1. What is used to identify the path to the next frame-relay switch in a Frame Relay network?
- CIR
- DLCI
- FECN
- BECN
2. Why are Frame Relay paths referred to as virtual?
- There are no dedicated circuits to and from the Frame Relay carrier.
- Frame Relay PVCs are created and discarded on demand.
- The connections between PVC endpoints act like dialup circuits.
- There are no dedicated circuits inside the Frame Relay carrier cloud.
3. Which statement accurately describes the split horizon problem with regard to a multipoint topology?
- Split horizon must be disabled for all non-IP protocols.
- Split horizon creates IP routing loops in multipoint domains.
- Split horizon does not apply to broadcasts, so it does not protect protocols that use broadcast updates.
- Split horizon prevents any point from accepting a valid update and forwarding to all the other points.
4. What are two reasons Frame Relay is more cost-effective than leased lines? (Choose two.)
- time division multiplexing
- uses less equipment
- optimized packet routing
- shares bandwidth across a large customer base
- dynamic IP addressing
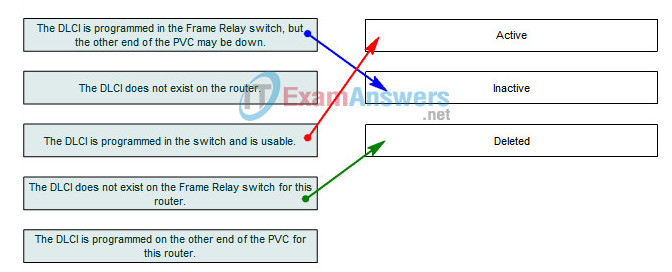
5. Match the status of a DLCI from the show frame-relay pvc command with its meaning.
6. What reliability advantage does Frame Relay offer over leased lines?
- Frame Relay access circuits are higher grade circuits than leased lines.
- The pathways for virtual circuits inside the carrier are meshed.
- From end to end, a single virtual circuit uses a fixed error-checked path.
- Frame Relay uses more sophisticated error detection methods.
7. Refer to the exhibit. What is placed in the address field of a frame that will travel from the Orlando office to the DC office?
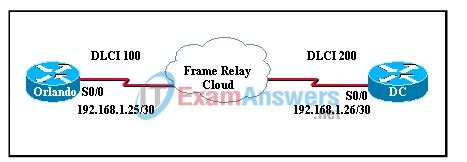
- MAC address of the Orlando router
- MAC address of the DC router
- 192.168.1.25
- 192.168.1.26
- DLCI 100
- DLCI 200
8. Which situation favors a multipoint topology over point-to-point?
- when VLSM cannot be used to conserve addresses
- when using routing protocols other than IP
- when using a frame mesh topology to save access circuits
- when using a routing protocol that requires broadcast updates
9. What is an advantage of configuring subinterfaces in a Frame Relay environment?
- makes the DLCIs globally significant
- eliminates the need for using Inverse ARP
- reduces split horizon issues
- improves flow control and bandwidth usage
10. Which protocol can provide error correction for data that is transmitted over a Frame Relay link?
- FECN
- FTP
- LMI
- TCP
- UDP
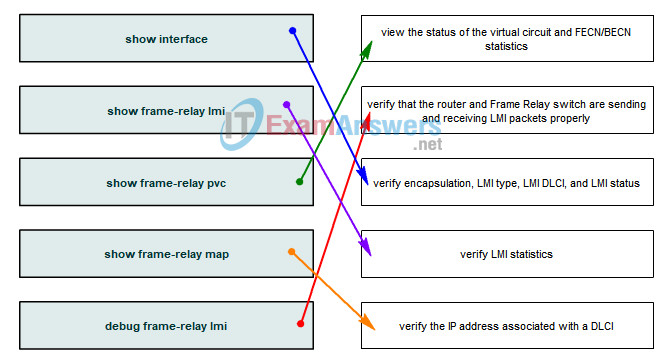
11. Drag the commands on the left to the description on the right.
12. At which rate does a service provider guarantee to transfer data into the Frame Relay network?
- baud rate
- timing rate
- data transfer rate
- committed information rate
13. How are DLCI numbers assigned?
- They are assigned by a DLCI server.
- They are assigned arbitrarily by the user.
- They are assigned by the service provider.
- They are assigned based on the host IP address.
14. A router can reach multiple networks through a Frame Relay interface. How does the router know which DLCI to assign to the IP address of the destination network?
- It consults the Frame Relay map.
- It consults the routing table to find the DLCI.
- It uses Frame Relay switching tables to map DLCIs to IP addresses.
- It uses RARP to find the IP address of the corresponding DLCI.
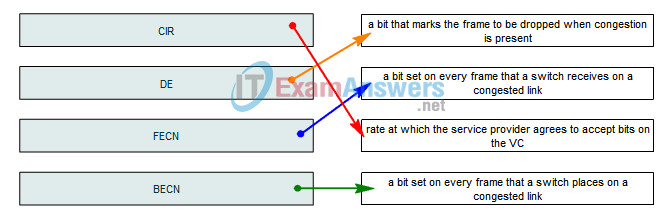
15. Drag the term on the left to the associated definition on the right.