1.1.2.5 Packet Tracer – Create a Simple Network Using Packet Tracer Answers
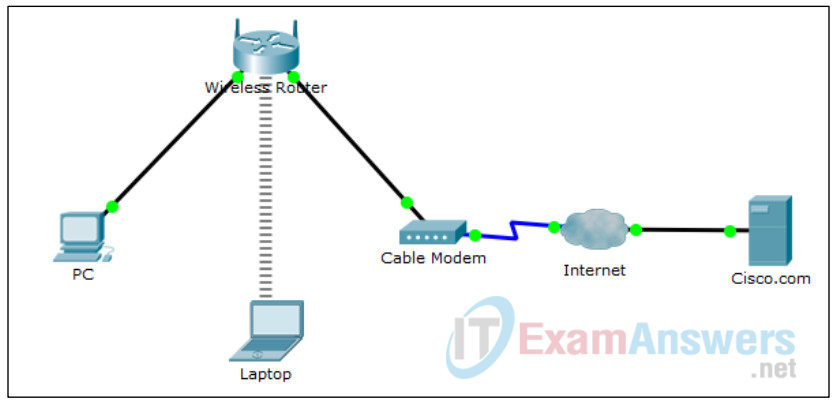
Topology
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC | Ethernet0 | DHCP | 192.168.0.1 | |
| Wireless Router WRT300N |
LAN | 192.168.0.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| Internet | DHCP | |||
| Cisco.com Server |
Ethernet0 | 208.67.220.220 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| Laptop | Wireless0 | DHCP |
Objectives
- Part 1: Build a Simple Network in the Logical Topology Workspace
- Part 2: Configure the Network Devices
- Part 3: Test connectivity between network devices
- Part 4: Save the File and Close Packet Tracer
Background / Scenario
In this activity you will build a simple network in Packet Tracer from scratch and then save the network as a Packet Tracer Activity File (.pkt).
Instructions
Part 1: Build a Simple Network in the Logical Topology Workspace
Step 1: Launch Packet Tracer.
a. Launch Packet Tracer on your PC or laptop computer
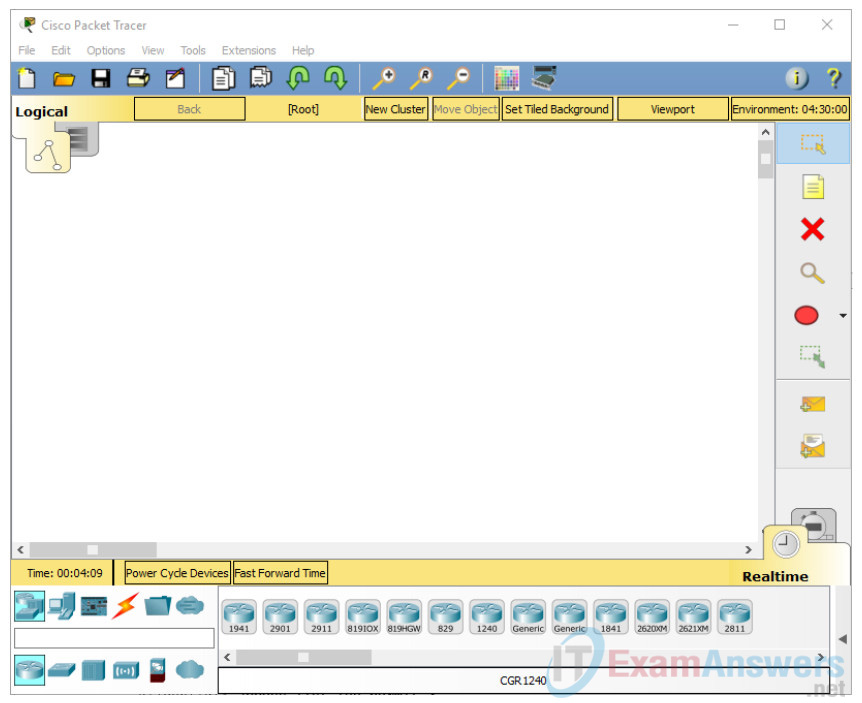
Double click on the Packet Tracer icon on your desktop or navigate to the directory that contains the Packet Tracer executable file and launch Packet Tracer. Packet Tracer should open with a blank default Logical topology workspace as shown in the figure.
Step 2: Build the topology
a. Add network devices to the workspace.
Using the device selection box, add the network devices to the workspace as shown in the topology diagram.
To place a device onto the workspace, first choose a device type from the Device-Type Selection box. Then, click on the desired device model from the Device-Specific Selection box. Finally, click on a location in the workspace to put your device in that location. If you want to cancel your selection, click the Cancel icon for that device. Alternatively, you can click and drag a device from the Device-Specific Selection box onto the workspace.
b. Add network devices to the workspace.
