1. Which are two problems associated with redundant switched Ethernet topologies? (Choose two.)
- broadcast storms
- routing loops
- multiple frame copies
- load balancing
- incorrect frame addressing
- unicast frame flooding
2. Refer to the exhibit. The network shown in the exhibit is not running spanning-tree algorithm. What would be the result if an ARP request were sent by the workstation?
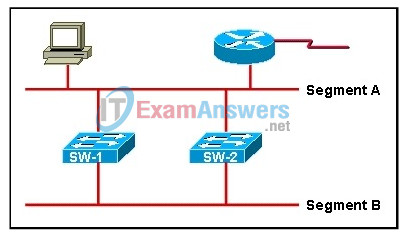
- The frame will loop between SW-1 and SW-2 until the TTL field drops to zero.
- The frame will loop until the TTL field reaches the default maximum value.
- The frame will be prevented from travelling the network by the router.
- The frame will loop between SW-1 and SW-2 repeatedly.
3. Refer to the exhibit. How will spanning tree prevent switching loops in the network shown in the exhibit if all switches have only the default VLAN configured?
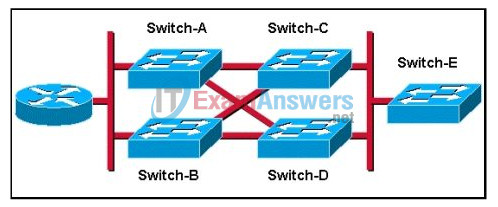
- Traffic will be load-balanced between all switches.
- A single switch will be elected as the root switch, and redundant paths to this switch will be blocked.
- Two of the switches will be elected root bridges, thus blocking traffic between the other two switches.
- Two of the switches will be elected designated switches, thus blocking traffic between the other two switches.
- Either Switch-A or Switch-B will be elected as root switch and Switch-C or Switch-D will become the designated switch.
4. What must a switch running spanning tree do when it is first turned on?
- adjust its bridge priority value
- learn the BIDs of all other switches in the network
- request the MAC address of all connected hosts
- select the BPDU with the greatest MAC address
- adjust its bridge priority value to network conditions
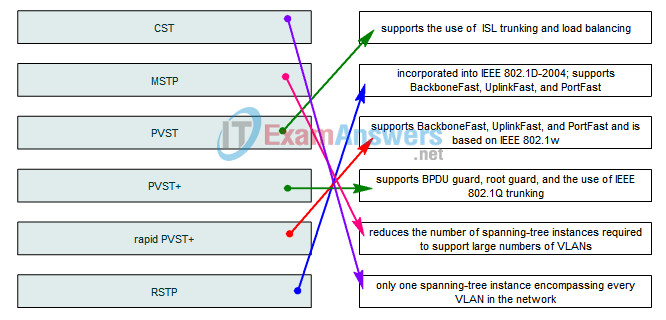
5. Drag the spanning-tree protocol variants on the left to the appropriate description on the right.
6. Which three ports will discard data traffic during STP operation? (Choose three.)
- blocking ports
- disabled ports
- designated ports
- root ports
- forwarding ports
- listening ports
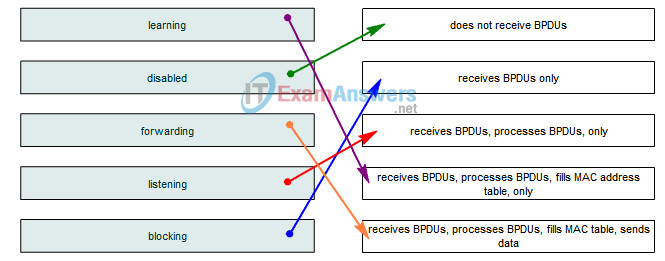
7. Match the Spanning Tree port states with their activities by dragging the options on the left to the correct targets on the right.
8. Which three timers determine the Spanning Tree Protocol performance and state changes? (Choose three.)
- blocking delay
- hello time
- port speed
- forward delay
- maximum age
- backward delay
9. Refer to the exhibit. What will be the result of the spanning tree root bridge selection process in the network shown in the exhibit if each switch contains only one VLAN?
