6.4.1 Packet Tracer – Basic VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design Answers
Topology
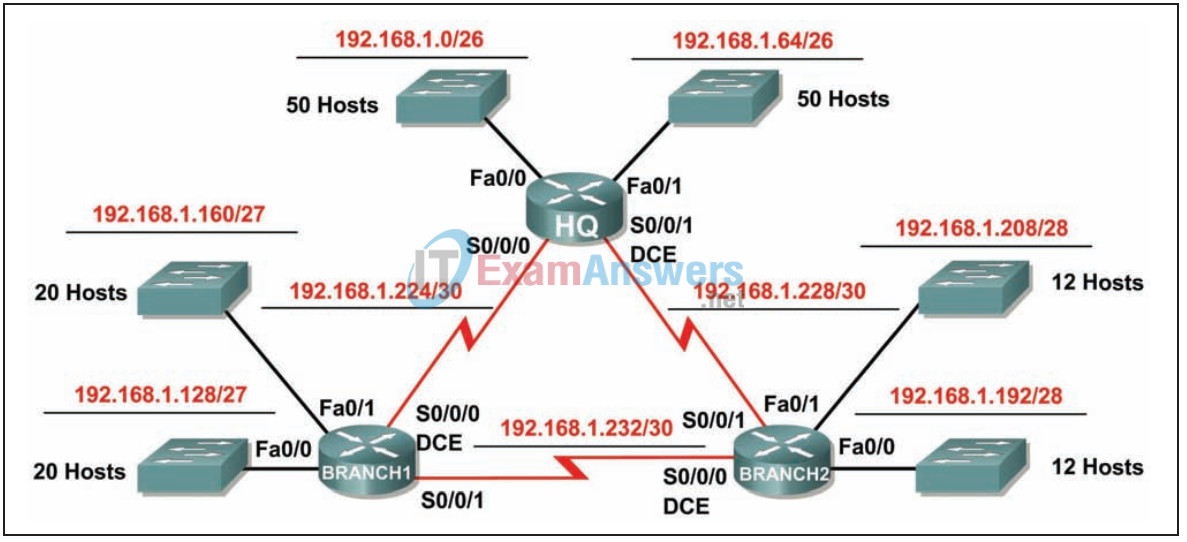
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQ | Fa0/0 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.192 | N/A |
| Fa0/1 | 192.168.1.65 | 255.255.255.192 | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.1.225 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.1.229 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Branch1 | Fa0/0 | 192.168.1.129 | 255.255.255.224 | N/A |
| Fa0/1 | 192.168.1.161 | 255.255.255.224 | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.1.226 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.1.233 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Branch2 | Fa0/0 | 192.168.1.193 | 255.255.255.240 | N/A |
| Fa0/1 | 192.168.1.209 | 255.255.255.240 | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.1.234 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.1.230 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
Learning Objectives
- Determine the number of subnets needed.
- Determine the number of hosts needed for each subnet.
- Design an appropriate addressing scheme using VLSM.
- Assign addresses and subnet mask pairs to device interfaces.
- Examine the use of the available network address space.
Introduction:
In this activity, you have been given the network address 192.168.1.0/24 to subnet and provide the IP addressing for the network shown in the topology diagram. VLSM will be used so that the addressing requirements can be met using the 192.168.1.0/24 network. The network has the following addressing requirements:
- The HQ LAN1 will require 50 host IP addresses.
- The HQ LAN2 will require 50 host IP addresses.
- The Branch1 LAN1 will require 20 host IP addresses.
- The Branch1 LAN2 will require 20 host IP addresses
- The Branch2 LAN1 will require 12 host IP addresses.
- The Branch2 LAN2 will require 12 host IP addresses.
- The link from HQ to Branch1 will require an IP address for each end of the link.
- The link from HQ to Branch2 will require an IP address for each end of the link.
- The link Branch1 to Branch2 will require an IP address for each end of the link.
Task 1: Examine network requirements.
Review your network requirements and answer the following questions. Please note that IP addresses will be required for each of the LAN interfaces.
1. How many subnets are needed? _9_
2. What is the maximum number of IP addresses needed for a single subnet?
_50_
3. How many IP addresses are needed for each of BranchBranch1’s LANs? _20_
4. How many IP addresses are needed for each of the BranchBranch2 LANs? _12_
5. How many IP addresses are needed for each of these WAN links between routers? _2_
6. What is the total number of IP addresses needed? _170_
7. What is the total number of IP addresses that are available on the 192.168.1.0/24 network? _254_
8. Can network addressing requirements be achieved using the 192.168.1.0/24 network? _Yes_
Task 2: Design an IP addressing scheme.
Step 1: Determine the subnet information for the largest segments.
In this case, the two HQ LANs are the largest subnets.
1. How many IP addresses are needed for each LAN? _50_
2. What is the smallest subnet that can be used to achieve this requirement?
_/26_
3. What is the maximum number of IP addresses that can be assigned on the subnet of this size? _62_
Step 2: Assign subnets to the HQ LANs.
Start from the beginning of the network 192.168.1.0/24.
1. Assign the first available subnet to HQ LAN1.
2. Complete the following table with the appropriate information.
HQ LAN1 subnet
| Network address | Subnet mask in decimal | Subnet mask in CIDR | First usable IP address | Last usable IP address | Broadcast address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.0 | 255.255.255.192 | /26 | 192.168.1.1 | 192.168.1.62 | 192.168.1.63 |
3. Assign the first available subnet to HQ LAN2.
4. Complete the following table with the appropriate information.
HQ LAN2 subnet
| Network address | Subnet mask in decimal | Subnet mask in CIDR | First usable IP address | Last usable IP address | Broadcast address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.64 | 255.255.255.192 | /26 | 192.168.1.65 | 192.168.1.126 | 192.168.1.127 |
Step 3: Determine the subnet information for the next larger segments.
