Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automation ( Version 7.00) – Modules 1 – 2: OSPF Concepts and Configuration Exam
1. What is a function of OSPF hello packets?
- to send specifically requested link-state records
- to discover neighbors and build adjacencies between them
- to ensure database synchronization between routers
- to request specific link-state records from neighbor routers
2. Which OPSF packet contains the different types of link-state advertisements?
- hello
- DBD
- LSR
- LSU
- LSAck
3. Which three statements describe features of the OSPF topology table? (Choose three.)
- It is a link-state database that represents the network topology.
- Its contents are the result of running the SPF algorithm.
- When converged, all routers in an area have identical topology tables.
- The topology table contains feasible successor routes.
- The table can be viewed via the show ip ospf database command.
- After convergence, the table only contains the lowest cost route entries for all known networks.
4. What does an OSPF area contain?
- routers that share the same router ID
- routers whose SPF trees are identical
- routers that have the same link-state information in their LSDBs
- routers that share the same process ID
5. What is used to facilitate hierarchical routing in OSPF?
- the use of multiple areas
- frequent SPF calculations
- autosummarization
- the election of designated routers
6. Which OSPF data structure is identical on all OSPF routers that share the same area?
- forwarding database
- link-state database
- adjacency database
- routing table
7. Which step does an OSPF-enabled router take immediately after establishing an adjacency with another router?
- builds the topology table
- exchanges link-state advertisements
- chooses the best path
- executes the SPF algorithm
8. A network engineer has manually configured the hello interval to 15 seconds on an interface of a router that is running OSPFv2. By default, how will the dead interval on the interface be affected?
- The dead interval will not change from the default value.
- The dead interval will now be 30 seconds.
- The dead interval will now be 60 seconds.
- The dead interval will now be 15 seconds.
9. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured the OSPF timers to the values that are shown in the graphic. What is the result of having those manually configured timers?
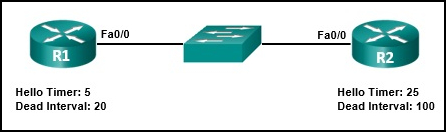
- R1 automatically adjusts its own timers to match the R2 timers.
- The R1 dead timer expires between hello packets from R2.
- The hello timer on R2 expires every ten seconds.
- The neighbor adjacency has formed.
10. To establish a neighbor adjacency two OSPF routers will exchange hello packets. Which two values in the hello packets must match on both routers? (Choose two.)
- dead interval
- router priority
- list of neighbors
- router ID
- hello interval
11. What is the default router priority value for all Cisco OSPF routers?
- 0
- 1
- 10
- 255
12. Which type of OSPFv2 packet contains an abbreviated list of the LSDB of a sending router and is used by receiving routers to check against the local LSDB?
- database description
- link-state update
- link-state request
- link-state acknowledgment
13. In an OSPF network when are DR and BDR elections required?
- when the two adjacent neighbors are interconnected over a point-to-point link
- when all the routers in an OSPF area cannot form adjacencies
- when the routers are interconnected over a common Ethernet network
- when the two adjacent neighbors are in two different networks
14. When an OSPF network is converged and no network topology change has been detected by a router, how often will LSU packets be sent to neighboring routers?
- every 5 minutes
- every 10 minutes
- every 30 minutes
- every 60 minutes
15. What will an OSPF router prefer to use first as a router ID?
- a loopback interface that is configured with the highest IP address on the router
- any IP address that is configured using the router-id command
- the highest active interface IP that is configured on the router
- the highest active interface that participates in the routing process because of a specifically configured network statement
16. What are the two purposes of an OSPF router ID? (Choose two.)
- to uniquely identify the router within the OSPF domain
- to facilitate router participation in the election of the designated router
- to enable the SPF algorithm to determine the lowest cost path to remote networks
- to facilitate the establishment of network convergence
- to facilitate the transition of the OSPF neighbor state to Full
17. Refer to the exhibit. If no router ID was manually configured, what would router Branch1 use as its OSPF router ID?
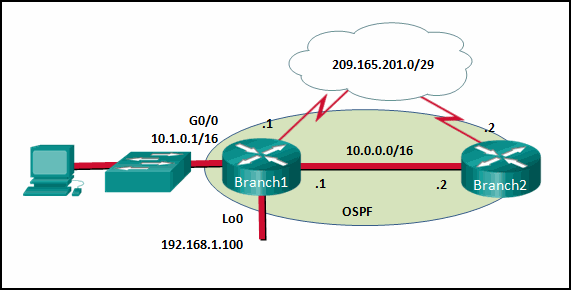
- 10.0.0.1
- 10.1.0.1
- 192.168.1.100
- 209.165.201.1
18. A network technician issues the following commands when configuring a router:
R1(config)# router ospf 11 R1(config-router)# network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
What does the number 11 represent?