Using the device selection box, add the network devices to the workspace as shown in the topology diagram.
To place a device onto the workspace, first choose a device type from the Device-Type Selection box. Then, click on the desired device model from the Device-Specific Selection box. Finally, click on a location in the workspace to put your device in that location. If you want to cancel your selection, click the Cancel icon for that device. Alternatively, you can click and drag a device from the Device-Specific Selection box onto the workspace.
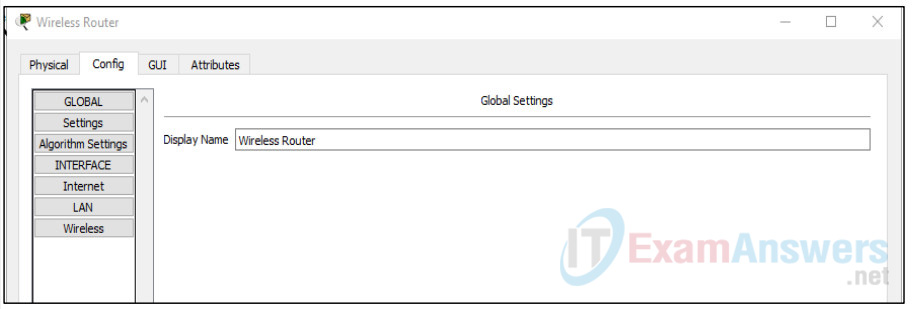
c. Change display names of the nework devices.
To change the display names of the network devices click on the device icon on the Packet Tracer Logical workspace, then click on the Config tab in the device configuration window. In the Config tab type the new name of the device into the Display Name box as show in the figure.
d. Add the physical cabling between devices on the workspace
Using the device selection box, add the physical cabling between devices on the workspace as shown in the topology diagram.
The PC will need a copper straight-through cable to connect to the Wireless Router. Select the copper straight-through cable in the Device-Selection box and attach it to the FastEthernet0 interface of the PC and the Ethernet 1 interface of the Wireless Router.
Note: Choose the WRT300N for the wireless router.
The Wireless Router will need a copper straight-through cable to connect to the Cable Modem. Select the copper straight-through cable in the Device-Selection box and attach it to the Internet interface of the Wireless Router and the Port 1 interface of the Cable Modem.
The Cable Modem will need a coaxial cable to connect to the Internet cloud. Select the coaxial cable in the Device-Selection box and attach it to the Port 0 interface of the Cable Modem and the coaxial interface of the Internet cloud.
The Interne cloud will need copper straight-through cable to connect to the Cisco.com server. Select the copper straight-through cable in the Device-Selection box and attach it to the Ethernet interface of the Internet cloud and the FastEthernet0 interface of the Cisco.com server.
Part 2: Configure the Network Devices
Step 1: Configure the Wireless Router
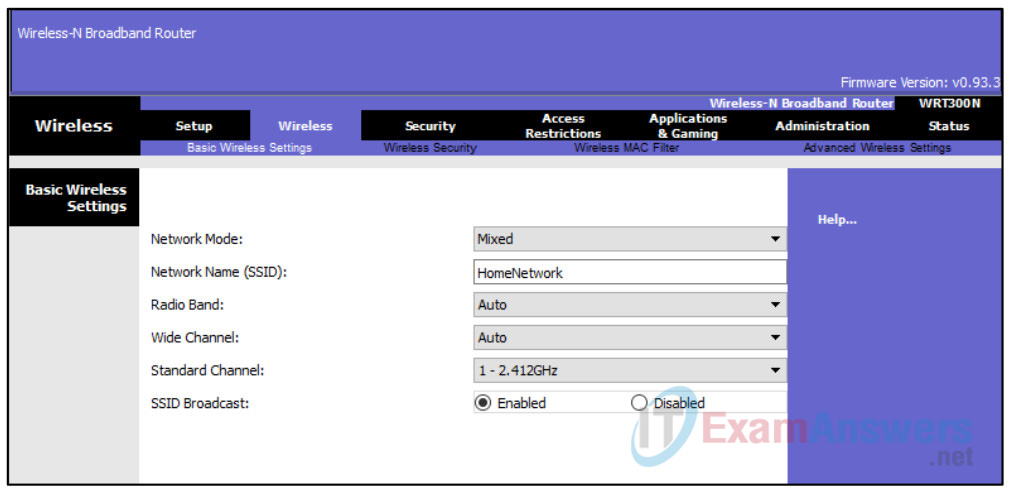
a. Create the wireless network on the Wireless Router
Click on the Wireless Router icon on the Packet Tracer Logical workspace to open the device configuration window.
In the Wireless Router configuration window click on the GUI tab to view configuration options for the Wireless Router.
