Networking Basics Checkpoint Exam: Network Access Answers
1. Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as two layers of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- transport
- network
- data link
- session
- physical
2. Which three acronyms/initialisms represent standards organizations? (Choose three.)
- TCP/IP
- MAC
- OSI
- IANA
- IETF
- IEEE
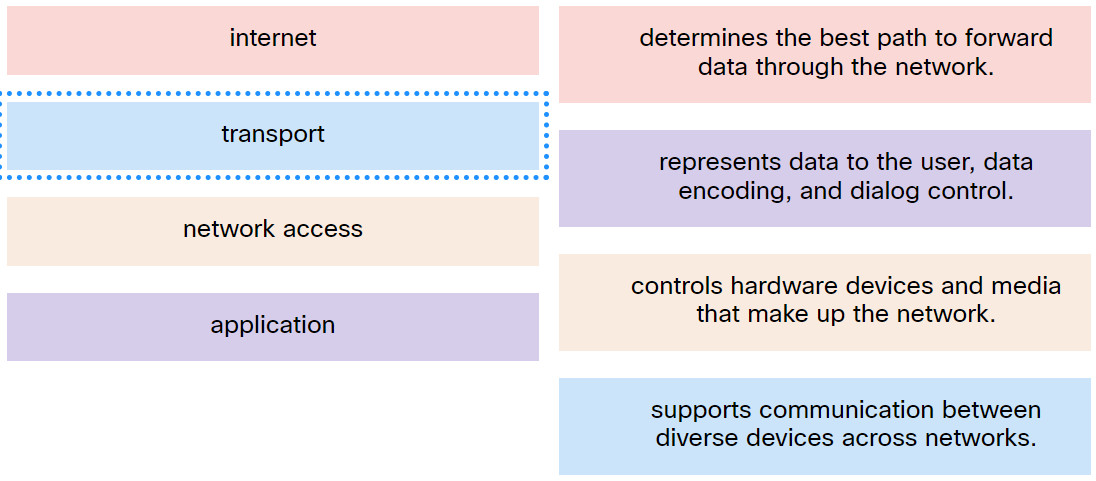
3. Match the TCP/IP model layer to the function.
4. Which statement defines a data communications protocol?
- an alliance of network device manufacturers
- a set of rules that govern the communication process
- an exchange agreement of network devices among vendors
- a set of product standards for types of network devices
5. Which statement is true about the TCP/IP and OSI models?
- The first three OSI layers describe general services that are also provided by the TCP/IP internet layer.
- The OSI Layer 7 and the TCP/IP application layer provide identical functions.
- The TCP/IP network access layer has similar functions to the OSI network layer.
- The TCP/IP transport layer and OSI Layer 4 provide similar services and functions.
6. Which three layers of the OSI model map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- application
- presentation
- session
- data link
- transport
- network
7. Which three elements do all communication methods have in common? (Choose three.)
- message priority
- message source
- message type
- message destination
- message data
- transmission medium
8. What two characteristics describe an Ethernet cable? (Choose two.)
- 4 pairs of twisted cables
- plastic core surrounded by multiple layers for isolation and protection
- color coded pairs of cables
- single copper core surrounded by a layer of insulation
- glass core surrounded by multiple layers for isolation and protection
9. Which data encoding technology is used in fiber-optic cables?
- modulation of specific frequencies of electromagnetic waves
- modulation of electrical voltage
- electrical pulses
- pulses of light
10. What is one advantage of using fiber optic cabling rather than copper cabling?
- It is able to be installed around sharp bends.
- It is easier to terminate and install than copper cabling.
- It is able to carry signals much farther than copper cabling.
- It is usually cheaper than copper cabling.
