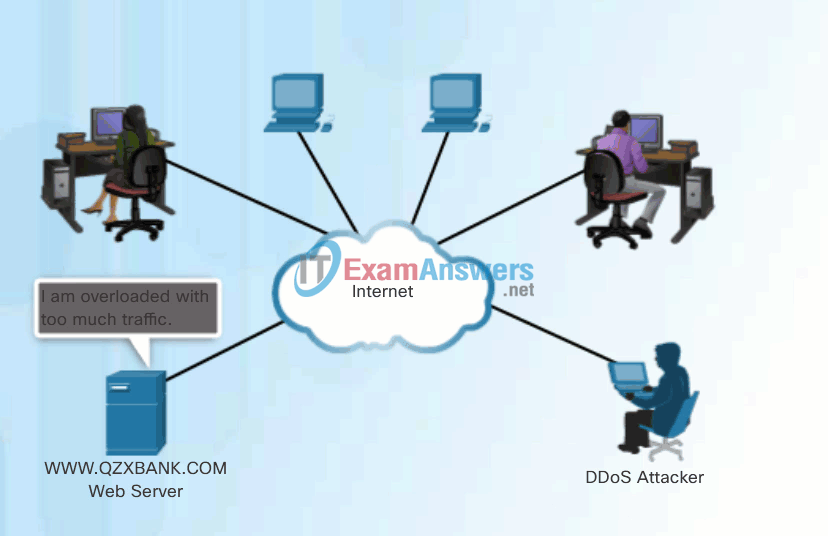
DDoS Attack
1.2.4.10 DDoS Attacks (Cont.)
Watch a Networking 101 video featuring Jimmy Ray Purser from Cisco discuss how to mitigate DDoS attacks.
1.2.4.11 Activity – Identify the Types of Network Attack
1.2.4.12 Lab: Social Engineering
In this lab, you will research examples of social engineering and identify ways to recognize and prevent it.
1.3 Mitigating Threats
1.3.1 Defending the Network
1.3.1.1 Network Security Professionals
Organizations experience productivity loss when their networks are slow or unresponsive. Business goals and profits are negatively impacted by data loss and data corruption. Therefore, from a business perspective, it is necessary to minimize the effects of hackers with bad intentions.
Network security professionals are responsible for maintaining data assurance for an organization and ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of information. Ironically, hacking has had the unintended effect of creating a high demand for network security professionals. As a result of increasing hacker exploits, the sophistication of hacker tools, and because of government legislation, network security solutions developed rapidly in the 1990s, creating new job opportunities in the field of network security.
The figure shows common network security specialist job roles within an enterprise. Regardless of job titles, network security professionals must always stay one step ahead of the hackers:
- They must constantly upgrade their skill set to keep abreast of the latest threats.
- They must attend training and workshops.
- They must subscribe to real-time feeds regarding threats.
- They must peruse security websites on a daily basis.
- They must maintain familiarity with network security organizations. These organizations often have the latest information on threats and vulnerabilities.
Note: Relative to other technology professions, network security has a very steep learning curve and requires a commitment to continuous professional development.

Network Security Professionals
1.3.1.2 Network Security Organizations
Network security professionals must collaborate with professional colleagues frequently. This includes attending workshops and conferences that are often affiliated with, sponsored by, or organized by, local, national, or international technology organizations.

- CERT: Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT) is a U.S. federally funded initiative chartered to work with the Internet community in detecting and resolving computer security incidents. The CERT Coordination Center (CERT/CC) coordinates communication among experts during security emergencies to help prevent future incidents. CERT also responds to major security incidents and analyzes product vulnerabilities. CERT manages changes relating to progressive intruder techniques and to the difficulty of detecting attacks and catching attackers. It also develops and promotes the use of appropriate technology and systems management practices to resist attacks on networked systems, to limit damage, and to ensure continuity of services.