Next, click on the Wireless tab in the GUI to view the wireless settings. The only setting that needs to be changed from the defaults is the Network Name (SSID). Here, type the name “HomeNetwork” as shown in the figure.
b. Configure the Internet connection on the Wireless Router
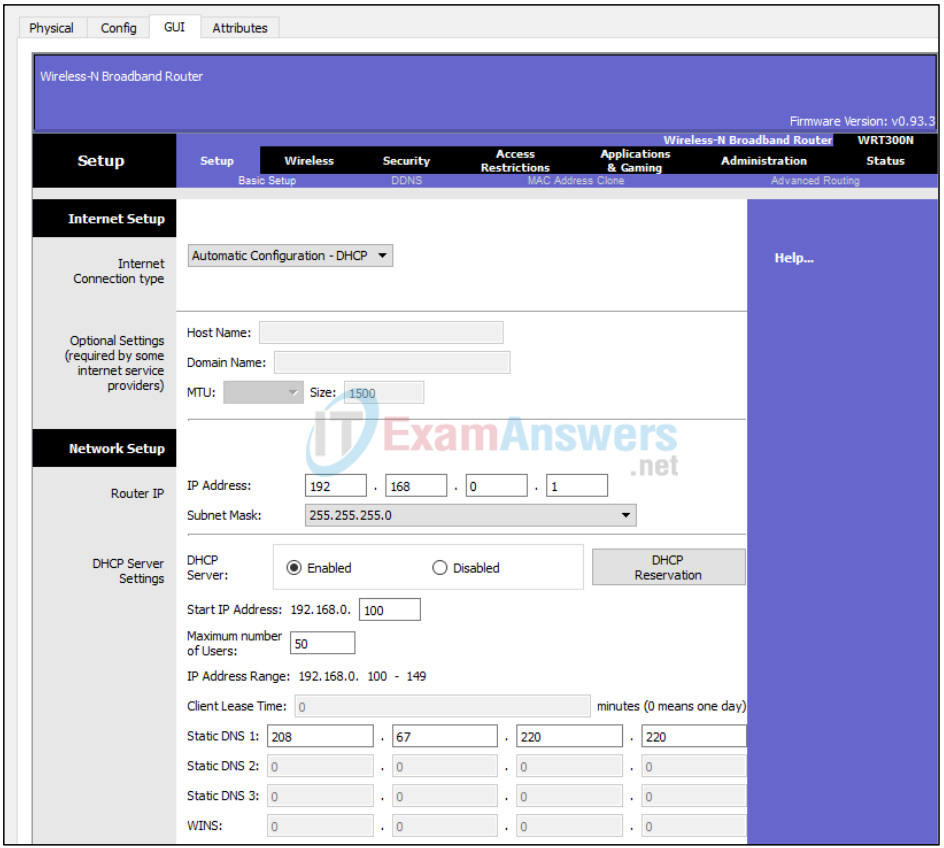
Click on the Setup tab in the Wireless Router GUI.
In the DHCP Server settings verify that the Enabled button is selected and configure the static IP address of the DNS server as 208.67.220.220 as shown in the figure.
c. Click on the Save Settings tab.
Step 2: Configure the Laptop
a. Configure the Laptop to access the wireless network
Click on the Laptop icon on the Packet Tracer Logical workspace and in the Laptop configuration windows select the Physical tab.
In the Physical tab you will need to remove the Ethernet copper module and replace it with the Wireless WPC300N module.
To do this, you first power the Laptop off by clicking the power button on the side of the laptop. Then remove the currently installed Ethernet copper module by clicking on the module on the side of the laptop and dragging it to the MODULES pane on the left of the Laptop window. Then install the Wireless WPC300N module by clicking on it in the MODULES pane and dragging it to the empty module port on the side of the laptop. Power the laptop back on by clicking on the Laptop power button again.
With the wireless module installed, the next task is to connect the laptop to the wireless network.
Click on the Desktop tab at the top of the Laptop configuration window and select the PC Wireless icon.