- the OSPF process ID on R1
- the cost of the link to R1
- the autonomous system number to which R1 belongs
- the administrative distance that is manually assigned to R1
- the area number where R1 is located
19. An OSPF router has three directly connected networks; 172.16.0.0/16, 172.16.1.0/16, and 172.16.2.0/16. Which OSPF network command would advertise only the 172.16.1.0 network to neighbors?
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.0 area 0
20. Refer to the exhibit. Which three statements describe the results of the OSPF election process of the topology that is shown in the exhibit? (Choose three.)
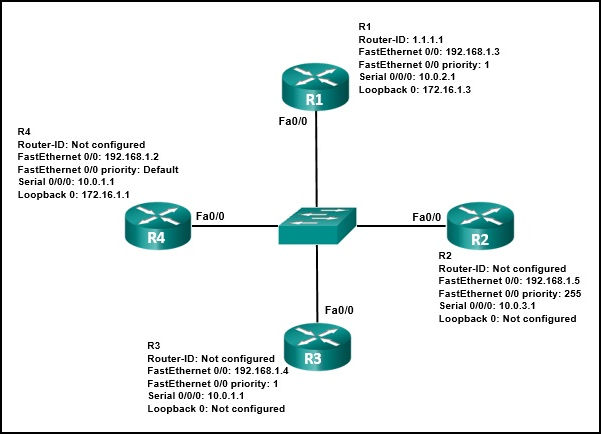
- R3 will be elected BDR.
- The R4 FastEthernet 0/0 priority is 128.
- The R4 router ID is 172.16.1.1.
- R1 will be elected BDR.
- The router ID on R2 is the loopback interface.
- R2 will be elected DR.
21. Refer to the exhibit. If the switch reboots and all routers have to re-establish OSPF adjacencies, which routers will become the new DR and BDR?
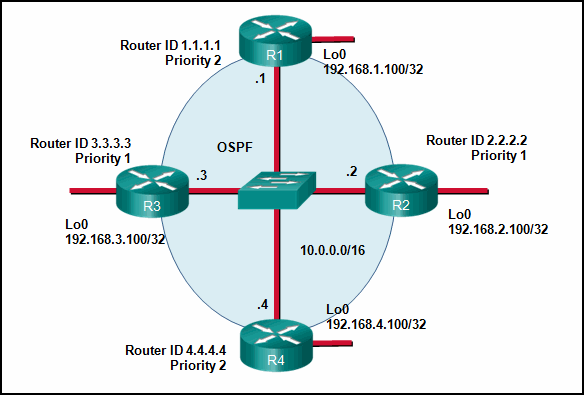
- Router R4 will become the DR and router R1 will become the BDR.
- Router R2 will become the DR and router R3 will become the BDR.
- Router R1 will become the DR and router R2 will become the BDR.
- Router R4 will become the DR and router R3 will become the BDR.
22. By default, what is the OSPF cost for any link with a bandwidth of 100 Mb/s or greater?
- 100000000
- 10000
- 1
- 100
23. Refer to the exhibit. What is the OSPF cost to reach the router A LAN 172.16.1.0/24 from B?
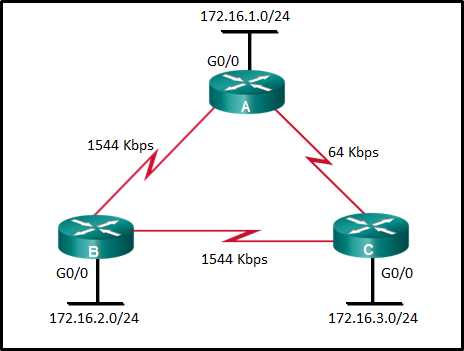
- 782
- 74
- 128
- 65
24. Refer to the exhibit. On which router or routers would a default route be statically configured in a corporate environment that uses single area OSPF as the routing protocol?
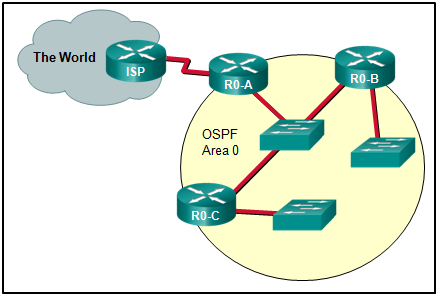
- R0-A
- ISP, R0-A, R0-B, and R0-C
- ISP
- R0-B and R0-C
- ISP and R0-A
- R0-A, R0-B, and R0-C
25. What command would be used to determine if a routing protocol-initiated relationship had been made with an adjacent router?
- ping
- show ip ospf neighbor
- show ip interface brief
- show ip protocols
26. Refer to the exhibit. Which command did an administrator issue to produce this output?

- R1# show ip ospf interface serial0/0/1
- R1# show ip route ospf
- R1# show ip ospf
- R1# show ip ospf neighbor
27. Which command is used to verify that OSPF is enabled and also provides a list of the networks that are being advertised by the network?
