Networking Basics Checkpoint Exam: Build a Small Network Answers
1. What is the order of bandwidth measurement from smallest to largest?
- Gbps, Tbps, Mbps, Kbps
- Tbps, Mbps, Kbps, Gbps
- Kbps, Mbps, Gbps, Tbps
- Kbps, Tbps, Mbps, Gbps
Explanation: Command bandwidth measurements are as follows from smallest to largest:
- Thousands of bits per second (Kbps) or Kilobits per second
- Millions of bits per second (Mbps) or Megabits per second
- Billions of bits per second (Gbps) or Gigabits per second
- Trillions of bits per second (Tbps) or Terabits per second
2. Which is a characteristic of the Internet?
- It is not centrally governed.
- It is localized to specific geographic locations.
- It is operated by the US government.
- It supports only wired network connections.
Explanation: The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that has no central governance. It is not limited to geographic boundaries and uses static public IP addresses for communication.
3. How many unique values are possible using a single binary digit?
Explanation: A bit is stored and transmitted as one of two possible discrete states. Each bit can only have one of two possible values, 0 or 1. The term bit is an abbreviation of “binary digit” and represents the smallest piece of data.
4. What allows digital devices to interconnect and transmit data?
- a sensor
- a smart phone
- a network
- a global positioning sensor
Explanation: A network connects people and devices through wired or wireless means.
5. What data representation is used when a computer or network device is processing data?
- binary
- text
- readable
- inferred
6. Which two devices are considered end devices? (Choose two.)
- laptop
- switch
- printer
- router
- hub
Explanation: A device that forms the interface between users and the underlying communication network is known as an end device. End devices are either the source or destination of a message.
7. Which three devices are considered intermediate devices in a network? (Choose three.)
- network printer
- wireless access point
- workstation
- switch
- server
- router
Explanation: Intermediate devices in a network provide network connectivity to end devices and transfer user data packets during data communications.
8. Match each device to a category.
Options matched to the correct selection.
| end devices |
intermediary devices |
| PC |
Firewall |
| Printer |
Router |
| Smart device |
Switch |
9. What are two types of wired high-speed Internet connections? (Choose two.)
- dial-up
- DSL
- cellular
- satellite
- cable
Explanation: Cable and DSL Internet technologies both use physical cabling to provide an Internet connection to a residence or a small business. Although dial-up is a wired technology, it does not provide a high-speed Internet connection. Satellite and cellular connections provide a wireless Internet connection.
10. A consumer places a smartphone close to a pay terminal at a store and the shopping charge is successfully paid. Which type of wireless technology was used?
Explanation: NFC is a wireless technology that allows data to be exchanged between devices that are in very close proximity to each other.
11. Which two methods are used to directly connect mobile devices such as tablets and smartphones to a data network? (Choose two.)
- Bluetooth
- cellular communications
- wired Ethernet
- Wi-Fi
- WiMax
Explanation: Mobile devices connect wirelessly to data networks using either Wi-Fi or a telecommunication provider cellular network. Bluetooth is used to connect to peripherals or other local devices over very short distances. Ethernet is a wired network access technology and is not used by mobile devices. Mobile devices do not typically implement WiMAX technology.
12. What are two methods typically used on a mobile device to provide internet connectivity? (Choose two.)
- NFC
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth
- cellular
- GPS
Explanation: Mobile devices commonly use Wi-Fi and cellular to connect to the internet. The cellular connection uses the cellular data network for a fee. The Wi-Fi connection uses an 802.11 wireless network in the area to connect to the internet.
13. A user is looking for a wireless headphone for listening to songs stored on a smartphone. What wireless technology would the headphone use?
- Wi-Fi
- 3G/4G
- infrared
- Bluetooth
Explanation: Bluetooth is a wireless technology for data exchange over a short distance. It is suitable for connecting devices with simple tasks, such as headsets, keyboards, mice, and printers. Wi-Fi is suitable for variety of applications with high speed wireless connectivity required or preferred. Infrared requires a direct line of sight between the transmitter and the receiver. 3G/4G are cellular network technologies to manage voice calls and data transmission between clients and service providers.
14. In the context of mobile devices, what does the term tethering involve?
- connecting a mobile device to another mobile device or computer to share a network connection
- connecting a mobile device to a hands-free headset
- connecting a mobile device to a 4G cellular network
- connecting a mobile device to a USB port on a computer in order to charge the mobile device
Explanation: Tethering allows a laptop or PC to use the Internet connection of a mobile device such as a cell phone, usually through a cellular data connection. This allows devices to connect to the Internet in locations where there is no Wi-Fi or cabled connection, but where there is still a cellular data connection.
15. What two radio frequency bands are used in home Wireless LANs? (Choose two.)
- 9 MHz
- 900 GHz
- 2.4 GHz
- 5 MHz
- 5 GHz
Explanation: The wireless technologies most frequently used in home networks are in the unlicensed 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency ranges.
16. Refer to the exhibit. Which router port connects to the modem provided by the service provider?
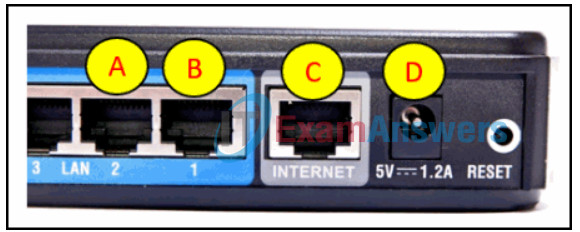
Explanation: The ports shown in the diagram are used as follows: The LAN ports, A and B, are used to connect wired devices on the home network. The Internet port, C, is connected to the modem. The port, labeled D, is the 5V DC power port that supplies power to the router.
17. Which technology is used to uniquely identify a WLAN network?
- WPA
- SSID
- MAC address table
- WEP
Explanation: When a wireless AP or router is being set up, an SSID is configured to uniquely identify the WLAN that is managed by the device.
18. Which feature is characteristic of MAC filtering in wireless networks?
- It allows only authorized users to detect the network.
- It restricts computer access to a wireless network.
- It is configured on the computer rather than on the router.
- It encrypts data that is transmitted on a wireless network.
Explanation: MAC address filtering uses the MAC address to identify which devices are allowed to connect to the wireless network.
19. A user is setting up a home wireless network. Which type of device must the user have in order to establish the wireless network and provide access to the internet for multiple home devices?
- wireless router
- hub
- patch panel
- switch
Explanation: A wireless router connects multiple wireless devices to the network. It will then aggregate the internet access requests from home devices to the internet.
20. Which wireless RF band do IEEE 802.11b/g devices use?
- 60 GHz
- 5 GHz
- 900 MHz
- 2.4 GHz
Explanation: 900 MHz is an FCC wireless technology that was used before development of the 802.11 standards. 900 MHz devices have a larger coverage range than the higher frequencies have and do not require line of sight between devices. 802.11b/g/n/ad devices all operate at 2.4 GHz. 802.11a/n/ac/ad devices operate at 5 GHz, and 802.11ad devices operate at 60 GHz.
21. Which items are collectively referred to as network media?
- PCs and laptops
- wires and radio waves
- firewalls and servers
- routers and switches
Explanation: Network media is a term used to describe the actual physical layer transport along the path over which an electrical signal travels as it moves from one component to another.
22. What information may be requested when pairing devices over Bluetooth?
- a PIN
- a username
- the SSID
- an IP address
Explanation: During the pairing process, a personal identification number (PIN) may be requested for authentication.