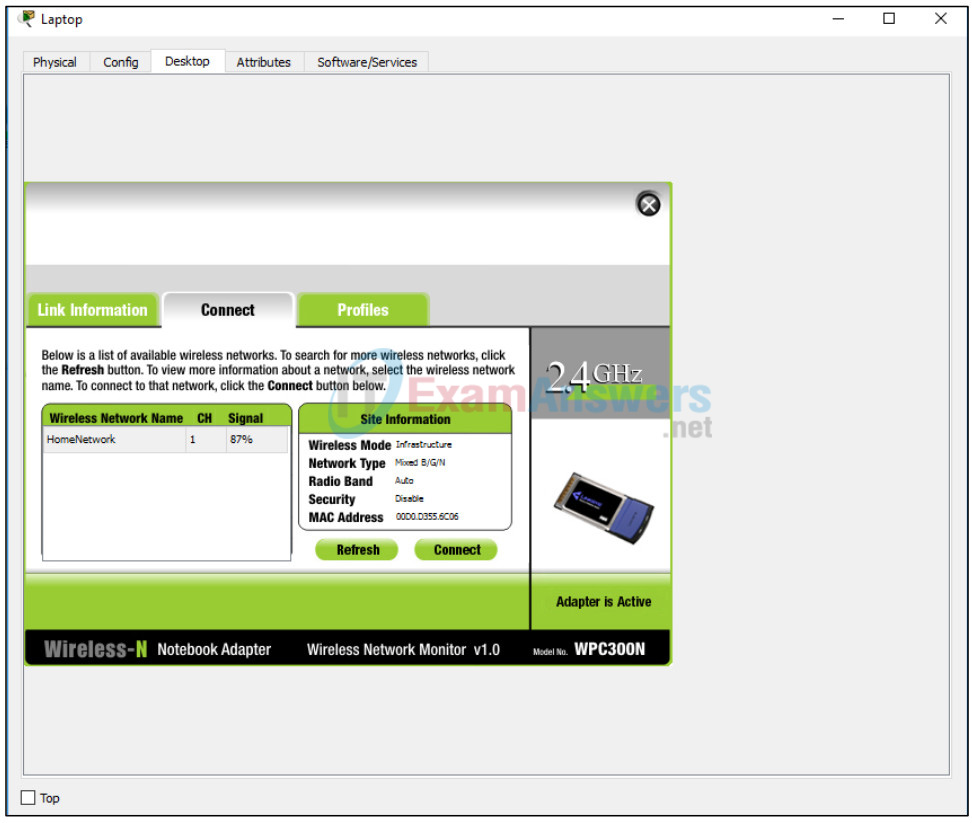
Once the Wireless-N Notebook Adapter settings are visible, select the Connect tab. The wireless network “HomeNetwork” should be visible in the list of wireless networks as shown in the figure.
Select the network, and click on the Connect tab found below the Site Information.
Step 3: Configure the PC
a. Configure the PC for the wired network
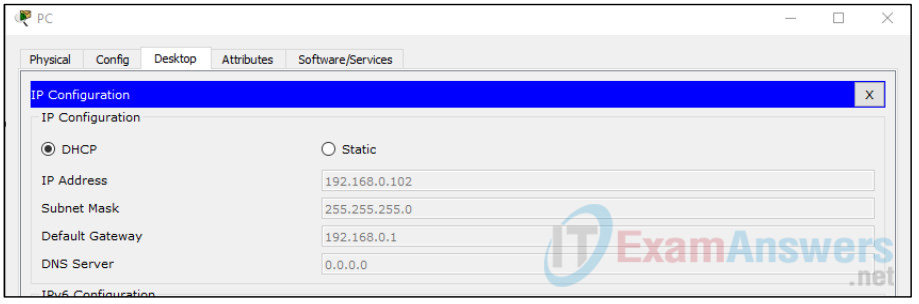
Click on the PC icon on the Packet Tracer Logical workspace and select the Desktop tab and then the IP Configuration icon.
In the IP Configuration window, select the DCHP radio button as shown in the figure so that the PC will use DCHP to receive an IPv4 address from the Wireless router. Close the IP Configuration window.
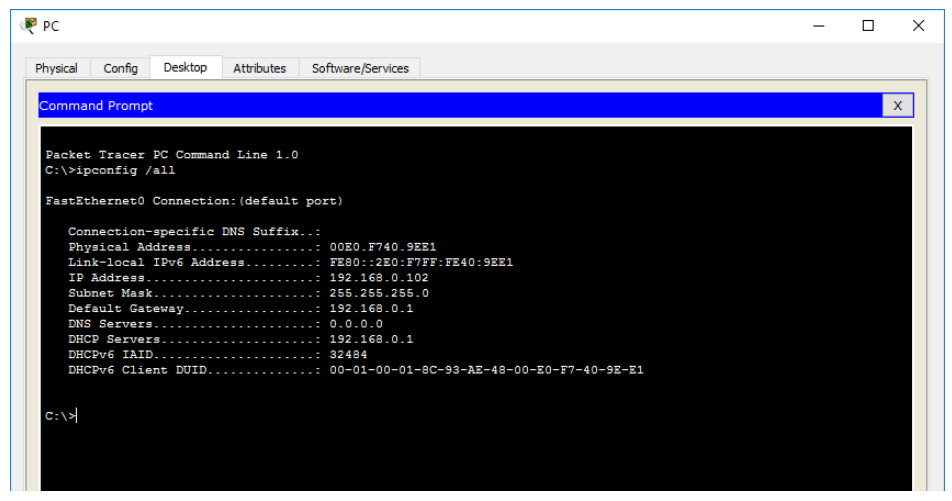
Click on the Command Prompt icon. Verify the PC has received an IPv4 address by issuing the ipconfig /all command from the Command as shown in the figure. The PC should receive an IPv4 address in the 192.168.0.x range.
