7.4.3 Packet Tracer – Troubleshooting DHCP and NAT Answers
Topology
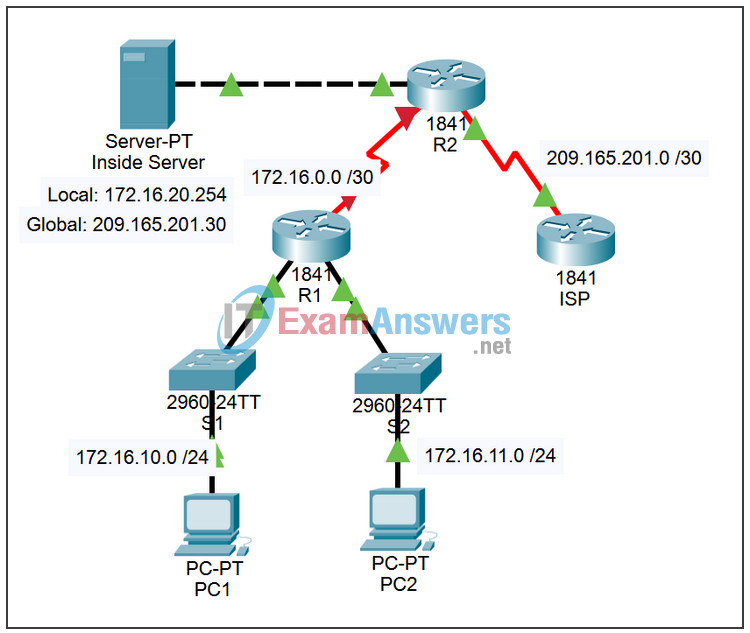
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | S0/0/0 | 172.16.0.1 | 255.255.255.252 |
| Fa0/0 | 172.16.10.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| Fa0/1 | 172.16.11.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| R2 | S0/0/0 | 172.16.0.2 | 255.255.255.252 |
| S0/0/1 | 209.165.201.1 | 255.255.255.252 | |
| Fa0/0 | 172.16.20.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| ISP | S0/0/1 | 209.165.201.2 | 255.255.255.252 |
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to:
- Find and correct network errors.
- Document the corrected network.
Scenario
The routers at your company were configured by an inexperienced network engineer. Several errors in the configuration have resulted in connectivity issues. Your boss has asked you to troubleshoot and correct the configuration errors and document your work. Using your knowledge of DHCP, NAT, and standard testing methods, find and correct the errors. Make sure all clients have full connectivity. The user EXEC password is cisco, and the privileged EXEC password is class.
Task 1: Find and Correct Network Errors
Step 1. Troubleshoot and correct all errors.
Use troubleshooting commands to discover errors and then correct them. When all errors are corrected, you should be able to ping from PC1 and PC2 to ISP. ISP should be able to ping the inside web server at its public IP address.
Step 2. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 100%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 2: Document the Corrected Network
On each router, issue the show run command and capture the configurations.
