3.6.1 Packet Tracer – Skills Integration Challenge Answers
Topology
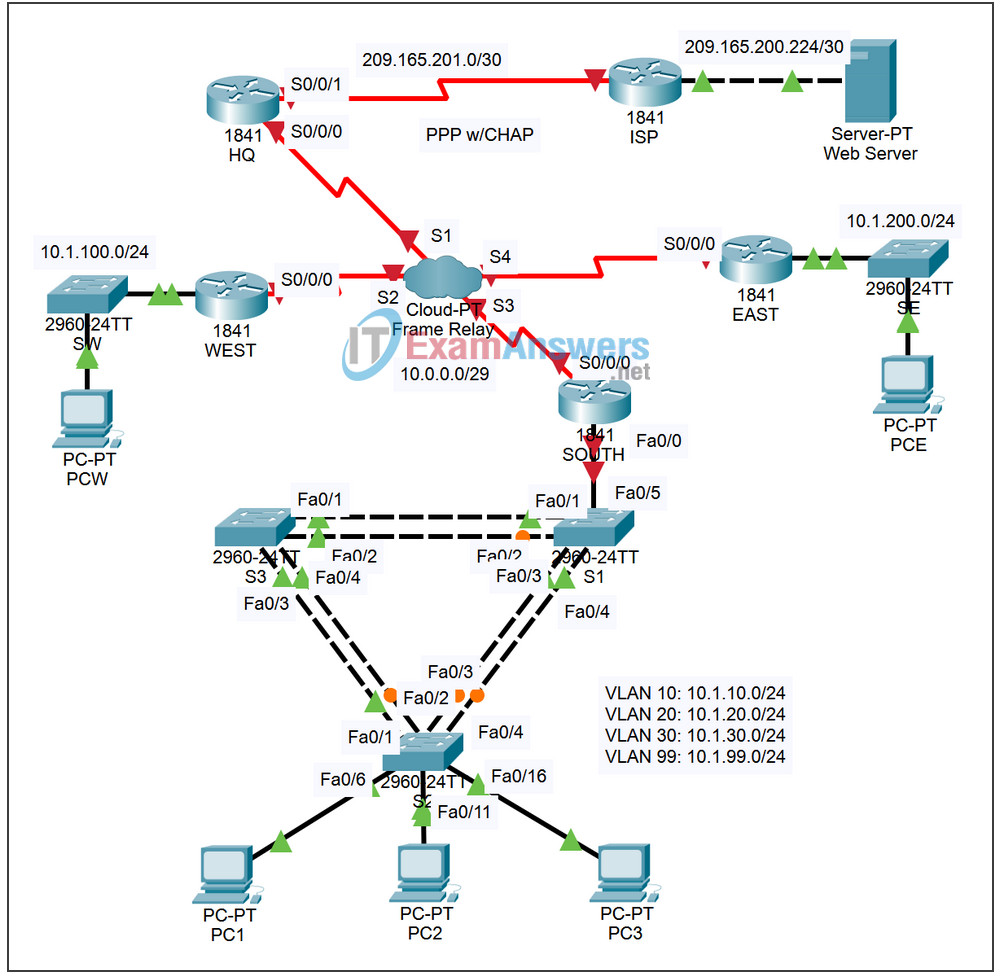
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask |
|---|---|---|---|
| HQ | S0/0/1 | 209.165.201.2 | 255.255.255.252 |
| S0/0/0 | 10.0.0.1 | 255.255.255.248 | |
| WEST | S0/0/0 | 10.0.0.2 | 255.255.255.248 |
| Fa0/0 | 10.1.100.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| SOUTH | S0/0/0 | 10.0.0.3 | 255.255.255.248 |
| Fa0/0.10 | 10.1.10.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| Fa0/0.20 | 10.1.20.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| Fa0/0.30 | 10.1.30.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| Fa0/0.99 | 10.1.99.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| EAST | S0/0/0 | 10.0.0.4 | 255.255.255.248 |
| Fa0/0 | 10.1.200.1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| ISP | S0/0/1 | 209.165.201.1 | 255.255.255.252 |
| Fa0/0 | 209.165.200.225 | 255.255.255.252 | |
| Web Server | NIC | 209.165.200.226 | 255.255.255.252 |
| S1 | VLAN99 | 10.1.99.11 | 255.255.255.0 |
| S2 | VLAN99 | 10.1.99.12 | 255.255.255.0 |
| S3 | VLAN99 | 10.1.99.13 | 255.255.255.0 |
Learning Objectives
- Configure PPP with CHAP.
- Configure full mesh Frame Relay.
- Configure static and default routing.
- Configure and test inter-VLAN routing.