Step 4: Configure the Internet cloud
a. Install network modules if necessary
Click on the Internet Cloud icon on the Packet Tracer Logical workspace and then click on the Physical tab. The cloud device will need two modules if they are not already installed. The PT-CLOUD-NM-1CX which is for the cable modem service connection and the PT-CLOUD-NM-1CFE which is for a copper Ethernet cable connection. If these modules are missing, power off the physical cloud devices by clicking on the power button and drag each module to an empty module port on the device and then power the device back on.
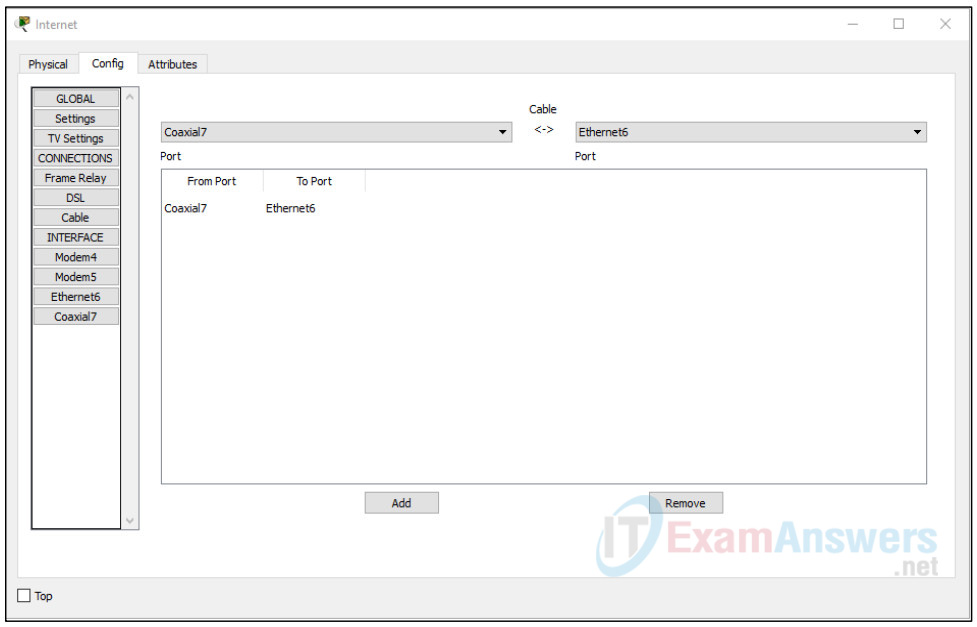
b. Identify the From and To Ports
Click on the Config tab in the Cloud device window. In the left pane click on Cable under CONNECTIONS. In the first drop down box choose Coaxial and in the second drop down box choose Ethernet then click the Add button to add these as the From Port and To Port as shown in the figure.
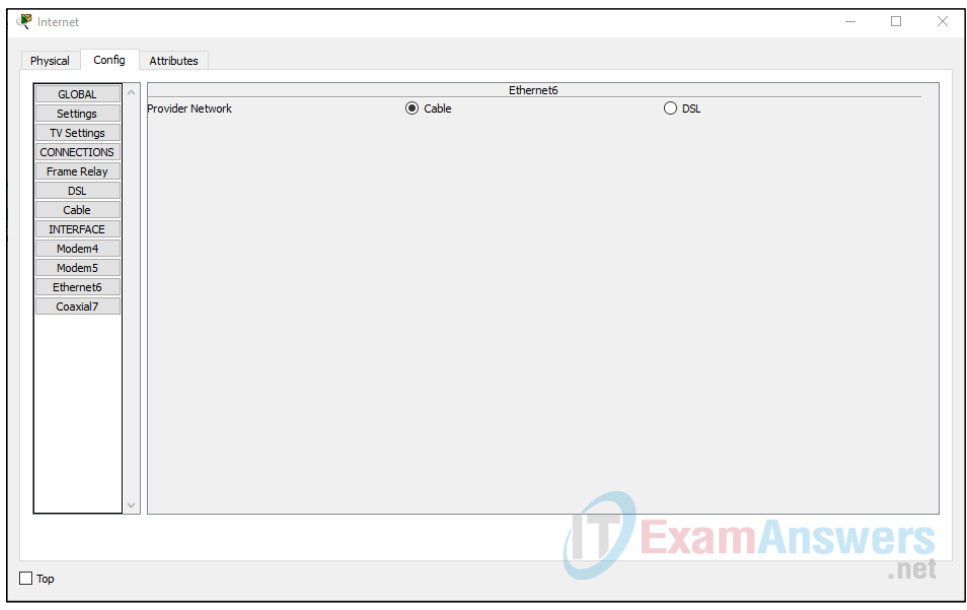
d. Identify the type of provider
While still in the Config tab click Ethernet under INTERFACE in the left pane. In the Ethernet configuration window select Cable as the Provider Network as shown in the figure.