- show ip interface brief
- show ip ospf interface
- show ip protocols
- show ip route ospf
28. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured OSPFv2 on the two Cisco routers but PC1 is unable to connect to PC2. What is the most likely problem?
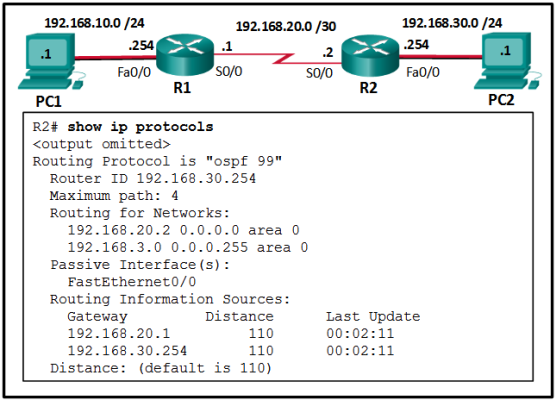
- Interface Fa0/0 has not been activated for OSPFv2 on router R2.
- Interface Fa0/0 is configured as a passive-interface on router R2.
- Interface S0/0 is configured as a passive-interface on router R2.
- Interface s0/0 has not been activated for OSPFv2 on router R2.
29. What is the recommended Cisco best practice for configuring an OSPF-enabled router so that each router can be easily identified when troubleshooting routing issues?
- Configure a value using the router-id command.
- Use the highest active interface IP address that is configured on the router.
- Use a loopback interface configured with the highest IP address on the router.
- Use the highest IP address assigned to an active interface participating in the routing process.
30. Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router running an algorithm to determine the best path to each destination?
- load balancing equal-cost paths
- declaring a neighbor to be inaccessible
- choosing the best route
- executing the SPF algorithm
31. An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 192.168.223.0 255.255.254.0. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
- 0.0.1.255
- 0.0.7.255
- 0.0.15.255
- 0.0.31.255
32. What is the format of the router ID on an OSPF-enabled router?
- a unique router host name that is configured on the router
- a unique phrase with no more than 16 characters
- a 32-bit number formatted like an IPv4 address
- an 8-bit number with a decimal value between 0 and 255
- a character string with no space
33. Question as presented:
DUAL is the algorithm used by EIGRP. In multiarea OSPF, OSPF is implemented using multiple areas, and all of them must be connected to the backbone area.
34. After modifying the router ID on an OSPF router, what is the preferred method to make the new router ID effective?
- HQ# copy running-config startup-config
- HQ# resume
- HQ# clear ip route *
- HQ# clear ip ospf process
35. In an OSPFv2 configuration, what is the effect of entering the command network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 ?
- It allows all 192.168.1.0 networks to be advertised.
- It tells the router which interface to turn on for the OSPF routing process.
- It changes the router ID of the router to 192.168.1.1.
- It enables OSPF on all interfaces on the router.
36. What is the reason for a network engineer to alter the default reference bandwidth parameter when configuring OSPF?
- to force that specific link to be used in the destination route
- to more accurately reflect the cost of links greater than 100 Mb/s
- to enable the link for OSPF routing
- to increase the speed of the link
37. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
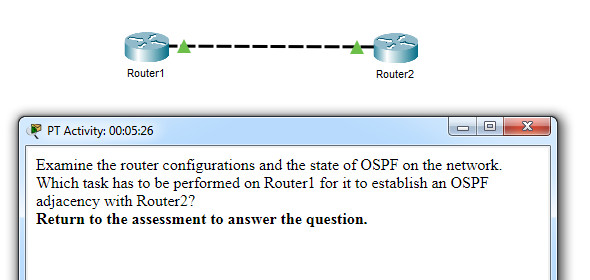
Which task has to be performed on Router 1 for it to establish an OSPF adjacency with Router 2?
- Issue the clear ip ospf process command.
- Change the subnet mask of interface FastEthernet 0/0 to 255.255.255.0.
- Remove the passive interface command from interface FastEthernet 0/0.
- Add the network 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 command to the OSPF process.
38. Match the description to the term. (Not all options are used.)
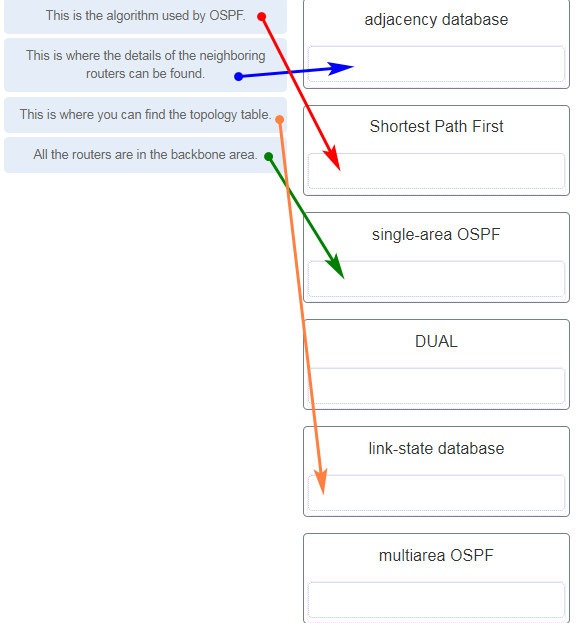
39. What is a benefit of multiarea OSPF routing?
- Topology changes in one area do not cause SPF recalculations in other areas.
