1. What is defined by an ISAKMP policy?
- the security associations that IPsec peers are willing to use
- the IP addresses of IPsec peers
- access lists that identify interesting traffic
- the preshared keys that will be exchanged between IPsec peers
2. Which are the five security associations to configure in ISAKMP policy configuration mode?
- Hash, Accounting, Group, Lifetime, ESP
- Hash, Authorization, Group, Lifetime, Encryption
- Hash, Authentication, Group, Lifetime, Encryption
- Hash, Authentication, GRE, Lifetime, ESP
3. What command or action will verify that a VPN tunnel has been established?
- Issue a show ip interface command.
- Issue a show crypto map command.
- Issue a show crypto isakmp sa command.
- Send interesting traffic from the VPN router interface.
4. What three protocols must be permitted through the company firewall for establishment of IPsec site-to-site VPNs? (Choose three.)
- AH
- HTTPS
- ESP
- ISAKMP
- NTP
- SSH
5. Refer to the exhibit. The ISAKMP policy for the IKE Phase 1 tunnel was configured, but the tunnel does not yet exist. Which action should be taken next before IKE Phase 1 negotiations can begin?
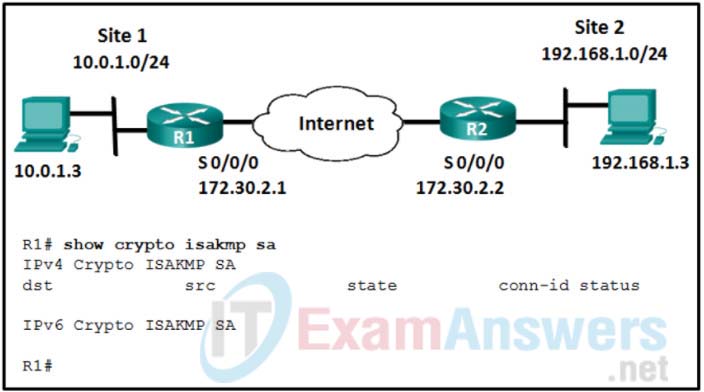
- Configure the set of encryption and hashing algorithms that will be used to transform the data sent through the IPsec tunnel.
- Configure an ACL to define interesting traffic.
- Configure the IPsec tunnel lifetime.
- Bind the transform set with the rest of the IPsec policy in a crypto map.
6. What is negotiated in the establishment of an IPsec tunnel between two IPsec hosts during IKE Phase 1?
- interesting traffic
- transform sets
- ISAKMP SA policy
- DH groups
7. A network analyst is configuring a crypto map and has just bound the ACL and the transform set to the map, and set the IPsec tunnel lifetime. What other step completes the configuration of the crypto map?
- Define the interesting traffic.
- Configure the DH group.
- Apply the map to an interface.
- Configure the SA policy.
8. What is the first step in establishing an IPsec VPN?
- negotiation of ISAKMP policies
- detection of interesting traffic
- creation of a secure tunnel to negotiate a security association policy
- creation of an IPsec tunnel between two IPsec peers
9. Refer to the exhibit. Given the partial output of the show version command on a router, if a network engineer wants to begin to configure an IPsec VPN, what would be the next step to take?
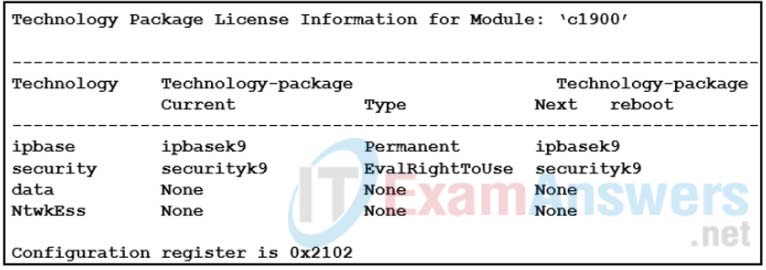
- Accept the EULA and activate the security technology package.
- Configure an ACL to define interesting traffic.
- Configure the ISAKMP policy for IKE phase 1.
- Configure a crypto map for the IPsec policy.
10. Refer to the exhibit. How will traffic that does not match access list 101 be treated by the router?
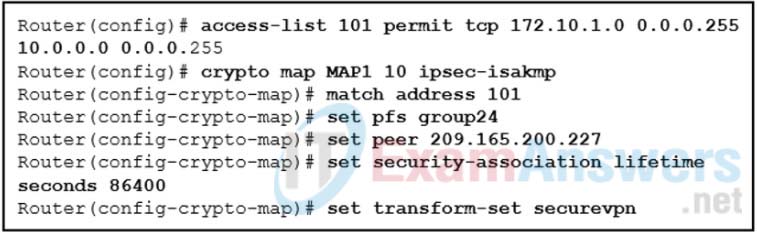
- It will be sent unencrypted.
- It will be sent encrypted.
- It will be blocked.
- It will be discarded.