- SANS: SysAdmin, Audit, Network, Security (SANS) Institute resources are largely free upon request and include the popular Internet Storm Center, the Internet’s early warning system; NewsBites, the weekly news digest; @RISK, the weekly vulnerability digest; flash security alerts; and more than 1,200 award-winning, original research papers. SANS also develops security courses.
- MITRE: The Mitre Corporation maintains a list of common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE) used by prominent security organizations.
- ISC2: International Information Systems Security Certification Consortium (ISC)2 provides vendor-neutral education products and career services in more than 135 countries, to 75,000+ certified industry professionals. Their mission is to make the cyber world a safer place by elevating information security to the public domain, and supporting and developing network security professionals around the world. They also provide information security certifications including the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP).
- INFOSYSSEC: Information Systems Security (InfoSysSec) is a network security organization that hosts a security news portal, providing the latest breaking news pertaining to alerts, exploits, and vulnerabilities.
- FIRST: Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST) is a security organization that brings together a variety of computer security incident response teams from government, commercial, and educational organizations to foster cooperation and coordination in information sharing, incident prevention and rapid reaction.
- MS-ISAC: The MS-ISAC is the focal point for cyber threat prevention, protection, response and recovery for the nation’s state, local, tribal, and territorial (SLTT) governments. The MS-ISAC 24×7 cyber security operations center provides real-time network monitoring, early cyber threat warnings and advisories, vulnerability identification and mitigation and incident response.
1.3.1.3 Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability
In addition to preventing and denying malicious traffic, network security professionals must also ensure that data is protected.
Cryptography, the study and practice of hiding information, is used extensively in modern network security. Today, each type of network communication has a corresponding protocol or technology designed to hide that communication from anyone other than the intended user.
Information security deals with protecting information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
As shown in the figure, cryptography ensures three components of information security:
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
Network data can be encrypted (made unreadable to unauthorized users) using various cryptography applications. The conversation between two IP phone users can be encrypted. The files on a computer can also be encrypted. These are just a few examples. Cryptography can be used almost anywhere that there is data communication. In fact, the trend is toward all communication being encrypted.
The concepts of confidentiality, integrity, and availability will be discussed often throughout this course.
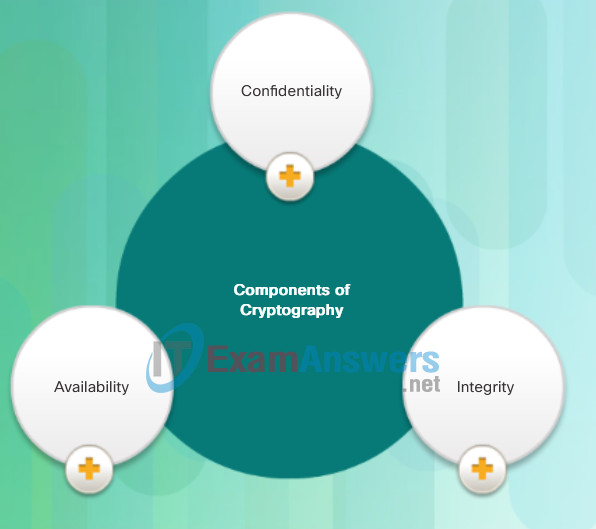
Components of Cryptography
- Confidentiality: Uses encryption algorithms to encrypt and hide data.
- Integrity: Uses hashing algorithms to ensure that data is unaltered during any operation.
- Availability: Assures that data is accessible. This is guaranteed by network hardening mechanisms and backup systems.
1.3.2 Domains of Network Security
1.3.2.1 Network Security Domains
It is vital for network security professionals to understand the reasons for network security. They must also be familiar with the organizations dedicated to network security, as well as the 12 network security domains.
Domains provide a framework for discussing network security.
There are 12 network security domains specified by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO)/International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Described by ISO/IEC 27002, these 12 domains serve to organize, at a high level, the vast realm of information under the umbrella of network security. These domains have some significant parallels with domains defined by the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) certification.
Click each domain in the figure for a brief description of that domain.
