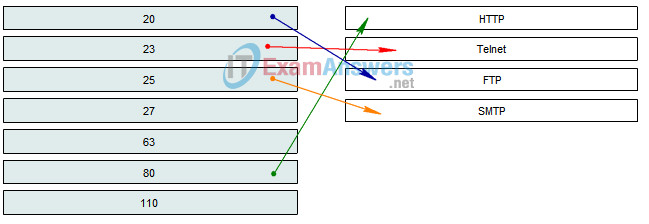
1. Match the TCP port numbers with the correct protocol by dragging the options on the left to the targets on the right. (Not all options are used.)
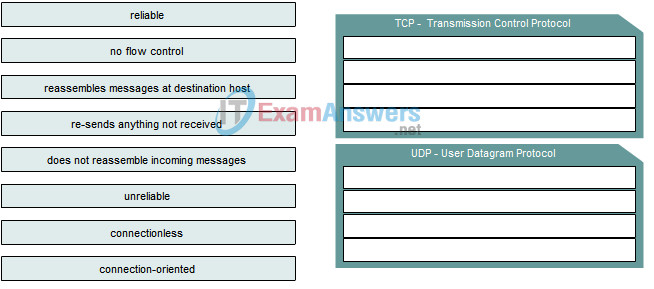
2. Categorize the options based on whether they describe TCP or UDP.
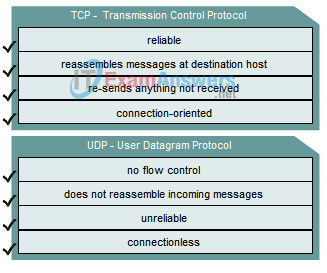
Answer
3. At the transport layer, which of the following controls is used to avoid a transmitting host overflowing the buffers of a receiving host?
- best effort
- encryption
- flow control
- compression
- congestion avoidance
4. End systems use port numbers to select the proper application. What is the smallest port number that can be dynamically assigned by a host system?
- 1
- 64
- 128
- 256
- 512
- 1024
5. During data transfer, what are the main responsibilities of the receiving host? (Choose two.)
- throughput
- encapsulation
- acknowledgment
- bandwidth
- segmentation
- reassembly
6. At which layer of the TCP/IP model does TCP operate?
- session
- transport
- network
- data link
7. What determines how much data a sending station running TCP/IP can transmit before it must receive an acknowledgment?
- segment size
- transmission rate
- bandwidth
- window size
- sequence number
8. What is the purpose of the sequence number in the TCP header?
- reassemble the segments into data
- identify the application layer protocol
- indicate the number of the next expected byte
- show the maximum number of bytes allowed during a session
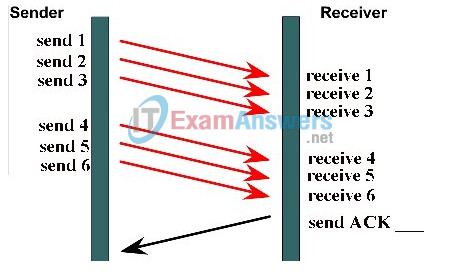
9. Which acknowledgement number should be sent by the receiver shown in the graphic?
- 3
- 4
- 6
- 7
- 9
- 12
10. What is the purpose of TCP/UDP port numbers?
- indicate the beginning of a three-way handshake
- reassemble the segments into the correct order
- identify the number of data packets that may be sent without acknowledgment
- track different conversations crossing the network at the same time