- Routers in all areas share the same link-state database and have a complete picture of the entire network.
- A backbone area is not required.
- Automatic route summarization occurs by default between areas.
40. Match the OSPF state with the order in which it occurs. (Not all options are used.)
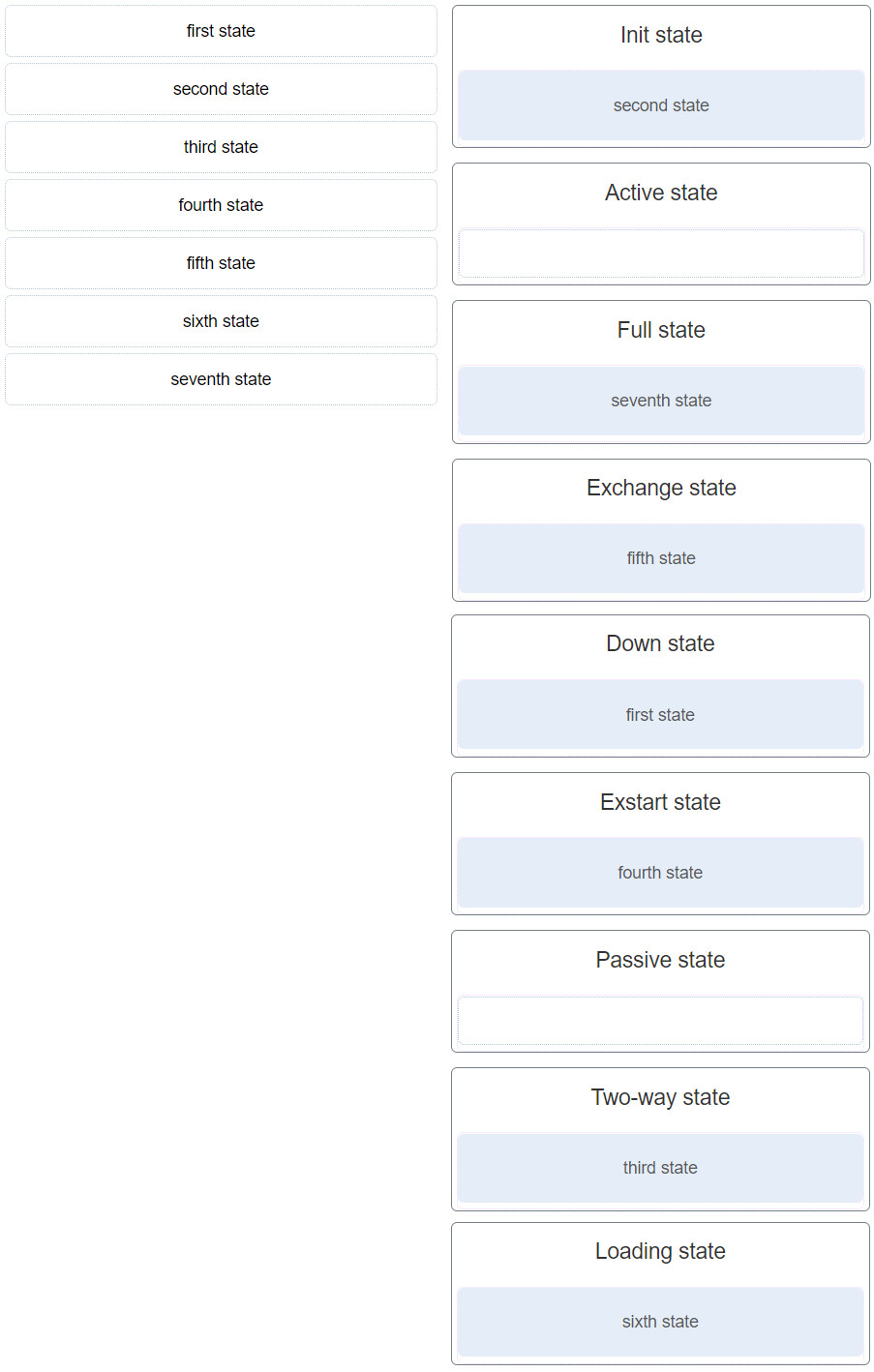
Modules 1 – 2: OSPF Concepts and Configuration Exam
41. What indicates to a link-state router that a neighbor is unreachable?
- if the router no longer receives hello packets
- if the router receives an update with a hop count of 16
- if the router receives an LSP with previously learned information
- if the router no longer receives routing updates
42. Which three OSPF states are involved when two routers are forming an adjacency? (Choose three.)
- Exchange
- Init
- ExStart
- Two-way
- Loading
- Down
43. Refer to the exhibit. Suppose that routers B, C, and D have a default priority, and router A has a priority 0. Which conclusion can be drawn from the DR/BDR election process?