The 12 domains are intended to serve as a common basis for developing organizational security standards and effective security management practices. They also help to facilitate communication between organizations.
These 12 domains provide a convenient separation of the elements of network security. While it is not important to memorize these 12 domains, it is important to be aware of their existence and formal declaration by the ISO. They will serve as a useful reference in your work as a network security professional.
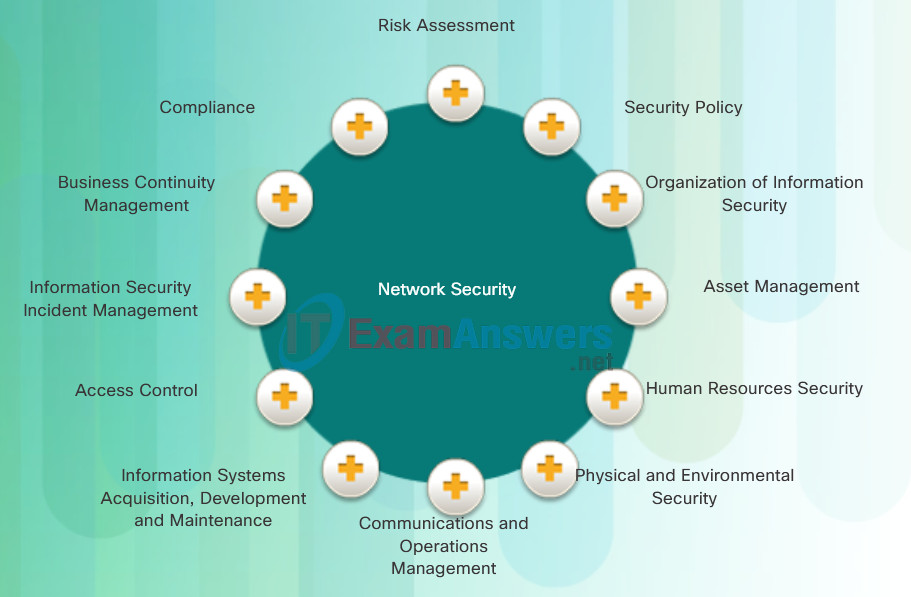
12 Domains of Network Security
- Risk Assessment: This is the first step in the risk management process. It determines the quantitative and qualitative value of risk related to a specific situation or recognized threat.
- Security Policy: A document that addresses the constraints and behaviors of members of an organization and often specifies how data can be accessed and what data is accessible by whom.
- Organization of Information Security: This is the governance model set out by an organization for information security.
- Asset Management: This is an inventory of and classification scheme for information assets.
- Human Resources Security: This addresses security procedures relating to employees joining, moving within, and leaving an organization.
- Physical and Environmental Security: This describes the protection of the computer facilities within an organization.
- Communications and Operations Management: This describes the management of technical security controls in systems and networks.
- Information Systems Acquisition, Development and Maintenance: This describes the integration of security into applications.
- Access Control: This describes the restriction of access rights to networks, systems, applications, functions, and data.
- Information Security Incident Management: This describes how to anticipate and respond to information security breaches.
- Business Continuity Management: This describes the protection, maintenance, and recovery of business-critical processes and systems.
- Compliance: This describes the process of ensuring conformance with information security policies, standards, and regulations.
1.3.2.2 Security Policy
One of the most important domains is the security policy domain. A security policy is a formal statement of the rules by which people that are given access to the technology and information assets of an organization, must abide. The concept, development, and application of a security policy are critical to keeping an organization secure. It is the responsibility of network security professionals to weave the security policy into all aspects of business operations within an organization.

1.3.2.3 Network Security Policy
The network security policy is a broad, end-to-end document designed to be clearly applicable to an organization’s operations. The policy is used to aid in network design, convey security principles, and facilitate network deployments.
The network security policy outlines rules for network access, determines how policies are enforced, and describes the basic architecture of the organization’s network security environment. Because of its breadth of coverage and impact, it is usually compiled by a committee, as shown in the figure. It is a complex document meant to govern items such as data access, web browsing, password usage, encryption, and email attachments.