- Configure VTP and trunking on switches.
- Configure VLANs on a switch.
- Configure and verify interface VLAN 99.
- Configure a switch as root for all spanning trees.
- Assign ports to VLANS.
- Test end-to-end connectivity.
Introduction:
This activity allows you to practice a variety of skills, including configuring Frame Relay, PPP with CHAP, static and default routing, VTP, and VLAN. Because there are close to 150 graded components in this activity, you may not see the completion percentage increase every time you configure a graded command. You can always click Check Results and Assessment Items to see if you correctly entered a graded command. Use the passwords cisco and class to access EXEC modes of the CLI for routers and switches.
Task 1: Configure PPP with CHAP Between Devices
Step 1. Configure and activate serial 0/0/1 on HQ.
Step 2. Configure PPP encapsulation on HQ for the link shared with ISP.
Step 3. Configure CHAP authentication on HQ.
Use cisco as the password.
Step 4. Verify connectivity between HQ and ISP.
The link between HQ and ISP should now be up, and you should be able to ping ISP. However, the link may take a few minutes in Packet Tracer before it comes up. To speed up the process, switch between Simulation and Realtime mode three or four times.
Step 5. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 4%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 2: Configure Full Mesh Frame Relay
The above topology diagram and the table below both show the DLCI mappings used in this full mesh Frame Relay configuration. Read the table from left to right. For example, the DLCI mappings you will configure on HQ are: 102 to WEST; 103 to SOUTH; and 104 to EAST.
| DLCI Mappings | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| From/To | HQ | WEST | SOUTH | EAST |
| HQ | N/A | 102 | 103 | 104 |
| WEST | 201 | N/A | 203 | 204 |
| SOUTH | 301 | 302 | N/A | 304 |
| EAST | 401 | 402 | 403 | N/A |
Note: HQ, WEST, and SOUTH are all using the default Frame Relay encapsulation cisco. However, EAST is using the encapsulation type IETF.
Step 1. Configure and activate the serial 0/0/0 interface on HQ.
Configure the interface with the following information:
- IP address
- Frame Relay encapsulation
- Mappings to WEST, SOUTH, and EAST (EAST uses IETF encapsulation)
- LMI type is ANSI
Step 2. Configure and activate the serial 0/0/0 interface on WEST.
Configure the interface with the following information:
- IP address
- Frame Relay encapsulation
- Mappings to HQ, SOUTH, and EAST (EAST uses IETF encapsulation)
- LMI type is ANSI
Step 3. Configure and activate the serial 0/0/0 interface on SOUTH.
Configure the interface with the following information:
- IP address
- Frame Relay encapsulation
- Mappings to HQ, WEST, and EAST (EAST uses IETF encapsulation)
- LMI type is ANSI
Step 4. Configure and activate the Serial 0/0/0 interface on EAST.
Configure the interface with the following information:
- IP address
- Frame Relay encapsulation using IETF
- Mappings to HQ, WEST and SOUTH
- LMI type is ANSI
Note: Packet Tracer does not grade your map statements. However, you must still configure the commands. You should now have full connectivity between the Frame Relay routers.
Step 5. Verify connectivity between Frame Relay routers.
The map on HQ should look like the following. Make sure all routers have full maps.
Serial0/0/0 (up): ip 10.0.0.2 dlci 102, static, broadcast, CISCO, status defined, active Serial0/0/0 (up): ip 10.0.0.3 dlci 103, static, broadcast, CISCO, status defined, active Serial0/0/0 (up): ip 10.0.0.4 dlci 104, static, broadcast, IETF, status defined, active
Verify that HQ, WEST, SOUTH, and EAST can now ping each other.
Step 6. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 28%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 3: Configure Static and Default Routing
No routing protocol is used in this topology. All routing is done through static and default routing.
Step 1. Configure static and default routes on HQ.
- HQ needs six static routes to the six remote LANs in the topology. Use the next-hop-ip argument in the static route configuration.
- HQ also needs a default route. Use the exit-interface argument in the default route configuration.
Step 2. Configure static and default routes on WEST.
- WEST needs five static routes to the five remote LANs in the topology. Use the next-hop-ip argument in the static route configuration.
- WEST also needs a default route. Use the next-hop-ip argument in the default route configuration.
Step 3. Configure static and default routes on SOUTH.
- SOUTH needs two static routes to the two remote LANs in the topology. Use the next-hop-ip argument in the static route configuration.
- SOUTH needs a default route. Use the next-hop-ip argument in the default route configuration.
Step 4. Configure static and default routes on EAST.
- EAST needs five static routes to the five remote LANs in the topology. Use the next-hop-ip argument in the static route configuration.
