1. Which destination address is used in an ARP request frame?
- 255.255.255.255
- the physical address of the destination host
- FFFF.FFFF.FFFF
- AAAA.AAAA.AAAA
- 0.0.0.0
Explanation: The purpose of an ARP request is to find the MAC address of the destination host on an Ethernet LAN. The ARP process sends a Layer 2 broadcast to all devices on the Ethernet LAN. The frame contains the IP address of the destination and the broadcast MAC address, FFFF.FFFF.FFFF. The host with the IP address that matches the IP address in the ARP request will reply with a unicast frame that includes the MAC address of the host. Thus the original sending host will obtain the destination IP and MAC address pair to continue the encapsulation process for data transmission.
2. Which network device can serve as a boundary to divide a Layer 2 broadcast domain?
- Ethernet bridge
- router
- access point
- Ethernet hub
Explanation: Layer 1 and 2 devices (LAN switch and Ethernet hub) and access point devices do not filter MAC broadcast frames. Only a Layer 3 device, such as a router, can divide a Layer 2 broadcast domain.
3. Which term refers to the process of placing one message format inside another message format?
- segmenting
- manipulation
- encapsulation
- encoding
Explanation: Encapsulation is the process of placing one type of message format into another. On computer networks this process is known as encapsulation. Once a message is encapsulated, it is called a frame.
4. What is the purpose of the core layer in the Cisco hierarchical network design model?
- flow control between networks
- aggregation point for smaller networks
- high-speed backbone switching
- network access to end devices
Explanation: In the three layer hierarchy, the access layer provides host connectivity to the network. The distribution layer interconnects smaller networks, and the core layer provides high-speed connections at the top of the hierarchy.
5. Which network device has the primary function to send data to a specific destination based on the information found in the MAC address table?
Explanation: If a MAC address is found in the MAC address table, then data is sent to the associated switch port. If the MAC address is not found in the MAC address table, the data is sent to all switch ports that have devices attached to the same network.
6. Refer to the exhibit. How is a frame sent from PCA forwarded to PCC if the MAC address table on switch SW1 is empty?
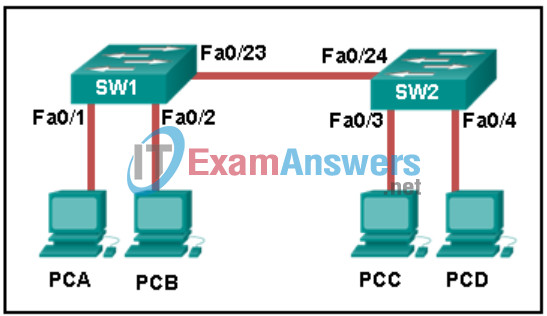
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on SW1, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 drops the frame because it does not know the destination MAC address.
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on the switch, excluding the interconnected port to switch SW2 and the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 forwards the frame directly to SW2. SW2 floods the frame to all ports connected to SW2, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
Explanation: When a switch powers on, the MAC address table is empty. The switch builds the MAC address table by examining the source MAC address of incoming frames. The switch forwards based on the destination MAC address found in the frame header. If a switch has no entries in the MAC address table or if the destination MAC address is not in the switch table, the switch will forward the frame out all ports except the port that brought the frame into the switch.
7. What information does an Ethernet switch examine and use to build its address table?
- source MAC address
- source IP address
- destination MAC address
- destination IP address
Explanation: An Ethernet switch examines the source MAC address of an incoming frame. If the source MAC address is not in the MAC address table, the switch will add it to the table with the associated ingress Ethernet port.
8. Which three fields are found in an 802.3 Ethernet frame? (Choose three.)
- destination logical address
- media type identifier
- source physical address
- destination physical address
- frame check sequence
- source logical address
Explanation: The fields of an Ethernet frame are the preamble, destination and source address, length, data, and FCS.
9. Which two devices would commonly be found at the access layer of the hierarchical enterprise LAN design model? (Choose two.)
- Layer 3 device
- modular switch
- access point
- firewall
- Layer 2 switch
Explanation: While some designs do route at the access layer, the two devices that should always be placed at the access layer of the hierarchical design model are an access point and a Layer 2 switch. A modular switch is commonly used at the core layer. Routing by a Layer 3 device is commonly used in the distribution layer. The firewall is a device in the Internet edge network design.
10. Which statement is true about broadcast and collision domains?
- Adding a router to a network will increase the size of the collision domain.
- The more interfaces a router has the larger the resulting broadcast domain.
- The size of the collision domain can be reduced by adding hubs to a network.
- Adding a switch to a network will increase the size of the broadcast domain.
Explanation: A switch that receives a broadcast frame will forward the frame out all other interfaces, including interfaces that connect to other switches. These switches will also perform the same forwarding action. By adding more switches to the network, the size of the broadcast domain increases.
11. How much data can be encapsulated into a normal sized Ethernet frame before it is sent over the network?
- 0 to 1024 bytes
- 64 to 1518 bytes
- 32 to 1500 bytes
- 46 to 1500 bytes
Explanation: According to the Ethernet standards, each Ethernet frame can carry 46 to 1500 bytes of user data. During the encapsulation process, other fields are added, such as destination MAC address, source MAC address, and FCS. The size of Ethernet frames is normally limited to a maximum of 1518 bytes and a minimum of 64 bytes.
12. What is the purpose of ARP in an IPv4 network?
- to build the MAC address table in a switch from the information that is gathered
- to forward data onward based on the destination IP address
- to forward data onward based on the destination MAC address.
- to obtain a specific MAC address when an IP address is known
Explanation: ARP performs two functions:
- To obtain a specific MAC address when an IP address is known, by broadcasting an ARP request message to all devices on a particular Ethernet network
- To use the gathered information to create a viewable table of IP address to MAC address mappings