When a policy is created, it must be clear what services will be made available to specific users. The network security policy establishes a hierarchy of access permissions, giving employees only the minimal access necessary to perform their work.
The network security policy outlines what assets should be protected and gives guidance on how they should be protected. This will then be used to determine the security devices and mitigation strategies and procedures that should be implemented on the network. One possible guideline that administrators can use when developing the security policy, and when determining various mitigation strategies, is the Cisco SecureX architecture.

Creating a Network Security Policy
1.3.2.4 Network Security Policy Objectives
A network security policy encompasses all requirements for securing network resources, not just equipment requirements and procedures.
A security policy is a set of objectives for the company, rules of behavior for users and administrators, and requirements for system and management, that collectively ensure the security of the network and computer systems in an organization. A security policy is a “living document”, meaning that the document is regularly updated as technology, business, and employee requirements change.
For example, employee laptops will be subject to various types of attacks, such as email viruses. A network security policy explicitly defines how frequently virus software updates and virus definition updates must be installed. Additionally, the network security policy includes guidelines for what users can and cannot do. This is normally stipulated as a formal acceptable use policy (AUP). The AUP must be as explicit as possible to avoid misunderstanding. For example, an AUP might list the specific websites or activities that are prohibited.
While the security policy should be comprehensive, it should also be succinct enough to be usable by the technology practitioners in the organization. The security policy should protect the assets of your organization by answering several security questions, as shown in the figure.

1.3.3 Introducing the Cisco SecureX Architecture
1.3.3.1 The Security Artichoke
A common analogy used to describe what a hacker must do to launch an attack was called the “Security Onion.” In the analogy, a hacker would have to peel away at a network’s defense mechanisms in a similar manner to peeling an onion.
The Borderless network has changed this analogy to the “Security Artichoke.” In this analogy, hackers no longer have to peel away each layer. They only need to remove certain ‘artichoke leafs’. The bonus is that each ’leaf’ of the network may reveal sensitive data that is not well secured. And leaf after leaf, it all leads the hacker to more data. The heart of the artichoke is where the most confidential data is found. Each leaf provides a layer of protection while simultaneously providing a path to attack.
Not every leaf needs to be removed in order to get at the heart of the artichoke. The hacker chips away at the security armor along the perimeter to get to the “heart” of the enterprise.
While Internet-facing systems are usually very well protected and boundary protections are typically solid, persistent hackers, aided by a mix of skill and luck, do eventually find a gap in that hard-core exterior through which they can enter and go where they please.
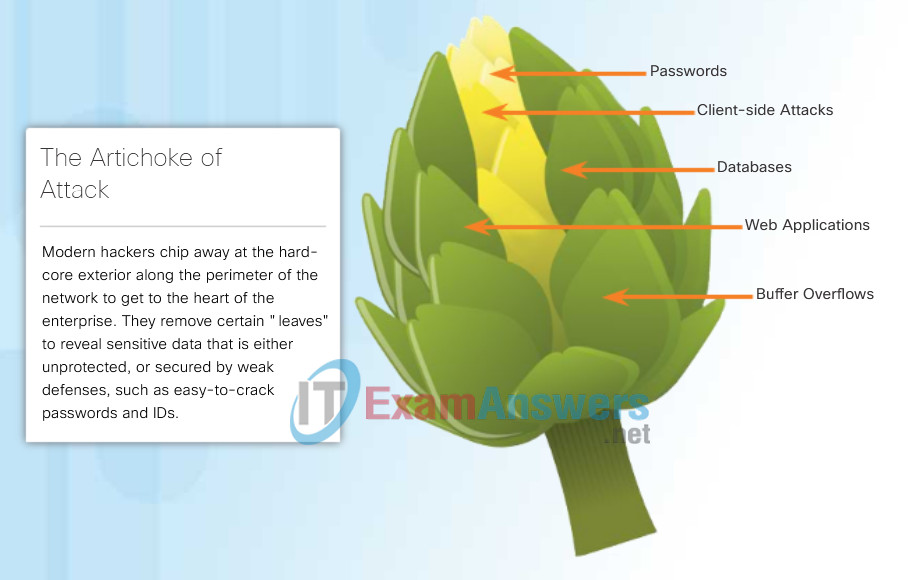
Security Artichoke
1.3.3.2 Evolution of Network Security Tools
In the 1990s, network security became an integral part of everyday operations. Tools and devices emerged that were dedicated to a particular network security function.