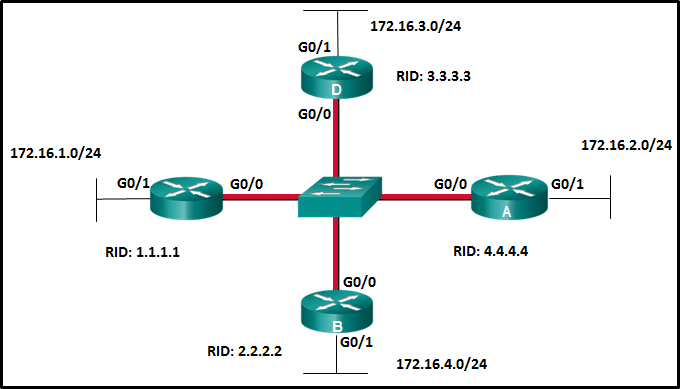
CCNA 3 v7 Modules 1 – 2: OSPF Concepts and Configuration Exam
- If the priority of router C is changed to 255, then it will become the DR.
- Router A will become the DR and router D will become the BDR.
- If the DR fails, the new DR will be router B.
- If a new router with a higher priority is added to this network, it will become the DR.
44. An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 64.102.0.0 255.255.255.128. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
- 0.0.31.255
- 0.0.0.63
- 0.0.63.255
- 0.0.0.127
45. Which command will a network engineer issue to verify the configured hello and dead timer intervals on a point-to-point WAN link between two routers that are running OSPFv2?
- show ipv6 ospf interface serial 0/0/0
- show ip ospf neighbor
- show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0/1
- show ip ospf interface serial 0/0/0
46. An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 128.107.0.0 255.255.255.192. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
- 0.0.63.255
- 0.0.0.63
- 0.0.0.3
- 0.0.0.7
47. Match each OSPF packet type to how it is used by a router. (Not all options are used.)
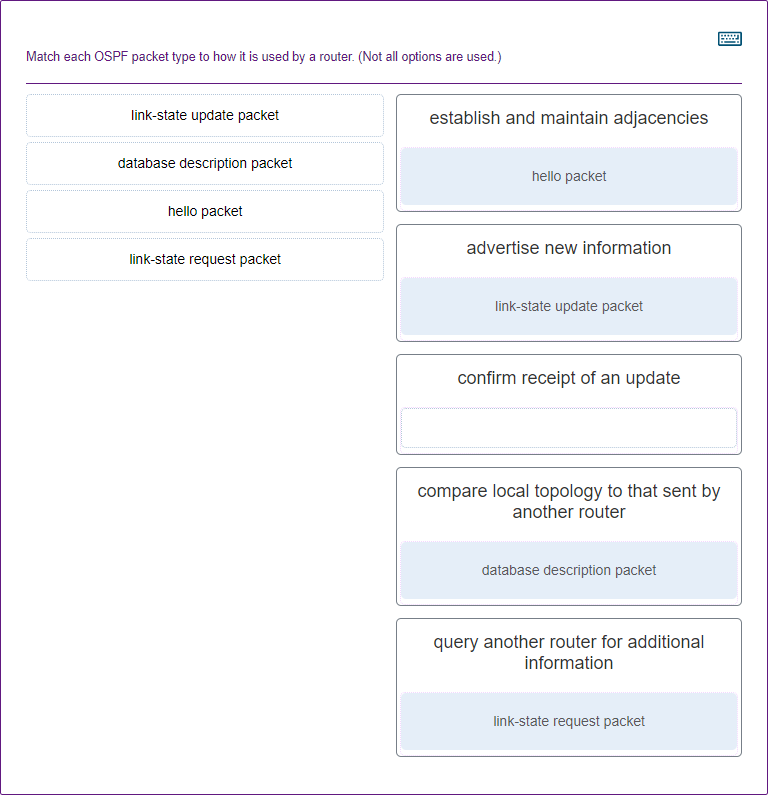
48. An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 192.168.181.0 255.255.254.0. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
- .0.63.255
- 0.0.15.255
- 0.0.1.255
- 0.0.31.255
49. An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 198.19.0.0 255.255.252.0. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
- 0.0.63.255
- 0.0.3.255
- 0.0.31.255
- 0.0.0.255
50. An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 128.107.0.0 255.255.252.0. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
- 0.0.3.255
- 0.0.0.7
- 0.0.0.3
- 0.0.63.255
51. Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router flooding link-state and cost information about each directly connected link?