Step 5: Configure the Cisco.com server
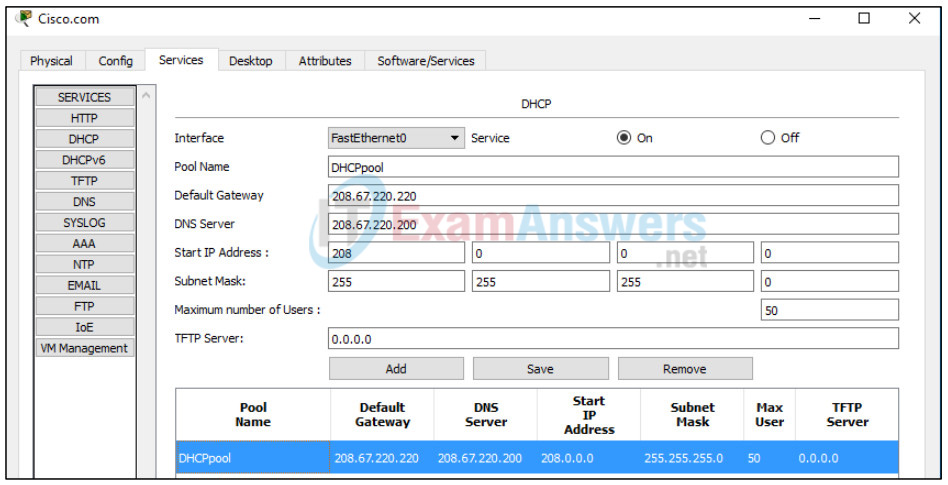
a. Configure the Cisco.com server as a DHCP server
Click on the Cisco.com server icon on the Packet Tracer Logical workspace and select the Services tab. Select DHCP from the SERVICES list in the left pane.
In the DHCP configuration window, configure a DHCP as shown in the figure with the following settings.
- Click On to turn the DCHP service on
- Pool name: DHCPpool
- Default Gateway: 208.67.220.220
- DNS Server: 208.67.220.220
- Starting IP Address: 208.67.220.1
- Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
- Maximum number of Users: 50
Click Add to add the pool
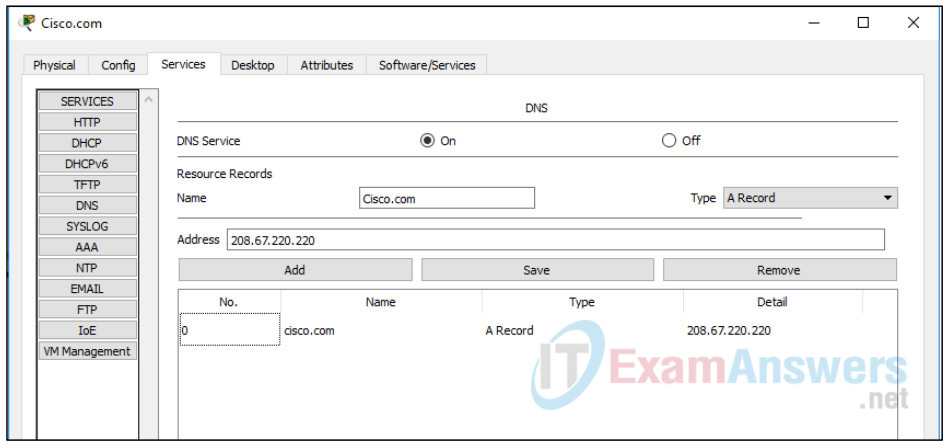
b. Configure the Cisco.com server as a DNS server to provide domain name to IPv4 address resolution.
Still in the Services tab, select DNS from the SERVICES listed in the left pane.
Configure the DNS service using the following settings as shown in the figure.
- Click On to turn the DNS service on
- Name: Cisco.com
- Type: A Record
- Address: 208.67.220.220
Click Add to add the DNS service settings
c. Configure the Cisco.com server Global settings.
Select the Config tab.
Click on Settings in left pane.
