Networking Basics Checkpoint Exam: Communication Between Networks Answers
1. What is the result if the default gateway address is misconfigured on a PC?
- The PC can communicate with devices in remote networks but not with those in the same network.
- The PC can communicate with devices both in remote networks and in the same network.
- The PC cannot communicate with any devices.
- The PC can communicate with devices in the same network but not with those in remote networks.
2. Which type of address can be shared through NAT to enable home network devices to send and receive data over the internet?
- registered public IP address
- private IPv6 address
- registered MAC address
- broadcast MAC address
3. When a LAN is connected to the internet using a wireless router, how do devices on the LAN communicate on the internet using NAT?
- Only a small group of high priority client devices can be chosen by the wireless router to communicate to the internet using NAT.
- Each device must wait to receive a token from the wireless router in order to communicate to the internet via NAT.
- All devices must share the single public IPv4 address assigned to the wireless router in order to communicate to the internet via NAT.
- Each LAN must select a single client device from the wireless router settings that can communicate to the internet via NAT.
4. What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
- A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
- The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.
- The host will have to use ARP to determine the correct address of the default gateway.
- The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
5. A home network is using NAT on the router connecting it to the internet. The PCs on the home network receive private IP addresses through DHCP. When a PC sends a packet to a web server on the internet, what is the source IP address in the packet header when it arrives at the web server?
- a registered public IP address assigned to the external router interface
- the broadcast IP address of the external network connecting to the ISP
- a registered public IP address statically configured on the PC
- the private IP address assigned to the PC through DHCP
6. A network administrator investigates a user problem. The user can reach hosts on the same network, but is unable to communicate to remote networks.The network administrator tries to ping the gateway address configured on the host device and is unsuccessful. What is the most likely cause of the problem?
- The IP address of the user is incorrectly configured.
- TCP/IP is not installed on the host device.
- The address of the remote device is incorrect.
- The default gateway address is incorrect.
7. Refer to the exhibit. The switches have a default configuration. Host A needs to communicate with host D, but host A does not have the MAC address for the default gateway. Which network devices will receive the ARP request sent by host A?
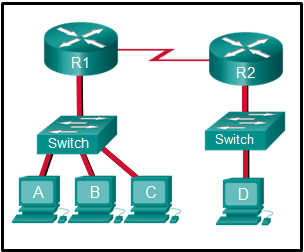
- only host D
- only router R1
- only hosts A, B, and C
- only hosts B and C
- only hosts A, B, C, and D
- only hosts B, C, and router R1
8. A host needs to reach another host on a remote network, but the ARP cache has no mapping entries. To what destination address will the host send an ARP request?
- the unicast IP address of the remote host
- the unicast MAC address of the remote host
- the subnet broadcast IP address
- the broadcast MAC address
9. What is the purpose of ARP in an IPv4 network?
- to build the MAC address table in a switch from the information that is gathered
- to forward data onward based on the destination MAC address.
- to obtain a specific MAC address when an IP address is known
- to forward data onward based on the destination IP address
10. Which destination address is used in an ARP request frame?
- 0.0.0.0
- FFFF.FFFF.FFFF
- AAAA.AAAA.AAAA
- 255.255.255.255
- the physical address of the destination host
11. The ARP table in a switch maps which two types of address together?
- Layer 2 address to a Layer 4 address
- Layer 4 address to a Layer 2 address
- Layer 3 address to a Layer 4 address
- Layer 3 address to a Layer 2 address
12. What action does the ARP process take when a host needs to build a frame, but the ARP cache does not contain an address mapping?
- The ARP process sends out an ARP request to the Ethernet broadcast address to discover the MAC address of the destination device.
- The ARP process sends out an ARP request to the IPv4 broadcast address to discover the MAC address of the destination device.
- The ARP process sends out an ARP request to the IPv4 broadcast address to discover the IPv4 address of the destination device.
- The ARP process sends out an ARP request to the Ethernet broadcast address to discover the IPv4 address of the destination device.
13. Which protocol is used by a computer to find the MAC address of the default gateway on an Ethernet network?
- DHCP
- UDP
- TCP
- ARP
14. When a router receives a packet, what information must be examined in order for the packet to be forwarded to a remote destination?