- building the topology table
- selecting the router ID
- exchanging link-state advertisements
- injecting the default route
52. Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router sending Hello packets out all of the OSPF-enabled interfaces?
- electing the designated router
- establishing neighbor adjacencies
- injecting the default route
- exchanging link-state advertisements
53. An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 64.100.0.0 255.255.255.0. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
- 0.0.0.31
- 0.0.0.255
- 0.0.0.63
- 0.0.0.127
54. Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router inserting best paths into the routing table?
- declaring a neighbor to be inaccessible
- executing the SPF algorithm
- load balancing equal-cost paths
- choosing the best route
55. What type of address is 64.101.198.197?
- public
- private
56. An OSPF router has three directly connected networks; 172.16.0.0/24, 172.16.1.0/24, and 172.16.2.0/24. Which OSPF network command would advertise only the 172.16.1.0 network to neighbors?
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
- router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.0 area 0
57. Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router building a link-state database based on received LSAs?
- selecting the router ID
- declaring a neighbor to be inaccessible
- executing the SPF algorithm
- building the topology table

Hi, if the OSPF interface priority is set to zero, the router cannot participate in the election process.
So will participate in the election only the routers B, C and D. Router D is the DR because it has the highest router ID and B will the BDR because it has the second highest router ID.
link for this exam please.
Examine the router configurations and the state of OSPF on the network.
Which task has to be performed on Router1 for it to establish an OSPF adjacency with Router2?
Return to the assessment to answer the question.
Q37. The correct answer is:
Change the subnet mask of interface FastEthernet 0/0 to 255.255.255.0.
A network technician issues the following commands when configuring a router:
R1(config)# router ospf 11
R1(config-router)# network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
What does the number 11 represent?
————–
An OSPF router has three directly connected networks; 172.16.0.0/16, 172.16.1.0/16, and 172.16.2.0/16. Which OSPF network command would advertise only the 172.16.1.0 network to neighbors?
To advertise only the 172.16.1.0/24 network the wildcard mask used in the network command must match the first 24-bits exactly. To match bits exactly, a wildcard mask uses a binary zero. This means that the first 24 bits of the wildcard mask must be zero. The low-order 8-bits can all be set to 1.
*NEW Question*
An OSPF router has three directly connected networks; 172.16.0.0/24, 172.16.1.0/24, and 172.16.2.0/24. Which OSPF network command would advertise only the 172.16.1.0 network to neighbors?
router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
router(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.0 area 0
Thank you for sharing.
An OSPF router has three directly connected networks; 172.16.0.0/24, 172.16.1.0/24, and 172.16.2.0/24. Which OSPF network command would advertise only the 172.16.1.0 network to neighbors?
I added. Thank you.
Still valid 23/09/2023 :)
wrong answares
Q55. What type of address is 64.101.198.197
What is the explanation for this? Why the answer is public?
Block 10.XXX, 172.XXX and 192.XXX are private IP blocks. Others public.
hi i don’t understand the answer of the question 43 because i think that it id the router that have router-id 4.4.4.4 that become DR
In the question it says that Router A has a priority of 0. This makes it so that router can never be a DR.
Which statement is correct about multiarea OSPF?
Topic 1.1.0 – A company with one large autonomous system or AS can be divided into
smaller areas. When this occurs and the OSPF routing protocol is implemented, the design is called multi-area OSPF. Multi-area OSPF decreases the frequency of the SPF calculation, thus lightening the load on the router. In a single area OSPF design, all the routers are located in area 0 or the backbone area.
OSPF can consolidate a fragmented OSPF area into one large area.
Arranging routers into areas partitions a large autonomous system in order to lighten the load on routers.
All routers are in one area called the backbone area (area 0).
OSPF multiarea increases the frequency of SPF calculation.
A router is participating in an OSPFv2 domain. What will always happen if the dead interval expires before
the router receives a hello packet from an adjacent DROTHER OSPF router?
OSPF will remove that neighbor from the router link-state database.
A new dead interval timer of 4 times the hello interval will start.
OSPF will run a new DR/BDR election.
SPF will run and determine which neighbor router is “down”.
Topic 1.2.0 – On Cisco routers the default dead interval is 4 times the hello interval, and
this timer has expired in this case. SPF does not determine the state of neighbor routers; it
determines which routes become routing table entries. A DR/DBR election will not always
automatically run; this depends on the type of network and on whether or not the router no
longer up was a DR or BDR.
What is the order of packet types used by an OSPF router to establish convergence?
Topic 1.2.0 – An OSPF router progresses in this order to convergence, using the
following packets:
1. Hello packet, used for OSPF election and establishing neighbor adjacencies
2. DBD packet, used to synchronize databases with neighbors
3. LSR packet, used to request more information in synchronizing databases
4. LSU packet, used to send link-state updates to neighbors
5. LSAck packet, used to acknowledge receipt of an LSU
Hello, LSAck, LSU, LSR, DBD
LSU, LSAck, Hello, DBD, LSR
Hello, DBD, LSR, LSU, LSAck
LSAck, Hello, DBD, LSU, LSR
What is a feature of the OSPF routing protocol?