One of the first network security tools was the intrusion detection system (IDS). IDS and now the newer intrusion prevention system (IPS), provide real-time detection of certain types of attacks. Unlike an IDS, an IPS can also automatically block the attack in real-time.
Another security device that was developed was the firewall. Firewalls were designed to prevent undesirable traffic from entering prescribed areas within a network, thereby providing perimeter security. The original firewalls were software features added to existing networking devices, such as routers.
Companies started to develop standalone dedicated firewall devices such as Cisco’s Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA). Organizations that do not require a dedicated firewall can still use routers like the Cisco ISR and implement its sophisticated stateful firewalls features.
To ensure that all of the security devices communicate cohesively, Cisco introduced its SecureX line of technology.
Early Firewall and IPS
1.3.3.3 SecureX Products
Increased user mobility, the influx of consumer devices, and movement of information to non-traditional locations has created complexities for securing the IT infrastructure. Deploying piecemeal security solutions can lead to duplicated efforts and inconsistent access policies, and requires increased integration and staffing to support.
Cisco SecureX products work together to provide effective security for any user, using any device, from any location, at any time. This is one of the primary reasons for relying on the Cisco SecureX architecture to help shape the security policy.
In the figure, click each of the five major product categories of the SecureX architecture for a brief description.
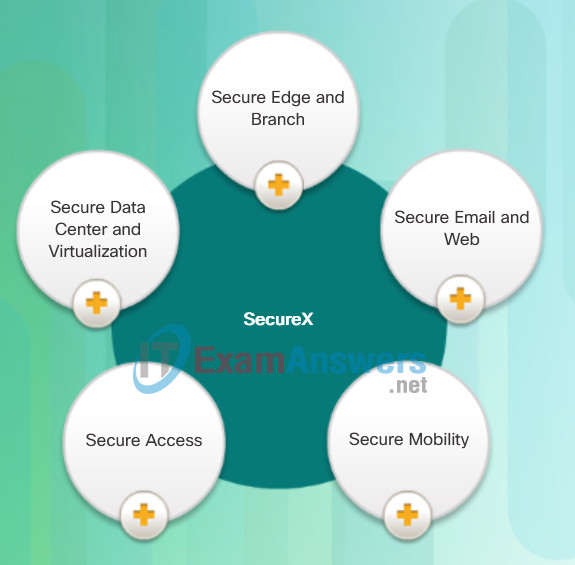
SecureX Product Families
- Secure Edge and Branch – The goal of the Cisco Secure Edge and Branch is to deploy devices and systems that detect and block attacks and exploits, and prevent intruder access. With firewall and intrusion prevention in standalone and integrated deployment options, organizations can avoid attacks and meet compliance requirements. Includes Cisco ISR G2, ASA 5500, FirePOWER 8000, and IPS 4500.
- Secure Email and Web – Cisco secure email and web solutions protect an organization from evolving email and web threats. They reduce costly downtime associated with email-based spam, viruses, and web threats. Includes the Cisco ESA and WSA appliances.
- Secure Mobility – Cisco Secure Mobility solutions promote highly secure mobile connectivity with VPN, wireless security, and remote workforce security solutions. These solutions extend network access safely and easily to a wide range of users and devices. Cisco Secure Mobility solutions offer the most comprehensive and versatile connectivity options, endpoints, and platforms to meet an organization’s changing mobility needs. Includes Cisco Identity Service Engine (ISE), Cisco TrustSec, Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Services, and Cisco Remote Access for ASA.