In this case, the two LANs on Branch1 are the next largest subnets.
1. How many IP addresses are needed for each LAN? _20_
2. What is the smallest subnet that can be used to achieve this requirement?
_/27_
3. What is the maximum number of IP addresses that can be assigned on the subnet of this size? _30_
Step 4: Assign subnet to BRANCH1 LANs.
Start with the IP address following the HQ LAN subnets.
1. Assign the next subnet to LAN1 of Branch1.
2. Complete the following table with the appropriate information.
Branch1 LAN1 Subnet
| Network address | Subnet mask in decimal | Subnet mask in CIDR | First usable IP address | Last usable IP address | Broadcast address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.128 | 255.255.255.224 | /27 | 192.168.1.129 | 192.168.1.158 | 192.168.1.159 |
3. Assign the next available subnet to LAN2 of Branch1.
4. Complete the following table with the appropriate information.
Branch1 LAN2 Subnet
| Network address | Subnet mask in decimal | Subnet mask in CIDR | First usable IP address | Last usable IP address | Broadcast address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.160 | 255.255.255.224 | /27 | 192.168.1.161 | 192.168.1.190 | 192.168.1.191 |
Step 5: Determine the subnet information for the next larger segments.
In this case, the two Branch2 LANs are the next largest subnets.
1. How many IP addresses are needed for each LAN? _12_
2. What is the smallest subnet that can be used to achieve this requirement? _/28_
3. What is the maximum number of IP addresses that can be assigned on the subnet of this size? _14_
Step 6: Assign subnet to BRANCH2 LANs.
Start with the IP address following the LAN subnets of Branch1.
1. Assign the next subnet to LAN1 of Branch2. Complete the following table with the appropriate information.
Branch2 LAN1 Subnet
| Network address | Subnet mask in decimal | Subnet mask in CIDR | First usable IP address | Last usable IP address | Broadcast address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.192 | 255.255.255.240 | /28 | 192.168.1.193 | 192.168.1.206 | 192.168.1.207 |
2. Assign the next available subnet to Branch2’s LAN2.
3. Complete the following table with the appropriate information.
Branch2 LAN2 Subnet
| Network address | Subnet mask in decimal | Subnet mask in CIDR | First usable IP address | Last usable IP address | Broadcast address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.208 | 255.255.255.240 | /28 | 192.168.1.209 | 192.168.1.222 | 192.168.1.223 |
Step 7: Determine the subnet information for the links between routers.
1. How many IP addresses are needed for each link? _2_
2. What is the smallest subnet that can be used to achieve this requirement?
_/30_
3. What is the maximum number of IP addresses that can be assigned on the subnet of this size? _2_
Step 8: Assign subnets to the links.
Start with the IP address following the Branch2 LAN subnets.
1. Assign the next available subnet for the link between the HQ and Branch1 routers.
2. Complete the following table with the appropriate information.
Link between HQ subnet and Branch1
| Network address | Subnet mask in decimal | Subnet mask in CIDR | First usable IP address | Last usable IP address | Broadcast address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.224 | 255.255.255.252 | /30 | 192.168.1.225 | 192.168.1.226 | 192.168.1.227 |
3. Assign the next available subnet for the link between the HQ and Branch2 routers.
4. Complete the following table with the appropriate information.
Link between HQ subnet and Branch2
| Network address | Subnet mask in decimal | Subnet mask in CIDR | First usable IP address | Last usable IP address | Broadcast address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.228 | 255.255.255.252 | /30 | 192.168.1.229 | 192.168.1.230 | 192.168.1.231 |
5. Assign the next available subnet for the link between the Branch1 and Branch2 routers.
6. Complete the following table with the appropriate information.
Link between Branch1 and Branch2 subnet
| Network address | Subnet mask in decimal | Subnet mask in CIDR | First usable IP address | Last usable IP address | Broadcast address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 192.168.1.232 | 255.255.255.252 | /30 | 192.168.1.233 | 192.168.1.234 | 192.168.1.235 |
Task 3: Assign IP addresses to network devices.
Assign the corresponding addresses for the device interfaces. Document the addresses to be used in the address table provided below the Topology Diagram.
Step 1: Assign addresses to the HQ router.
1. Assign the first valid host address on the HQ LAN 1 subnet to the LAN interface Fa0/0.
2. Assign the first valid host address on the HQ LAN 2 subnet to the LAN interface Fa0/1.
3. Assign the first valid host address on the link between HQ and subnet Branch1 to interface S0/0/0.
4. Assign the first valid host address on the link between HQ and the Branch2 subnet to interface S0/0/1.
Step 2: Assign addresses to the Branch1 router.
1. Assign the first valid host address on the LAN1 subnet of BRANCH1 to the LAN interface Fa0/0.
2. Assign the first valid host address on the LAN2 subnet of BRANCH1 to the LAN interface Fa0/1.
3. Assign the last valid host address on the link between Branch1 and the HQ subnet to interface S0/0/0.
4. Assign the first valid host address on the link between Branch1 and the Branch2 subnet to interface S0/0/1.
Step 3: Assign addresses to the Branch2 router.
1. Assign the first valid host address on the LAN1 subnet of Branch2 to the LAN interface Fa0/0.
Assign the first valid host address on the LAN 2 subnet of Branch2 to the LAN interface Fa0/1.
2. Assign the last valid host address on the link between HQ and Branch2 subnet to interface S0/0/1.
3. Assign the last valid host address on the link between Branch1 and the Branch2 subnet to interface S0/0/0.
