1. Refer to the exhibit. Which two commands must be configured to allow communication between the 192.168.1.0/24 and 10.0.0.0/8 networks? (Choose two.)
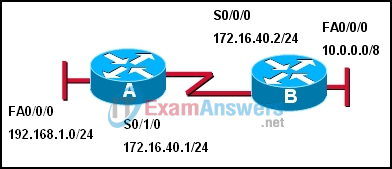
- A(config)# ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 172.16.40.2
- A(config)# ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 s 0/0/0
- A(config)# ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 10.0.0.1
- B(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.40.1
- B(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.40.2
- B# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
2. Which statement is true concerning configuring static routes using next hop addresses?
- Routers cannot use more then one static route with a next hop address.
- When the router identifies that a packet is destined for a route associated with a next hop address in the routing table, the router requires no further information and can immediately forward the packet.
- Routers configured with a static route using a next hop address must either have the exit interface listed in the route or have another route with the network of the next hop and an associated exit interface.
- Routes associated with next hop addresses are more efficient than routes going to exit interfaces.
3. Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator must remove the route to the 10.0.0.0 network. What command will accomplish this task?
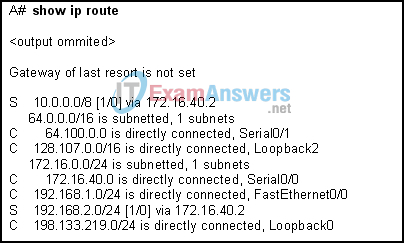
- no ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 172.16.40.2
- no router rip
- no ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 172.16.40.2
- no network 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.0
4. Refer to the exhibit. What command was used on Router1 to produce the output shown in the graphic?
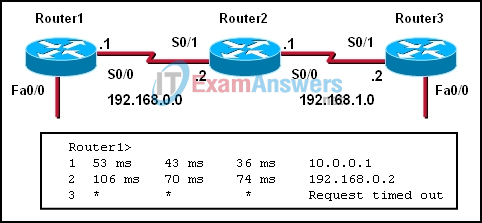
- traceroute
- extended ping
- show ip route
- show cdp neighbor detail
5. Observe the graphic. Which command correctly configures a static default route on R1?
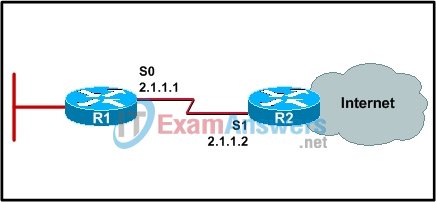
- R1(config-if)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0
- R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s1
- R1(config-if)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 2.1.1.2
- R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 2.1.1.2
- R1(config-router)#default-information originate
6. Which three are characteristics of a static route? (Choose three.)
- reduces the memory and processing burdens on a router
- ensures that there is always a path available
- used for networks with multiple routes to a destination network
- used for routers that connect to stub networks
- used for networks with a single route to a destination network
- reduces configuration time
7. Which of the following is a function of the IOS command show cdp neighbors?
- It displays the port type and platform of neighboring Cisco routers.
- It displays the device capability code of all non-Cisco routers.
- It displays platform information for all devices in the network.
- It displays the protocol encapsulations used by neighboring routers.
8. Refer to the exhibit. Which type of connector is shown in the exhibit?

- the DB-60 DTE end of the serial cable for 1600 and 2500 series routers
- the DTE end of a smart serial cable used with newer routers
- the EIA/TIA-530 DCE end of a serial cable that plugs into the CSU/DSU
- the V.35 DCE end of a serial cable that plugs into the CSU/DSU
- the EIA/TIA-232 DCE end of a serial cable that plugs into the CSU/DSU
- the EIA/TIA-449 DCE end of a serial cable that plugs into the CSU/DSU
9. Which statement is true concerning directly connected routes?
- They appear in the routing table as soon as cables are connected to the router.
- They appear in the routing table when the routing protocol is configured on the router.
- They appear in the routing table when the no shutdown command is entered in the router interface configuration mode.
- They appear in the routing table when an IP address is configured on an interface, and the show interface command shows the interface is up, line protocol is up.
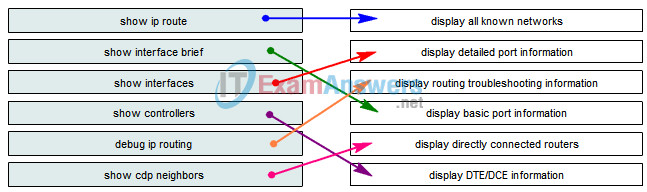
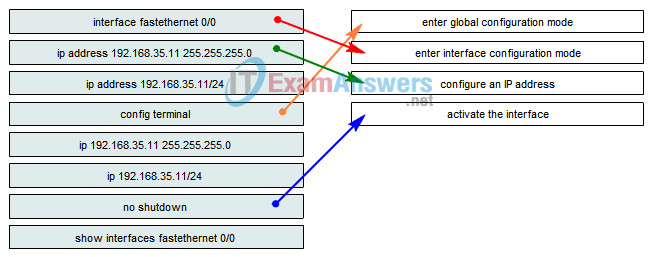
10. Drag the commands on the left to the associated configuration task on the right.
11. Drag the commands on the left to the description of their output on the right.