Module Group 2: Network Protocols and Architecture Pretest Exam Answers
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Modules 5 – 8: Network Protocols and Architecture Pre-Test Exam Answers
How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank.
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
1. What are three private IPv4 address? (Choose three.)
- 10.1.1.1
- 172.32.5.2
- 192.168.5.5
- 224.6.6.6
- 192.167.10.10
- 172.16.4.4
Explanation:Private IP addresses are reserved to be exclusively used for internal networks and they cannot be used on the Internet. IPv4 addresses in the networks, 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/16-172.31.0.0/16, and 192.168.0.0/24-192.168.255.0/24, are designated as private IPv4 addresses.
2. A network design engineer has been asked to design the IP addressing scheme for a customer network. The network will use IP addresses from the 192.168.30.0/24 network. The engineer allocates 254 IP addresses for the hosts on the network but excludes 192.168.30.0/24 and 192.168.30.255/24 IP addresses. Why must the engineer exclude these two IP addresses?
- 192.168.30.0/24 and 192.168.30.255/24 IP addresses are reserved for the email and DNS servers.
- 192.168.30.0/24 is the network IP address and 192.168.30.255/24 is the IP broadcast address.
- 192.168.30.0/24 and 192.168.30.255/24 IP addresses are reserved for outside Internet connectivity.
- 192.168.30.0/24 is the IP address reserved for the default gateway, and 192.168.30.255/24 is the IP address reserved for the DHCP server.
Explanation:The IPv4 addressing system is a hierarchical addressing system. An IPv4 address is made up of two parts, the network address and the host address. When the host portion is all “0s” in binary, it is designated as a network address. When the host portion is all “1s” in binary, it is designated as a broadcast address. These two addresses cannot be assigned to individual hosts.
3. Which statement describes a MAC address?
- It is 128-bits in length.
- It identifies the source and destination addresses of hosts on the Internet.
- It contains two portions, the network portion and the host portion.
- It is a physical address assigned to an Ethernet NIC by the manufacturer.
Explanation:The Media Access Control (MAC) address is a physical address assigned to each Ethernet NIC by manufacturers. It is 48-bits in length. The MAC address is used to identify the source and destination on a local Ethernet network. It cannot be routed to remote networks.
4. Which two layers of the OSI model specify protocols that are associated with Ethernet standards? (Choose two.)
- physical layer
- session layer
- data link layer
- transport layer
- network layer
Explanation:Ethernet standards specify protocols that operate at Layer 1 (physical layer) and Layer 2 (data link layer) of the OSI model and it is the technology used by almost all wired local-area networks.
5. Which three fields are found in an 802.3 Ethernet frame? (Choose three.)
- source physical address
- media type identifier
- frame check sequence
- source logical address
- destination physical address
- destination logical address
Explanation:The fields of an Ethernet frame are the preamble, destination and source address, length, data, and FCS.
6. Which network device can serve as a boundary to divide a Layer 2 broadcast domain?
- router
- access point
- Ethernet bridge
- Ethernet hub
Explanation:Layer 1 and 2 devices (LAN switch and Ethernet hub) and access point devices do not filter MAC broadcast frames. Only a Layer 3 device, such as a router, can divide a Layer 2 broadcast domain.
7. A host is trying to send a packet to a device on a remote LAN segment, but there are currently no mappings in the ARP cache. How will the device obtain a destination MAC address?
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the destination device.
- It will send the frame and use the device MAC address as the destination.
- It will send the frame with a broadcast MAC address.
- It will send an ARP request for the MAC address of the default gateway.
- It will send an ARP request to the DNS server for the destination MAC address.
Explanation:When sending a packet to a remote destination, a host will need to send the packet to a gateway on the local subnet. Because the gateway will be the Layer 2 destination for the frame on this LAN segment, the destination MAC address must be the address of the gateway. If the host does not already have this address in the ARP cache, it must send an ARP request for the address of the gateway.
8. Refer to the exhibit. How is a frame sent from PCA forwarded to PCC if the MAC address table on switch SW1 is empty?
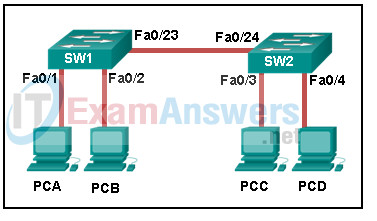
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Modules 5 – 8: Network Protocols and Architecture Pre-Test Exam
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on SW1, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 floods the frame on all ports on the switch, excluding the interconnected port to switch SW2 and the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 forwards the frame directly to SW2. SW2 floods the frame to all ports connected to SW2, excluding the port through which the frame entered the switch.
- SW1 drops the frame because it does not know the destination MAC address.