- Secure Access – Secure Access technologies are put in place to enforce network security policies, secure user and host access controls, and control network access, based on dynamic conditions. Includes Cisco Identity Service Engine (ISE), Cisco TrustSec, Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Services, and Cisco Remote Access for ASA.
- Secure Data Center and Virtualization – Cisco Secure Data Center and Virtualization solutions protect high-value data and data center resources with threat defense, secure virtualization, segmentation, and policy control. Includes Cisco Adaptive Security Virtual Appliance (ASAv), Cisco 5585-X, Cisco Virtual Gateway, and more.
1.3.3.4 SecureX Security Technology
The Cisco SecureX architecture is designed to provide effective security for any user, using any device, from any location, and at any time. This new security architecture uses a higher-level policy language that takes into account the full context of a situation – who, what, where, when and how. With highly distributed security policy enforcement, security is pushed closer to where the end user is working.
This architecture includes the following five major components:
- Scanning Engines
- Delivery Mechanisms
- Security Intelligence Operations (SIO)
- Policy Management Consoles
- Next-Generation Endpoints
In the figure, click each of the five major components of the SecureX architecture for a brief description.

Cisco SecureX Architecture
- Scanning Engines – These are the foundation of security enforcement and can be viewed as the workhorses of policy enforcement. They are the proxies or network-level devices that examine content, identify applications, and authenticate users. A scanning engine can be a firewall/IPS, a proxy, or an interesting fusion of the two. Scanning engines can run multiple layers of antimalware signatures, behavioral analyses, and content inspection engines.
- Delivery Mechanisms – These are the mechanisms by which scanning elements are introduced into the network. This includes the traditional network appliance, a module in a switch or a router, or an image in a Cisco security cloud.
- Security Intelligence Operations – The “brains” that distinguish good traffic from malicious traffic. The Cisco SIO encompasses multi-terabyte traffic monitoring databases, thousands of servers in multiple data centers, and hundreds of engineers and technicians with a single purpose — identifying and stopping malicious traffic.
- Policy Management Consoles – These consoles are separate from the scanners that enforce policy. By separating policy creation and management from enforcement, it is possible to have a single point of policy definition that spans multiple enforcement points such as email, instant messaging, and the Web.
- Next-Generation Endpoints – This is the critical piece that ties everything together. The next-generation endpoint can be any of a multitude of devices. Regardless of the endpoint type, all connections coming on or off of it must be routed by the device through one of the network-based scanning elements previously described.
1.3.3.5 Centralized Context-Aware Network Scanning Element
The SecureX architecture can significantly improve business efficiency and flexibility. However, that flexibility creates complexities for the IT infrastructure and any efforts to keep the infrastructure secure.
To scale this new computing model, a context-aware network scanning element that uses policies to enforce security can be deployed. A context-aware scanning element is a network security device that examines packets on the wire, but also looks at external information to understand the full context of the situation. To be context aware, the scanner must consider the ‘who, what, where, when, and how’ of a packet as it relates to security.
These scanning elements are available as stand-alone appliances, software modules running on routers, or as images within the Cloud. They are managed from a central policy console that uses a high level language that mirrors an organization’s business language and understands the context of the situation.
A context-aware policy uses a simplified descriptive business language to define security policies based on five parameters:
- The person’s identity
- The application in use
- The type of device being used for access
- The location
- The time of access
This centralized policy is pushed across the entire networked environment for distributed enforcement. This distributed enforcement ensures consistent security implementation across network zones, branch offices, remote workers, virtualized devices, and Cloud-based services.
1.3.3.6 Cisco Security Intelligence Operations
To help keep the Cisco Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS), Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA), Email Security Appliance (ESA), and Web Security Appliance (WSA) devices secure, Cisco designed the Security Intelligence Operations (SIO). The SIO is a Cloud-based service that connects global threat information, reputation-based services, and sophisticated analysis, to Cisco network security devices.
