1. Which destination IPv4 address does a DHCPv4 client use to send the initial DHCP Discover packet when the client is looking for a DHCP server?
- 224.0.0.1
- 255.255.255.255
- the IP address of the default gateway
- 127.0.0.1
Explanation: Broadcast communications on a network may be directed or limited. A directed broadcast is sent to all hosts on a specific network. A limited broadcast is sent to 255.255.255.255. When a DHCP client needs to send a DHCP Discover packet in order to seek DHCP servers, the client will use this IP address of 255.255.255.255 as the destination in the IP header because it has no knowledge of the IP addresses of DHCP servers.
2. Which is a DHCPv4 address allocation method that assigns IPv4 addresses for a limited lease period?
- pre-allocation
- automatic allocation
- manual allocation
- dynamic allocation
Explanation: Dynamic allocation is the most commonly implemented allocation mechanism. It leases the IP parameters for a predefined period of time.
3. Which DHCPv4 message will a client send to accept an IPv4 address that is offered by a DHCP server?
- unicast DHCPACK
- unicast DHCPREQUEST
- broadcast DHCPREQUEST
- broadcast DHCPACK
Explanation: When a DHCP client receives DHCPOFFER messages, it will send a broadcast DHCPREQUEST message for two purposes. First, it indicates to the offering DHCP server that it would like to accept the offer and bind the IP address. Second, it notifies any other responding DHCP servers that their offers are declined.
4. Refer to the exhibit. A user is configuring a PC with the IP settings as displayed, but the operating system will not accept them. What is the problem?
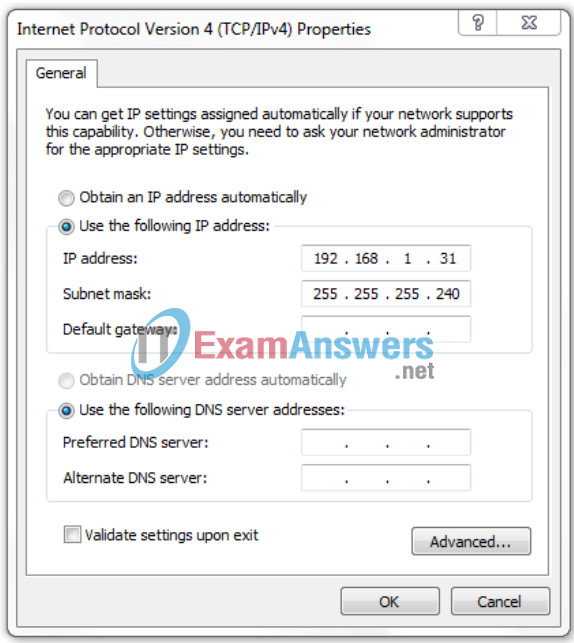
- The DNS settings are not configured.
- The subnet mask is wrong.
- The IP address is not a usable host address.
- The gateway address is not configured.
Explanation: The subnetwork address 192.168.1.16/28 has a range of valid IP addresses from 192.168.1.17 – 192.168.1.30 that can be allocated to hosts in that sub-network. The last IP address of the subnetwork is 192.168.1.31 and this is the broadcast address for that given subnetwork. It cannot be assigned to a host and thus the operating system will not permit that setting.
5. Which two types of devices are typically assigned static IP addresses? (Choose two.)
- printers
- web servers
- workstations
- laptops
- hubs
Explanation: Servers and peripherals are often accessed by an IP address, so these devices need predictable IP addresses. End-user devices often have dynamic addresses that are assigned. Hubs do not require IPv4 addresses to operate as intermediary devices.
6. A DHCP-enabled client PC has just booted. During which two steps will the client PC use broadcast messages when communicating with a DHCP server? (Choose two.)
- DHCPNAK
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPACK
Explanation: All DHCP messages between a DHCP-enabled client and a DHCP server are using broadcast messages until after the DHCPACK message. The DHCPDISCOVER and DHCPREQUEST messages are the only messages that are sent by a DHCP-enabled client. All DHCP messages between a DHCP-enabled client and a DHCP server use broadcast messages when the client is obtaining a lease for the first time.
7. Which two reasons generally make DHCP the preferred method of assigning IP addresses to hosts on large networks? (Choose two.)
- It eliminates most address configuration errors.
- It reduces the burden on network support staff.
- It provides an address only to devices that are authorized to be connected to the network.
- It guarantees that every device that needs an address will get one.
- It ensures that addresses are only applied to devices that require a permanent address.
Explanation: DHCP is generally the preferred method of assigning IP addresses to hosts on large networks because it reduces the burden on network support staff and virtually eliminates entry errors. However, DHCP itself does not discriminate between authorized and unauthorized devices and will assign configuration parameters to all requesting devices. DHCP servers are usually configured to assign addresses from a subnet range, so there is no guarantee that every device that needs an address will get one.
8. If more than one DHCP server is available on the local network, in which order will DHCP messages be sent between a host and a DHCP server?
- discover, offer, request, acknowledgment
- request, acknowledgment, discover, offer
- request, discover, offer, acknowledgment
- acknowledgment, request, offer, discover
Explanation: A DHCP host broadcasts a DHCP discover message to locate available servers. If more than one DHCP server is available, each server will respond to the host with a unicast DHCP offer message, which offers a lease to the client. The client then broadcasts a DHCP request message that identifies the specific server and offer that the client will accept. The identified server will unicast a DHCP acknowledgment message to finalize the offer.
9. A DHCP server is used to assign IP addresses dynamically to the hosts on a network. The address pool is configured with 192.168.10.0/24. There are 3 printers on this network that need to use reserved static IP addresses from the pool. How many IP addresses in the pool are left to be assigned to other hosts?
Explanation: If the block of addresses allocated to the pool is 192.168.10.0/24, there are 254 IP addresses to be assigned to hosts on the network. As there are 3 printers which need to have their addresses assigned statically, then there are 251 IP addresses left for assignment.
10. Which statement is true about DHCP operation?
- The DHCPDISCOVER message contains the IP address and subnet mask to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway.
- If the client receives several DHCPOFFER messages from different servers, it sends a unicast DHCPREQUEST message to the server from which it chooses to obtain the IP information.
- When a device that is configured to use DHCP boots, the client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network.
- A client must wait for lease expiration before it sends another DHCPREQUEST message.
Explanation: The client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network. A DHCP server replies with a DHCPOFFER message. This message offers to the client a lease that contains such information as the IP address and subnet mask to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway. After the client receives the lease, the received information must be renewed through another DHCPREQUEST message prior to the lease expiration.

