8.1.2 Packet Tracer – Network Discovery and Documentation Answers
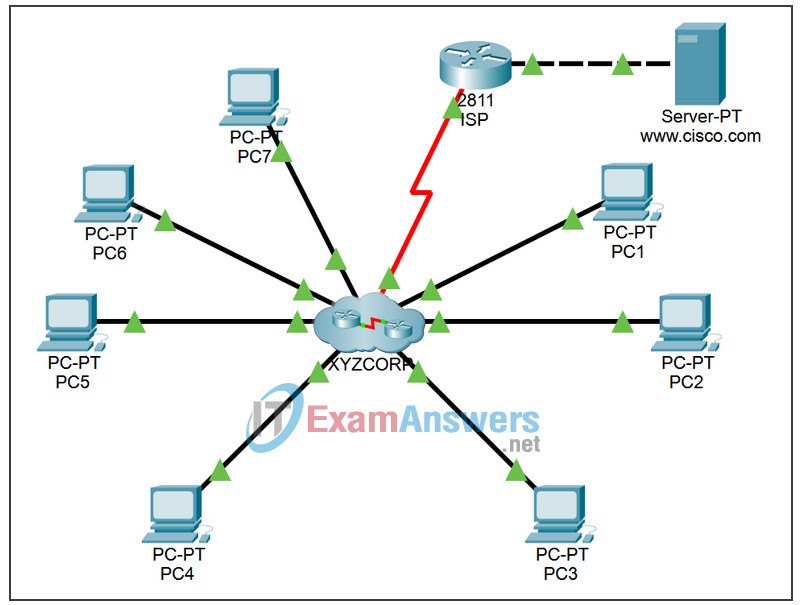
Topology
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | NIC | |||
| PC2 | NIC | |||
| PC2 | NIC | |||
| PC3 | NIC | |||
| PC4 | NIC | |||
| PC5 | NIC | |||
| PC6 | NIC | |||
| PC7 | NIC |
Learning Objectives
- Test connectivity.
- Discover PC configuration information.
- Discover the configuration information of the default gateway.
- Discover routes and neighbors in the network.
- Draw the network topology.
Introduction
This activity covers the steps to take to discover a network using primarily the telnet, show cdp neighbors detail, and show ip route commands. This is Part I of a two-part activity. The topology you see when you open the Packet Tracer activity does not reveal all of the details of the network. The details have been hidden using the cluster function of Packet Tracer. The network infrastructure has been collapsed, and the topology in the file shows only the end devices. Your task is to use your knowledge of networking and discovery commands to learn about the full network topology and document it.
Task 1: Test Connectivity
Step 1. Converge and test the network.
Packet Tracer needs a little help to converge the network. Ping between the PCs and between the PCs and the www.cisco.com server to speed up convergence and to test the network. All PCs should be able to ping one another as well as the server. Remember it may take a few pings before they are successful.
Task 2: Discover PC Configuration Information
Step 1. Access the PC1 command prompt.
Click PC1, the Desktop tab, and then Command Prompt.
Step 2. Determine the addressing information for PC1.
To determine the current IP addressing configuration, enter the ipconfig /all command.
Note: In Packet Tracer, you must enter a space between ipconfig and /all.
Step 3. Document the information for PC1 in the addressing table.
Step 4. Repeat for the other PCs.
Repeat steps 1-3 for PCs 2-7.
Task 3: Discover the Configuration Information of the Default Gateway
Step 1. Test connectivity between PC1 and its default gateway.
From PC1, ping the default gateway to ensure you have connectivity.
Step 2. Telnet to the default gateway.
Use the telnet ip-address command. The IP address is that of the default gateway. When prompted for the password, type cisco.
Step 3. View current interface configurations.
Use both the show ip interface brief and show protocols command to determine the current interface configurations.
What is the difference between these two commands?
Step 4. Document the hostname and interface configuration in the addressing table.
Task 4: Discover Routes and Neighbors in the Network
Step 1. On the same router, display the routing table.
Display the routing table with the show ip route command. You should see five connected routes and six routes learned through RIP, one of which is a default route.
In addition to the routes, what other useful information does the routing table provide to help you further discover and document the network?
Step 2. Discover directly connected Cisco devices.
On the same router, use the show cdp neighbors detail command to discover other directly connected Cisco devices.
Step 3. Document the neighbor information and test connectivity.
The show cdp neighbors detail command lists information for one neighbor, including its IP address. Document the hostname and IP address of the neighbor. Then ping the IP address to test connectivity. The first two or three pings fail while ARP resolves the MAC address.
Step 4. Telnet to the neighbor and discover directly connected Cisco devices.
Telnet to the neighbor and use the show cdp neighbors detail command to discover other directly connected Cisco devices.
You should see three devices listed this time. Why is the router listed more than once?
Step 5. Document the hostnames and IP addresses of the neighbors and test connectivity.
Document and ping the new neighbors you have discovered. Remember, the first two or three pings fail while ARP resolves MAC addresses.
Step 6. Telnet to each neighbor and check for additional Cisco devices.
Telnet to each of the new neighbors you have discovered, and use the show cdp neighbors detail command to check for any additional Cisco devices. The access password is cisco.
Step 7. Continue discovering and documenting the network.
Exit the telnet sessions to return to the default gateway router for PC1. From this router, telnet to other routers in the network to continue discovering and documenting the network. Remember to use the show ip route and show ip cdp neighbors commands to discover IP addresses you can use for Telnet.
Task 5: Draw the Network Topology
Step 1. Draw a topology.
Now that you have discovered all the network devices and documented their addresses, use the addressing table to draw a topology.
Hint: There is a Frame Relay cloud in the middle of the network.
Step 2. Keep this documentation.
Your topology diagram is needed for the next activity.