- source MAC address
- source IP address
- destination MAC address
- destination IP address
15. Refer to the exhibit. What does the router do after it determines that a data packet from Network 1 should be forwarded to Network 2?
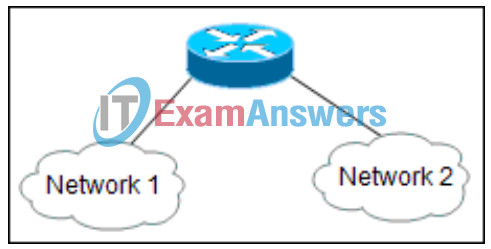
Networking Basics Module 12 – 14 Checkpoint Exam
- It reassembles the frame with different MAC addresses than the original frame.
- It reassembles the data packet with different IP addresses than the original data packet.
- It reassembles both the packet and the frame with different destination IP and MAC addresses.
- It sends the frame with the same information as it was received.
16. Which portion of the network layer address does a router use to forward packets?
- host portion
- gateway address
- broadcast address
- network portion
17. Refer to the exhibit. Workstation A sends an IP packet to workstation B. Which two statements describe the encapsulation of the packet as it passes through the network? (Choose two.)
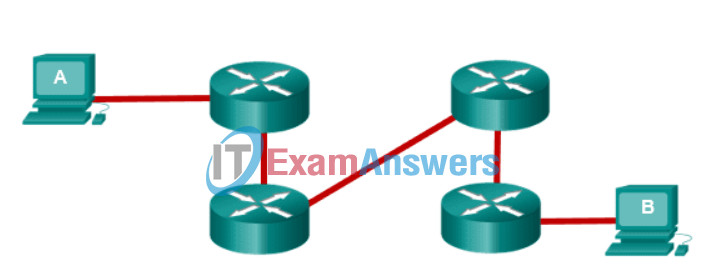
- The destination Layer 2 address of the frame does not change as it is forwarded.
- The Layer 3 header is stripped from the packet when it is received at each router.
- The Layer 2 header of the frame is reassembled when it is forwarded by each router.
- The Layer 2 header is stripped from the frame when it is received by each router.
- The source Layer 3 address is changed when it is received at each router.
18. What are two functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- It builds a routing table based on ARP requests.
- It controls the flow of data via the use of Layer 2 addresses.
- A router connects multiple IP networks.
- It provides segmentation at Layer 2.
- It determines the best path to send packets.
19. Why is it important for the router to maintain an accurate routing table?
- to identify all of the routers in a large network
- to provide Layer 2 addressing information for the next hop
- to prevent broadcasts from occurring on the LAN
- to determine the best path to reach the destination network
20. Refer to the exhibit. Consider the IP address configuration shown from PC1. What is a description of the default gateway address?
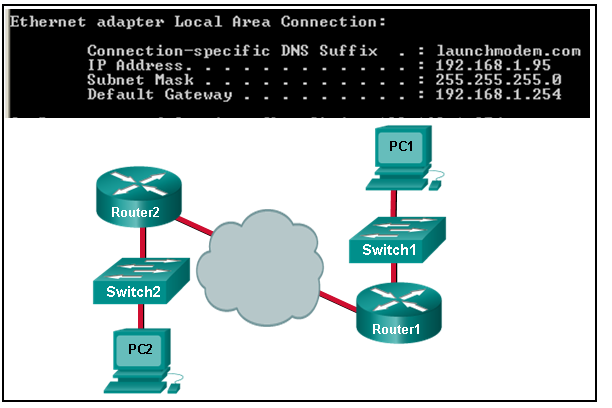
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the PC1 LAN to Router1.
- It is the IP address of the Router1 interface that connects the company to the Internet.
- It is the IP address of the ISP network device located in the cloud.
- It is the IP address of Switch1 that connects PC1 to other devices on the same LAN.

20.
Multiple choice question
Which two functions are primary functions of a router? (Choose two.)
packet forwarding
path selection
17. Refer to the exhibit. Workstation A sends an IP packet to workstation B. Which two statements describe the encapsulation of the packet as it passes through the network? (Choose two.)
The Layer 2 header is stripped from the frame when it is received by each router.
The Layer 2 header of the frame is reassembled when it is forwarded by each router.