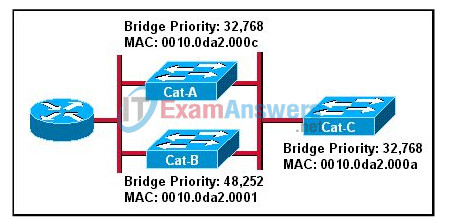
- Cat-A will be the root bridge.
- Cat-B will be the root bridge.
- Cat-C will be the root bridge.
- Cat-A and Cat-B will be the root bridges.
- Cat-A and Cat-C will be the root bridges.
10. The per-VLAN Spanning Tree Protocol plus (PVST+) provides support for which IEEE standard?
- 802.1Q
- 802.1D
- 802.1w
- 802.1
11. Which two characteristics are associated with Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol? (Choose two.)
- supports UplinkFast and BackboneFast
- preferred protocol for preventing Layer 2 loops
- forward delay and max-age timers are unneeded
- lacks backward compatibility with IEEE 802.1D
- compatible with rapid PVST+
12. What is a characteristic of an RSTP edge port?
- It remains in learning state until it receives a BPDU from the root bridge.
- It goes directly from the listening state to the forwarding state.
- Once enabled, it immediately transitions to the forwarding state.
- It generates and propagates topology changes when it transitions to a disabled status.
13. When implementing RSTP for non-edge ports, which two categories of link types are available? (Choose two.)
- shared
- multipoint
- redundant
- point-to-point
- dedicated
14. What method does RSTP use to decrease the time it takes to designate a new root port when the existing root port fails?
- smaller values for forward-delay and max-age timers than STP
- pre-negotiated alternate ports for the root port
- TCN BPDUs originating from the affected switch
- an improved spanning-tree algorithm
15. A switch currently has only one VLAN configured and is running a single instance of rapid spanning tree. Which action will create a second rapid spanning tree instance?
- creating a second VLAN
- entering the spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst command
- assigning a port to a VLAN other than VLAN 1
- connecting to another switch
16. Refer to the exhibit. Spanning-tree port priorities are listed beneath each interface. S4 port Gi0/2 is currently in RSTP discarding state. What action would change the state to forwarding?
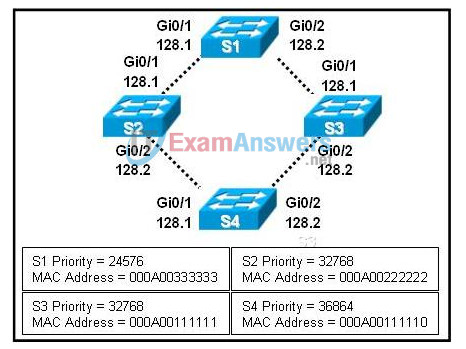
- Changing the physical port connections so that Gi0/2 connects to S2, and Gi0/1 connects to S3.
- Using the spanning-tree vlan priority command to increase the priority of Gi0/2 for all VLANs.
- Changing the port role for Gi0/1 to non-designated, using the spanning-tree port priority command.
- Making S4 the root bridge by manually configuring the MAC address to a lower value than S1.
17. Refer to the exhibit. Which two statements are true regarding the VLAN0001 spanning-tree environment that switch SW4 is participating in? (Choose two.)

- Spanning tree for VLAN0001 is using the default hello time interval.
- The root bridge was selected because of its lower MAC address.
- The root port on SW4 is FastEthernet0/14.
- SW4 is directly connected to port 16 on the root switch.
- The root bridge does not have an aging time.
- SW4 is using the timers advertised by the root switch.
18. Refer to the exhibit. Why would interface fa0/4 have spanning-tree portfast disabled?

- Interface fa0/4 is not active.
- Interface fa0/4 could not transition into forwarding mode and was thus disabled.
- Interface fa0/4 did not receive a BPDU allowing portfast to be enabled.
- Interfaces fa0/1 – 3 are connected to end workstations, while interface fa0/4 is connected to another Layer 2 device.
