1. Which of the following matches a router component with its function?
- FLASH – stores the bootstrap program
- ROM – stores the startup configuration file
- NVRAM – stores the operating system image
- RAM – stores the routing tables and ARP cache
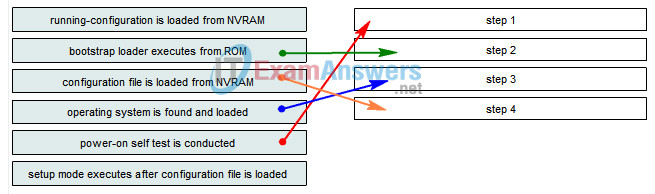
2. Construct the sequence of events that occurs during the router startup process. (Not all options apply.)
3. Which two commands can a technician use to determine if router serial ports have IP addresses that are assigned to them? (Choose two.)
- show interfaces
- show interfaces ip brief
- show controllers all
- show ip config
- show ip interface brief
4. Which of the following commands will set the privileged mode password to “quiz”?
- LAB_A(config)# enable secret quiz
- LAB_A(config)# password secret quiz
- LAB_A(config)# enable password secret quiz
- LAB_A(config)# enable secret password quiz
5. Which routing principle is correct?
- If one router has certain information in its routing table, all adjacent routers have the same information.
- Routing information about a path from one network to another implies routing information about the reverse, or return path.
- Every router makes its routing decisions alone, based on the information it has in its own routing table.
- Every router makes its routing decisions based on the information it has in its own routing table and its neighbor routing tables.
6. What two tasks do dynamic routing protocols perform? (Choose two.)
- discover hosts
- update and maintain routing tables
- propagate host default gateways
- network discovery
- assign IP addressing
7. A network engineer is configuring a new router. The interfaces have been configured with IP addresses but no routing protocols or static routes have been configured yet. What routes are present in the routing table?
- default routes
- broadcast routes
- direct connections
- No routes. The routing table is empty.
8. What two statements are correct regarding how a router forwards packets? (Choose two.)
- If the packet is destined for a remote network, the router forwards the packet out all interfaces that might be a next hop to that network.
- If the packet is destined for a directly connected network, the router forwards the packet out the exit interface indicated by the routing table.
- If the packet is destined for a remote network, the router forwards the packet based on the information in the router host table.
- If the packet is destined for a remote network, the router sends the packet to the next hop IP in the routing table.
- If the packet is destined for a directly connected network, the router forwards the packet based on the destination MAC address.
- If the packet is destined for a directly connected network, the router forwards the packet to the switch on the next hop VLAN.
9. Which statement is true regarding metrics used by routing protocols?
- A metric is the quantitative value a routing protocol uses to measure a given route.
- A metric is a Cisco proprietary means to convert distances to a standard unit.
- Metrics represent a composite value of the amount of packet loss occurring for all routing protocols.
- Metrics are used by the router to determine if a packet has an error and should be dropped.
- Metrics are only used by dynamic routing protocols.
10. Refer to the exhibit. Which port is used to connect a router to a LAN switch?
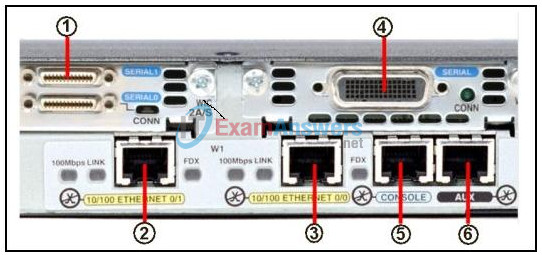
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 1 or 4
- 2 or 3
- 5 or 6
11. The network administrator configured the ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 serial 0/0 command on the router. How will this command appear in the routing table assuming the serial0/0 interface is up?
- D 0.0.0.0/0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
- S* 0.0.0.0/0 is directly connected, Serial0/0
- S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.2.2
- C 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 192.168.2.2