As illustrated in Figure 1, Cisco SIO is the world’s largest Cloud-based security ecosystem, using almost a million live data feeds from deployed Cisco ESA, WSA, ASA, and IPS solutions. The researchers, analysts, and developers at SIO then weigh and process the data, automatically categorizing threats and creating rules using more than 200 parameters. Rules are dynamically delivered to deployed Cisco SecureX IPS, ESA, WSA, and ASA security devices every three to five minutes.
As shown in Figure 2, the SIO can authenticate valid email traffic, filter nefarious websites, and identify hostile actions and malicious content on endpoints. The SIO uses a variety of sources when identifying and categorizing threats:
- Blacklist and reputation filters
- Information gathered by spam traps, honeypots, and crawlers
- Identifying and registering valid website domains
- Known database of attack signatures
- Performing content inspection
- Using third party partnerships
- A full-time threat research team consisting of dedicated white hat network specialists
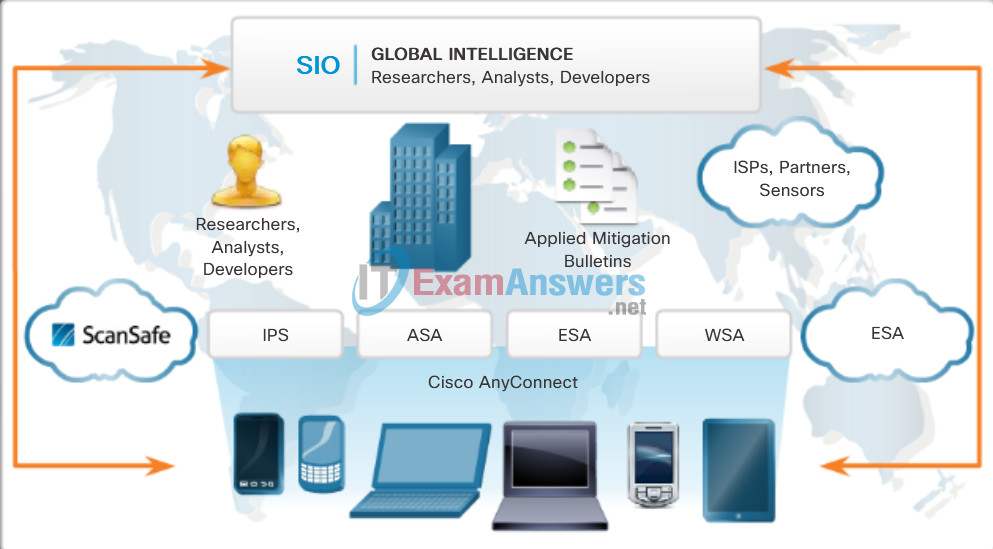
Cisco SIO Operation
Defend With Intelligence
1.3.4 Mitigating Common Network Attacks
1.3.4.1 Defending the Network
Constant vigilance and ongoing education are required to defend your network against attack. The following are best practices for securing a network:
- Develop a written security policy for the company.
- Educate employees about the risks of social engineering, and develop strategies to validate identities over the phone, via email, or in person.
- Control physical access to systems.
- Use strong passwords and change them often.
- Encrypt and password-protect sensitive data.
- Implement security hardware and software such as firewalls, IPSs, virtual private network (VPN) devices, antivirus software, and content filtering.
- Perform backups and test the backed up files on a regular basis.
- Shut down unnecessary services and ports.
- Keep patches up-to-date by installing them weekly or daily, if possible, to prevent buffer overflow and privilege escalation attacks.
- Perform security audits to test the network.
The next few pages provide overviews about mitigating some of the threats discussed in this chapter.
1.3.4.2 Mitigating Malware
Malware including viruses, worms, and Trojan horses, can cause serious problems on networks and end devices. Network administrators have several means of mitigating these attacks.
Note: Mitigation techniques are often referred to in the security community as “countermeasures”.
