1. Which information is used by routers to forward a data packet toward its destination?
- destination data-link address
- source IP address
- destination IP address
- source data-link address
Explanation: The destination IP address is the IP address for the receiving device. This IP address is used by routers to forward the packet to its destination.
2. A router receives a packet from the Gigabit 0/0 interface and determines that the packet needs to be forwarded out the Gigabit 0/1 interface. What will the router do next?
- look into the routing table to determine if the destination network is in the routing table
- look into the ARP cache to determine the destination IP address
- create a new Layer 2 Ethernet frame to be sent to the destination
- route the packet out the Gigabit 0/1 interface
Explanation: Once a router receives a packet and looks inside the header to determine the destination network, the router compares the destination network to the routing table to determine if the packet is to be routed or dropped. If routed, the router attaches a new Layer 2 header based on the technology that is used by the outgoing port that is used. The packet is then routed out the destination port as designated by the routing table. The ARP cache is used to match an IP address with a MAC address.
3. Refer to the exhibit. The IP address of which device interface should be used as the default gateway setting of host H1?
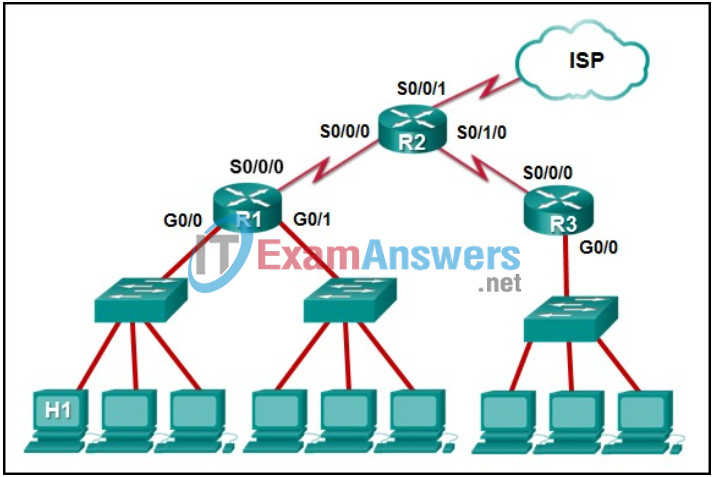
- R2: S0/0/0
- R1: G0/0
- R2: S0/0/1
- R1: S0/0/0
Explanation: The default gateway for host H1 is the router interface that is attached to the LAN that H1 is a member of. In this case, that is the G0/0 interface of R1. H1 should be configured with the IP address of that interface in its addressing settings. R1 will provide routing services to packets from H1 that need to be forwarded to remote networks.
4. During the process of forwarding traffic, what will the router do immediately after matching the destination IP address to a network on a directly connected routing table entry?
- look up the next-hop address for the packet
- discard the traffic after consulting the route table
- switch the packet to the directly connected interface
- analyze the destination IP address
Explanation: A router receives a packet on an interface and looks at the destination IP address. It consults its routing table and matches the destination IP address to a routing table entry. The router then discovers that it has to send the packet to the next-hop address or out to a directly connected interface. When the destination address is on a directly connected interface, the packet is switched over to that interface.
5. What will a router do if it cannot determine where to forward an incoming packet?
- The router will drop it.
- The router will forward it out all interfaces.
- The router will save it in the sending queue and try to forward it again later.
- The router will send an incident message to the network administrator.
Explanation: A router contains a routing table of all locally connected networks and the interfaces that connect to them. The routing tables can also contain the routes that the router uses to reach remote networks. Entries can be made to the routing table in two ways: the table can be dynamically updated by information received from other routers in the network by using a routing protocol, or entries can be manually entered by a network administrator. If the router cannot determine where to forward a packet, it will drop it.
6. In implementing a LAN in a corporation, what are three advantages of dividing hosts between multiple networks connected by a distribution layer? (Choose three.)
- It makes the hosts invisible to those on other local network segments.
- It provides increased security.
- It increases traffic bandwidth between segments through distribution layer devices.
- It splits up broadcast domains and decreases traffic.
- It reduces complexity and expense by using LAN switch devices.
- Only LAN switches are needed.
Explanation: Some advantages of dividing end devices between multiple networks connected by a distribution layer include the following:
- It is more appropriate for larger and complex networks.
- It splits up broadcast domains and decreases traffic.
- It can improve performance on each segment.
- It makes the machines invisible to those on other local network segments.
- It can provide increased security.
- It can improve network organization.
7. What type of route is indicated by the code C in an IPv4 routing table on a Cisco router?
- dynamic route that is learned through EIGRP
- default route
- static route
- directly connected route
Explanation: Some of the IPv4 routing table codes include the following:
- C – directly connected
- S – static
- D – EIGRP
- * – candidate default
8. Which portion of the network layer address does a router use to forward packets?
- host portion
- network portion
- gateway address
- broadcast address
Explanation: There are two parts to an a network layer address, the network and host portions. Routers are not concerned about delivering packets to hosts. Routers are concerned with delivering packets to the network that a destination host is a member of.
9. What role does a router play on a network?
- connecting smaller networks into a single broadcast domain
- forwarding frames based on a MAC address
- selecting the path to destination networks
- forwarding Layer 2 broadcasts
Explanation: When a computer sends a packet onto the network, the packet includes a source and destination IP address. Routers use the destination IP address in a packet to forward the packet to the correct destination network.
10. A router receives an incoming packet and determines that the destination host is located on a LAN directly attached to one of the router interfaces. Which destination address will the router use to encapsulate the Ethernet frame when forwarding the packet?
- MAC address of the SVI on the switch
- MAC address of the default gateway of the LAN
- MAC address of the interface of the connected router
- MAC address of the destination host
Explanation: When a router encapsulates the frame to forward a packet out an Ethernet interface, it includes a destination MAC address. When the destination host is on the same local network as the router interface, the router will use the MAC address of the host as the destination MAC address of the Ethernet frame.
11. Which address should be configured as the default gateway address of a client device?
- the Layer 2 address of the switch port that is connected to the workstation
- the IPv4 address of the router interface that is connected to the same LAN
- the Layer 2 address of the switch management interface
- the IPv4 address of the router interface that is connected to the internet
Explanation: The default gateway is used when a host needs to send messages to destinations that are located in remote networks. The default gateway address is configured on the host with the IPv4 address of the router interface that is connected to the same local network as the host.