- EAST needs a default route. Use the next-hop-ip argument in the default route configuration.
Step 5. Verify connectivity from EAST and WEST LANs to the Web Server.
- All routers should now be able to ping the Web Server.
- The WEST PC (PCW) and the EAST PC (PCE) should now be able to ping each other and the Web Server.
Step 6. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 43%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 4: Configure and Test Inter-VLAN Routing
Step 1. Configure inter-VLAN routing on SOUTH.
Using the addressing table, activate Fast Ethernet 0/0 on SOUTH and configure inter-VLAN routing. The subinterface number corresponds to the VLAN number. VLAN 99 is the native VLAN.
Step 2. Test inter-VLAN routing on SOUTH.
HQ, WEST, and EAST should now be able to ping each of the subinterfaces on SOUTH.
Step 3. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 56%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed. The routers are now fully configured.
Task 5: Configure VTP and Trunking on the Switches
Step 1. Configure VTP settings on S1, S2, and S3.
- S1 is the server. S2 and S3 are clients.
- The domain name is CCNA.
- The password is cisco.
Step 2. Configure trunking on S1, S2, and S3.
Trunking ports for S1, S2, and S3 are all ports attached to another switch or router. Set all trunking ports to trunk mode, and assign VLAN 99 as the native VLAN.
Step 3. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 81%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 6: Configure VLANs on the Switch
Step 1. Create and name the VLANs.
Create and name the following VLANs on S1 only:
- VLAN 10, name = Faculty/Staff
- VLAN 20, name = Students
- VLAN 30, name = Guest(Default)
- VLAN 99, name = Management&Native
Step 2. Verify VLANs were sent S2 and S3.
What command displays the following output?
VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 8 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 64 Number of existing VLANs : 9 VTP Operating Mode : Client VTP Domain Name : CCNA VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled VTP V2 Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0xF5 0x50 0x30 0xB6 0x91 0x74 0x95 0xD9 Configuration last modified by 0.0.0.0 at 3-1-93 00:12:30
What command displays the following output?
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- ------------------------------ --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8
Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12
Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16
Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20
Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24
Gig1/1, Gig1/2
10 Faculty/Staff active
20 Students active
30 Guest(Default) active
99 Management&Native active
<output omitted>
Step 3. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 84%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 7: Configure and Verify VLAN 99
Step 1. On S1, S2, and S3 complete the following steps:
- Configure and activate VLAN 99
- Configure the default gateway
- Verify that S1, S2, and S3 can now ping SOUTH at 10.1.99.1
Step 2. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 92%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 8: Configure S1 as Root for All Spanning Trees
Step 1. Configure S1 as the root bridge for all spanning trees, including VLANs 1, 10, 20, 30, and 99.
Notice that S3 won the root war and is currently the root bridge for all spanning trees. Set the priority to 4096 on S1 for all spanning trees.
Step 2. Verify that S1 is now the root for all spanning trees.
Only the output for VLAN 1 is shown below. However, S1 should be the root for all spanning trees.
What command displays the following output?
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 4097
Address 00D0.BC79.4B57
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 4097 (priority 4096 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 00D0.BC79.4B57
Aging Time 300
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/2 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/3 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/4 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
Fa0/5 Desg FWD 19 128.3 Shr
<output omitted>
Step 3. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 96%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 9: Assign Ports to VLANS
Step 1. Assign ports on S2 to VLANs.
Packet Tracer only grades the ports that are attached to PC1, PC2, and PC3.
- Configure the port for access mode
- Assign the port to its VLAN
The VLAN port mappings are as follows:
- VLAN 99: Fa0/1 – Fa0/5
- VLAN 10: Fa0/6 – Fa0/10
- VLAN 20: Fa0/11 – Fa0/15
- VLAN 30: Fa0/16 – Fa0/20
- Unused: Fa0/21 – Fa0/24; Gig1/1; Gig1/2
Unused ports should be shut down for security purposes.
Step 2. Verify VLAN port assignments.
What command was used to get the following output showing the VLAN assignments?
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- ------------------------------ --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/5, Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23
Fa0/24, Gig1/1, Gig1/2
10 Faculty/Staff active Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9
Fa0/10
20 Students active Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Fa0/13, Fa0/14
Fa0/15
30 Guest(Default) active Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19
Fa0/20
99 Management&Native active
1002 fddi-default active
1003 token-ring-default active
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trnet-default active
Step 3. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 100%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 10: Test End-to-End Connectivity
Although Packet Tracer may take some time to converge, pings will eventually succeed from PC1, PC2 and PC3. Test connectivity to PCW, PCE, and the Web Server. If necessary, switch between Simulation and Realtime mode to accelerate convergence.