The primary means of mitigating virus and Trojan horse attacks is antivirus software. Antivirus software helps prevent hosts from getting infected and spreading malicious code. It requires much more time to clean up infected computers than it does to maintain up-to-date antivirus software and antivirus definitions on the same machines.
Antivirus software is the most widely deployed security product on the market today. Several companies that create antivirus software, such as Symantec, McAfee, and Trend Micro, have been in the business of detecting and eliminating viruses for more than a decade. Many corporations and educational institutions purchase volume licensing for their users. The users are able to log in to a website with their account and download the antivirus software on their desktops, laptops, or servers.
Antivirus products have update automation options so that new virus definitions and new software updates can be downloaded automatically or on demand. This practice is the most critical requirement for keeping a network free of viruses and should be formalized in a network security policy.
Antivirus products are host-based. These products are installed on computers and servers to detect and eliminate viruses. However, they do not prevent viruses from entering the network, so a network security professional must be aware of the major viruses and keep track of security updates regarding emerging viruses.
1.3.4.3 Mitigating Worms
Worms are more network-based than viruses. Worm mitigation requires diligence and coordination on the part of network security professionals.
As shown in the figure, the response to a worm attack can be broken down into four phases:
- Containment
- Inoculation
- Quarantine
- Treatment
1.3.4.4 Mitigating Reconnaissance Attacks

1.3.4.5 Mitigating Access Attacks

1.3.4.6 Mitigating DoS Attacks

1.3.5 Cisco Network Foundation Protection Framework
1.3.5.1 NFP Framework
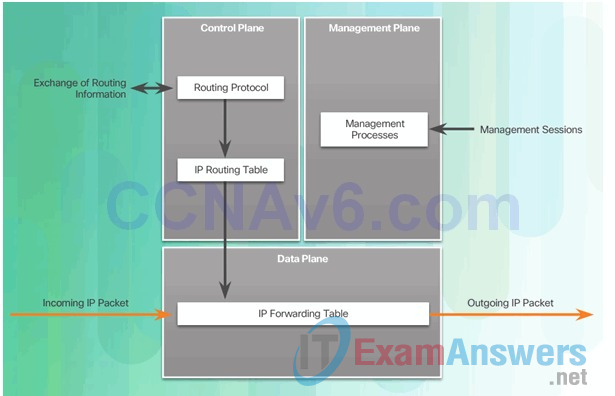
1.3.5.2 Securing the Control Plane
1.3.5.3 Securing the Management Plane
1.3.5.4 Securing the Data Plane
1.4 Chapter Summary
1.4.1 Conclusion
1.4.1.1 Lab: Researching Network Attacks and Security Audit Tools
1.4.1.1 Lab – Researching Network Attacks and Security Audit Tools
New Trends
As new technologies and end user devices come to market, businesses and consumers must continue to adjust to this ever-changing environment. The role of the network is transforming to enable the connections between people, devices, and information. There are several new networking trends that will effect organizations and consumers. Some of the top trends include:
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
- Online collaboration
- Video communications
- Cloud computing

1.4.1.2 Chapter 1: Modern Network Security Threats
Bring Your Own Device
The concept of any device, to any content, in any manner, is a major global trend that requires significant changes to the way devices are used. This trend is known as Bring Your Own Device (BYOD).
BYOD is about end users having the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business or campus network. With the growth of consumer devices, and the related drop in cost, employees and students can be expected to have some of the most advanced computing and networking tools for personal use. These personal tools include laptops, netbooks, tablets, smartphones, and e-readers. These can be devices purchased by the company or school, purchased by the individual, or both.
BYOD means any device, with any ownership, used anywhere. For example, in the past, a student who needed to access the campus network or the Internet had to use one of the school’s computers. These devices were typically limited and seen as tools only for work done in the classroom or in the library. Extended connectivity through mobile and remote access to the campus network gives students tremendous flexibility and more learning opportunities for the student.