Topic 1.1.0 – OSPF uses the SPF algorithm to choose the best path. Routing changes
trigger routing updates (no 30-second updates). In IPv4, OSPF uses MD5 authentication
between two neighboring OSPF routers. In IPv6, OSPFv3 does not include any authentication capabilities of its own. Instead it relies entirely on IPsec to secure communications between neighbors. Routers can be grouped into areas to support a hierarchical system.
OSPF authentication is congured in the same way on IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
The SPF algorithm chooses the best path based on 30-second updates.
It scales well in both small and large networks.
Routers can be grouped into autonomous systems to support a hierarchical system.
What is used to create the OSPF neighbor table?
Topic 1.1.0 – The adjacency database is used to create the OSPF neighbor table. The
link-state database is used to create the topology table, and the forwarding database is used to create the routing table.
routing table
link-state database
adjacency database
forwarding database
What is identical on all OSPF routers within a single area?
Topic 1.1.0 – When the LSP ooding process completes, all OSPF routers will learn the same link-state information in the routing area. This information is used to build a complete link-state database, which will be the same on all OSPF routers within that specic area.
static routes
routing table
link-state database
neighbor table
What function is performed by the OSPF designated router?
Topic 1.3.0 – OSPF designated routers are elected on multiaccess networks to
disseminate LSAs to other OSPF routers. By having a single router disseminate LSAs, the exchanging of LSAs is more ecient.
maintaining the link-state database
summarizing routes between areas
dissemination of LSAs
redistribution of external routes into OSPF
What are two reasons for creating an OSPF network with multiple areas? (Choose two.)
Topic 1.1.0 – If a router is not running OSPF, it is not congurable with an OSPF area. OSPF areas have no direct relationship with the Internet. Routers that run OSPF can connect to the Internet, but multiple OSPF areas are not required for this purpose. OSPF areas help to decrease the demand for router memory and processing power
by limiting OSPF protocol trac, keeping link-state databases small, and requiring fewer SPF recalculations. Multiarea OSPF requires additional steps to congure and therefore does not simplify the conguration process.
to reduce SPF calculations
to provide areas in the network for routers that are not running OSPF
to simplify conguration
to reduce use of memory and processor resources
to ensure that an area is used to connect the network to the Internet
At which OSPF state are neighbor routers converged and able to exchange routing updates?
Topic 1.3.0 – OSPF neighbors that reach the Full state are converged and can exchange routing information.
Full
ExStart
Exchange
Two-Way
What happens immediately after two OSPF routers have exchanged hello packets and have formed a neighbor adjacency?
Topic 1.2.0 – During the exchange of hello packets, OSPF routers negotiate the election process and set the OSPF parameters. DBD packets are exchanged after that step has been completed. DBD packets contain abbreviated lists of link-state information. After that information has been exchanged, OSPF routers exchange Type 3 LSR packets to request further information.
They exchange abbreviated lists of their LSDBs.
They request more information about their databases.
They exchange DBD packets in order to advertise parameters such as hello and dead intervals.
They negotiate the election process if they are on a multiaccess network.
An OSPF router has three directly connected networks; 172.16.0.0/16, 172.16.1.0/16, and 172.16.2.0/16. Which OSPF network command would advertise only the 172.16.1.0 network to neighbors?
router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
I found this to be the right answer.
router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.0 area 0
the correct answer.
network 172.16.1.0 0.0.255.255 area 0 matches 172.16.0.0/16
An OSPF router has three directly connected networks; 172.16.0.0/16, 172.16.1.0/16, and 172.16.2.0/16. Which OSPF network command would advertise only the 172.16.1.0 network to neighbors?
router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
This is the right answer
In an OSPF network when are DR and BDR elections required?
La correcta es:
In Q.13 there is the answer is:
So please verify the correct one which is?
1.An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 192.168.181.0 255.255.254.0. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
2.In an OSPFv2 configuration, what is the effect of entering the command network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 ?
Thanks for sharing!
In an OSPFv2 configuration, what is the effect of entering the command network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 ?
shaking shathamanyu mr.universe of kurnool
The topic are all unpreachable but we hope the easiest way to learn all this questions rather than this type of method
very nice
A network technician issues the following commands when configuring a router:
R1(config)# router ospf 11
R1(config-router)# network 10.10.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
What does the number 11 represent?
True answer: the OSPF process ID on R1
Dose all the question will be on CCNA 200-301 exam?
Sorry for the question juts want to verify,
Thank you Admin.
No, 200-301 in here: https://itexamanswers.net/ccna-200-301-dumps-full-questions-exam-study-guide-free.html
After modifying the router ID on an OSPF router, what is the preferred method to make the new router ID effective?
HQ# clear ip ospf process
In an OSPFv2 configuration, what is the effect of entering the command network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 ?