Explanation:When a switch powers on, the MAC address table is empty. The switch builds the MAC address table by examining the source MAC address of incoming frames. The switch forwards based on the destination MAC address found in the frame header. If a switch has no entries in the MAC address table or if the destination MAC address is not in the switch table, the switch will forward the frame out all ports except the port that brought the frame into the switch.
9. A router receives a packet from the Gigabit 0/0 interface and determines that the packet needs to be forwarded out the Gigabit 0/1 interface. What will the router do next?
- route the packet out the Gigabit 0/1 interface
- look into the routing table to determine if the destination network is in the routing table
- create a new Layer 2 Ethernet frame to be sent to the destination
- look into the ARP cache to determine the destination IP address
Explanation:Once a router receives a packet and looks inside the header to determine the destination network, the router compares the destination network to the routing table to determine if the packet is to be routed or dropped. If routed, the router attaches a new Layer 2 header based on the technology that is used by the outgoing port that is used. The packet is then routed out the destination port as designated by the routing table. The ARP cache is used to match an IP address with a MAC address.
10. When IPv4 is configured for a computer on a network, what does the subnet mask identify?
- the dynamic subnetwork configuration
- the device that the computer uses to access another network
- the part of the IP address that identifies the network
- the pool of addresses assigned within the network
Explanation:The IP addressing system is a hierarchical addressing system. An IP address is made up of two parts: the network address and the host address. For IPv4, the subnet mask is used to identify which portion of an IPv4 address is the network address and which portion is the host address.
11. Which network does a host with IP address 172.32.65.13 reside on if it is using a default subnet mask?
- 172.32.65.0
- 172.32.32.0
- 172.32.65.32
- 172.32.0.0
Explanation:In classful IPv4 addressing, a network with the first octet of 172 is a Class B network with the default subnet mask 255.255.0.0. Thus the network address is 172.32.0.0.
12. Which three layers of the OSI model are comparable in function to the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- application
- network
- presentation
- transport
- data link
- session
- physical
Explanation:The TCP/IP model consists of four layers: application, transport, internet, and network access. The OSI model consists of seven layers: application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, and physical. The top three layers of the OSI model: application, presentation, and session map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model.
13. Which layer of the OSI model defines services to segment and reassemble data for individual communications between end devices?
- application
- session
- network
- transport
- presentation
Explanation:The OSI model consists of seven layers: application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, and physical. The transport layer defines services to segment, transfer, and reassemble the data for individual communications between the end devices.
14. Refer to the exhibit. The IP address of which device interface should be used as the default gateway setting of host H1?
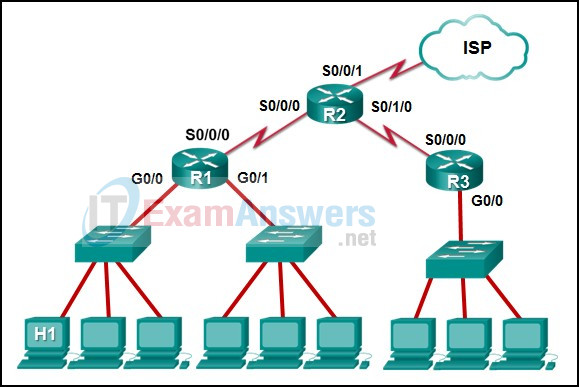
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Modules 5 – 8: Network Protocols and Architecture Pre-Test Exam
- R1: G0/0
- R2: S0/0/1
- R1: S0/0/0
- R2: S0/0/0
Explanation:The default gateway for host H1 is the router interface that is attached to the LAN that H1 is a member of. In this case, that is the G0/0 interface of R1. H1 should be configured with the IP address of that interface in its addressing settings. R1 will provide routing services to packets from H1 that need to be forwarded to remote networks.
15. Which portion of the network layer address does a router use to forward packets?
- host portion
- network portion
- broadcast address
- gateway address
Explanation:There are two parts to an a network layer address, the network and host portions. Routers are not concerned about delivering packets to hosts. Routers are concerned with delivering packets to the network that a destination host is a member of.
16. In implementing a LAN in a corporation, what are three advantages of dividing hosts between multiple networks connected by a distribution layer? (Choose three.)
- It provides increased security.
- It reduces complexity and expense by using LAN switch devices.
- Only LAN switches are needed.
- It splits up broadcast domains and decreases traffic.
- It makes the hosts invisible to those on other local network segments.
- It increases traffic bandwidth between segments through distribution layer devices.
Explanation:Some advantages of dividing end devices between multiple networks connected by a distribution layer include the following:
It is more appropriate for larger and complex networks.
It splits up broadcast domains and decreases traffic.
It can improve performance on each segment.
It makes the machines invisible to those on other local network segments.
It can provide increased security.
It can improve network organization.