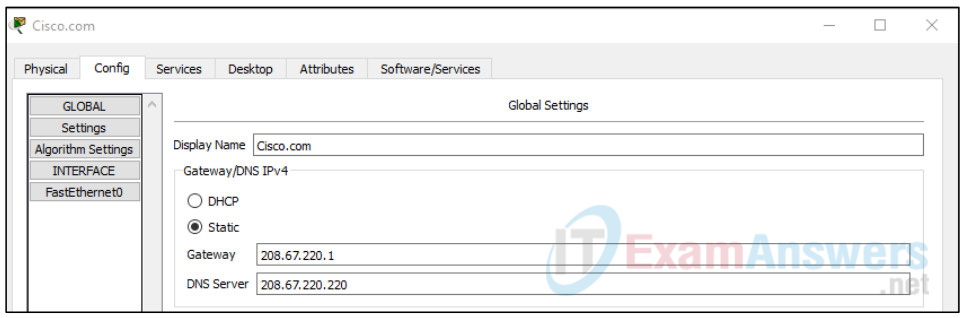
Configure the Global settings of the server as follows:
- Select Static
- Gateway: 208.67.220.1
- DNS Server: 208.67.220.220
d. Configure the Cisco.com server FastEthernet0 Interface settings.
Click on FastEthernet in left pane of the Config tab
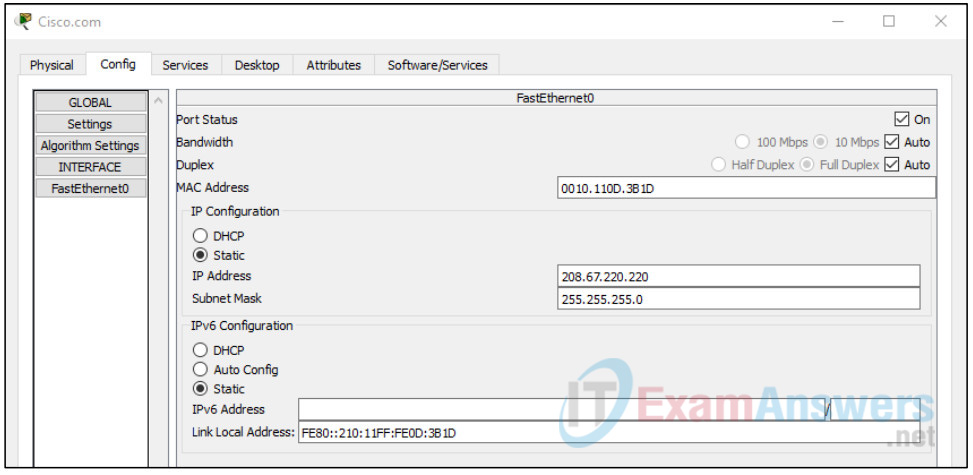
Configure the FastEthernet Interface settings of the server as follows:
- Select Static under IP Configuration
- IP Address: 208.67.220.220
- Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Part 3: Verify Connectivity
Step 1: Refresh the IPv4 settings on the PC
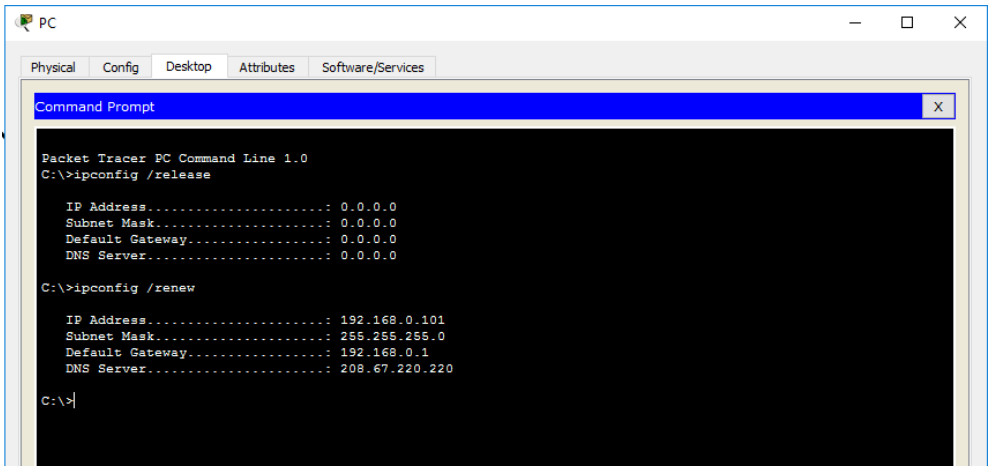
a) Verify that the PC is receiving IPv4 configuration information from DHCP.
Click on the PC on the Packet Tracer Logical workspace and then the select the Desktop tab of the PC configuration window.
Click on the Command Prompt icon
In the command prompt refresh the IP settings by issuing the commands ipconfig /release and then ipconfig /renew. The output should show that the PC has an IP address in the 192.168.0.x range, a subnet mask, a Default Gateway, and DNS server address as shown in the figure.