It tells the router which interface to turn on for the OSPF routing process.
It tells the router which interface to turn on for the OSPF routing process.
An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 64.100.0.0 255.255.255.0. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
In an OSPFv2 configuration, what is the effect of entering the command network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 ?
It tells the router which interface to turn on for the OSPF routing process.
Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router sending Hello packets out all of the OSPF-enabled interfaces?
By default, what is the OSPF cost for any link with a bandwidth of 100 Mb/s or greater?
1
Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router sending Hello packets out all of the OSPF-enabled interfaces?
Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router inserting best paths into the routing table?
-declaring a neighbor to be inaccessible
-executing the SPF algorithm
-load balancing equal-cost paths
-choosing the best route (ANSWER)
This is marked as incorrect on the current test.
Correct answer is: executing the SPF algorithm
I have question
Which two step in the link-state routing process is described by a router flooding link-state and cost information about each directly connected link ?
– establish neighbor adjacencies
– exchange link -state advertisements
– electing the designated router
– injecting the default route
What type of address is 64.101.198.197?
public
private
1. Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router flooding link-state
and cost information about each directly connected link?
• building the topology table
• exchanging link-state advertisements
• selecting the router ID
• injecting the default route
hi, do you advice me to study all the dumps, i.e previous versions and the recent 200-301 questions when reading for my ccna and how similar to actual questions. Thanks.
Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router sending Hello packets out all of the OSPF-enabled interfaces?
electing the designated router
-> establishing neighbor adjacencies
injecting the default route
exchanging link-state advertisements
Navigation
Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router flooding link-state and cost information about each directly connected link?
* establishing neighbor adjacencies
* electing the designated router
* injecting the default route
* exchanging link-state advertisements
Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router flooding link-state and cost information about each directly connected link?
* building the topology table
* injecting the default route
* exchanging link-state advertisements
* selecting the router ID
Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router building a link-state database based on received LSAs?
building the topology table
All choise
**New Question**
Match each OSPF packet type to how it is used by a router. (Not all options are used.)
https://imgur.com/jsq8FrG
**Wrong Answer**
An OSPF router has three directly connected networks; 172.16.0.0/16, 172.16.1.0/16, and 172.16.2.0/16. Which OSPF network command would advertise only the 172.16.1.0 network to neighbors?
O router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 area 0
X router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
I agree with Mike(1) that it should be 0.0.0.255 but they must have gotten the subnet mask and wildcard mask mixed up when they put answer in.
(1)https://itexamanswers.net/ccna-3-v7-modules-1-2-ospf-concepts-and-configuration-exam-answers.html#comment-42876
Fixed, thanks so much!!
Hi Cake and Mike! It is a whole network that connected to the router, not a single IP, and it is a network with a prefix 16 means wildcard 0.0.255.255. So I think the right answer is there, they just highlighted the wrong answer.
new question
Match each OSPF packet type to how it is used by a router. (Not all options are used.)
establish and maintain adjacencies
advertise new information
confirm receipt of an update
compare local topology to that sent by another router
query another router for additional information
Does anyone know where to download the PKA file for Q37? Or does anyone have a screenshot of what the PT Activity is?
27
An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 198.19.0.0 255.255.252.0. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
0.0.63.255
0.0.3.255
0.0.31.255
0.0.0.255
no it the answer please help!!!
0.0.3.255
Does any one have the full details for Q33? It appears to be only part of the Question.
An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 128.107.0.0 255.255.252.0. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
0.0.3.255
0.0.0.7
0.0.0.3
0.0.63.255
It’s the first answear i think:
0.0.3.255
0.0.3.255
I think the number 19 is showing wrong answer. According to the explanation in green, the correct answer should be: router(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0 0.0.255.255 area 0
I think so too, maybe this is a confusion of cisco.
No because you don’t want all the 172.16.0.0 networks. You just want the 172.16.1.0 network so the subnet mask for that network would be 255.255.255.0. So the wildcard mask would be 0.0.0.255. Make sense?
It makes sense.
An administrator is configuring single-area OSPF on a router. One of the networks that must be advertised is 128.107.0.0 255.255.255.192. What wildcard mask would the administrator use in the OSPF network statement?
0.0.63.255
0.0.0.63 answer
0.0.0.3
0.0.0.7
Thanks you so much!!
I had the following question not seen above:
Which command will a network engineer issue to verify the configured hello and dead timer intervals on a point-to-point WAN link between two routers that are running OSPFv2?
X show ip ospf interface serial 0/0/0
show ipv6 ospf interface serial 0/0/0
show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0/1
show ip ospf neighbor
Added, thanks pro!
Some questions you guys missed. There were a decent amount of other questions not listed but I got those correct.
Which step in the link-state routing process is described by a router building a link-state database based on received LSAs?
building the topology table
Which three OSPF states are involved when two routers are forming an adjacency? (Choose three.)
Init
Two-way
Down
Added! Thank you