11. Which type of network cable is commonly used in backbone networks and telephone companies?
- twisted-pair cable
- shielded twisted-pair cable
- fiber-optic cable
- coaxial cable
12. Which two applications are suitable for deploying coaxial cables? (Choose two.)
- to connect network devices in backbone networks
- to connect data centers with high bandwidth requirements over long distances
- to connect PC computers in an office
- to connect various components in a satellite communication system
- to connect a TV set to the wall plug at home
13. Which criterion can be used to select the appropriate type of network media for a network?
- the types of data that need to be prioritized
- the number of intermediary devices that are installed in the network
- the cost of the end devices that are used in the network
- the environment where the selected medium is to be installed
14. Refer to the graphic. What type of cabling is shown?
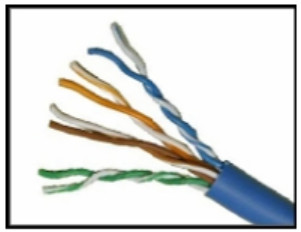
- glass fiber-optic
- coaxial
- plastic fiber-optic
- twisted-pair
15. Which type of address does a switch use to build the MAC address table?
- source IP address
- destination IP address
- source MAC address
- destination MAC address
16. Which term refers to the process of placing one message format inside another message format?
- segmenting
- encapsulation
- manipulation
- encoding
17. Refer to the exhibit. A PC with the MAC address of 0800.069d.3841 attached to port Fa0/8 is sending data to a device that has the MAC address of 6400.6a5a.6821. What will the switch do first to handle the data transfer?
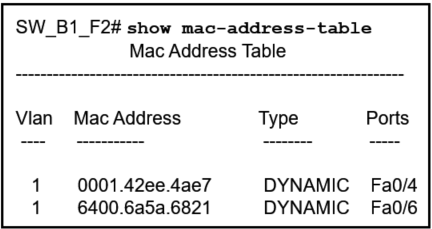
- The switch will add the address 6400.6151.6821 to the MAC address table.
- The switch will send the frame to ports Fa0/4 and Fa0/6.
- The switch will add the address 0800.069d.3841 to the MAC address table.
- The switch will send the frame to port Fa0/6.
- The switch will flood the frame out all ports except port Fa0/8.
18. Refer to the exhibit. How is a frame sent from PCA forwarded to PCC if the MAC address table on switch SW1 is empty?
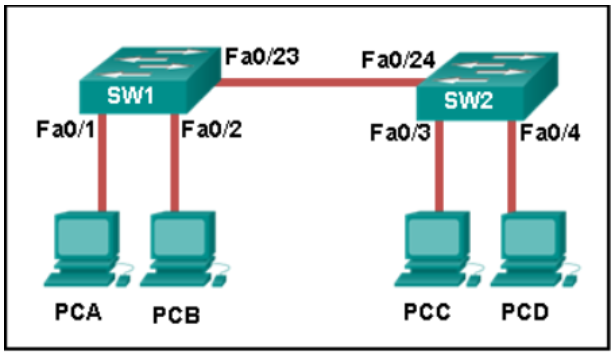
- SW1 forwards the frame directly to SW2. SW2 floods the frame to all ports connected to SW2, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on the switch, excluding the interconnected port to switch SW2 and the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 drops the frame because it does not know the destination MAC address.
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on SW1, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
19. What are two actions performed by a Cisco switch? (Choose two.)
- utilizing the MAC address table to forward frames via the destination MAC address
- building a routing table that is based on the first IP address in the frame header
- using the source MAC addresses of frames to build and maintain a MAC address table
- forwarding frames with unknown destination IP addresses to the default gateway
- examining the destination MAC address to add new entries to the MAC address table
20. Which information does a switch use to populate the MAC address table?
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the incoming port
- the source MAC address and the incoming port
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the outgoing port
- the destination MAC address and the incoming port
- the destination MAC address and the outgoing port
- the source MAC address and the outgoing port
21. How much data can be encapsulated into a normal sized Ethernet frame before it is sent over the network?
- 64 to 1518 bytes
- 0 to 1024 bytes
- 46 to 1500 bytes
- 32 to 1500 bytes
22. A network technician is researching the use of fiber optic cabling in a new technology center. Which two issues should be considered before implementing fiber optic media? (Choose two.)
- Fiber optic cabling requires different termination and splicing expertise from what copper cabling requires.
- Fiber optic cabling requires specific grounding to be immune to EMI.
- Fiber optic cabling is susceptible to loss of signal due to RFI.
- Fiber optic cable is able to withstand rough handling.
- Fiber optic provides higher data capacity but is more expensive than copper cabling.

A network technician is researching the use of fiber optic cabling in a new technology center. Which two issues should be considered before implementing fiber optic media? (Choose two.)
Fiber optic cabling is susceptible to loss of signal due to RFI.
***Fiber optic cabling requires different termination and splicing expertise from what copper cabling requires.
Fiber optic cabling requires specific grounding to be immune to EMI.
***Fiber optic provides higher data capacity but is more expensive than copper cabling.
Fiber optic cable is able to withstand rough handling.
I added. Thank you.