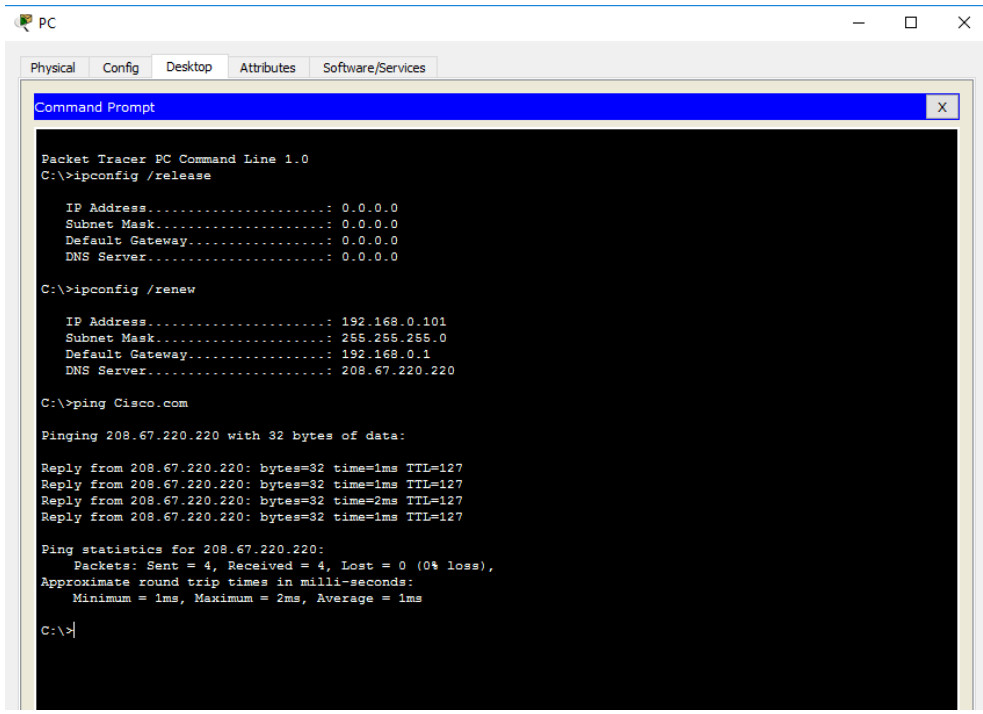
b) Test connectivity to the Cisco.com server from the PC
From the command prompt issuing the command ping Cisco.com. It may take a few seconds for the ping to return. Four replies should be received as shown in the figure.
Part 4: Save the File and Close Packet Tracer
Step 1: Save the File as a Packet Tracer Activity File (*.pkt)
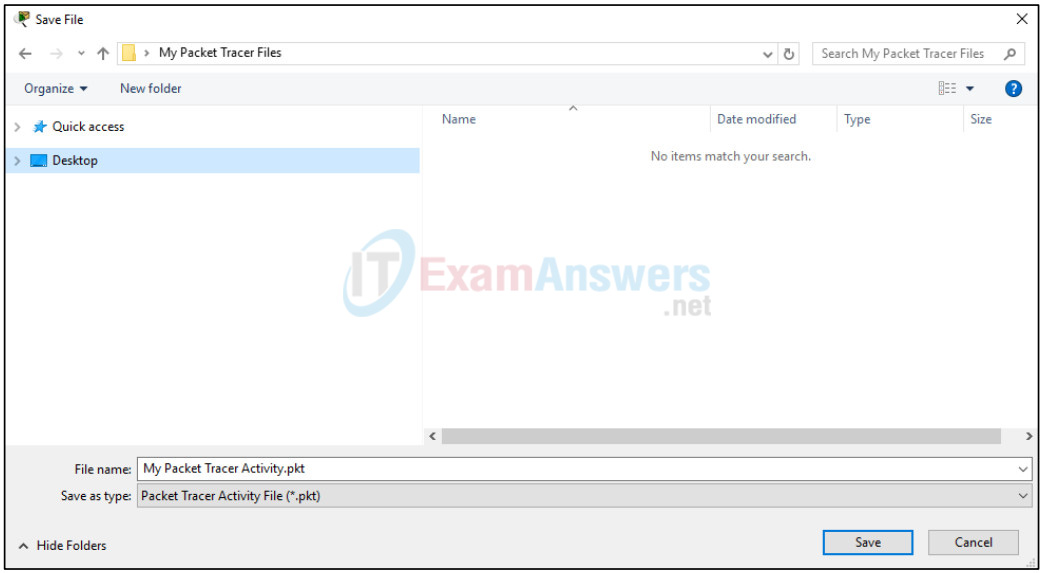
To save the completed network click on File in the Packet Tracer Menu bar and then select Save As… from the dropdown menu. In the the Save File window choose a directory to save the file to and give the file an appropriate file name. The Save as type defaults to Packet Tracer Activity File (*.pkt). Click Save to save the file.
Step 2: Close Packet Tracer
To close Packet Tracer you can either click the “X” in the top right corner of the Packet Tracer window, or click on Exit in the File drop down menu.

what type of cisco packet tracer to a download to complete the job