5.5.2 Packet Tracer – Propagating the Default Route in RIP Answers
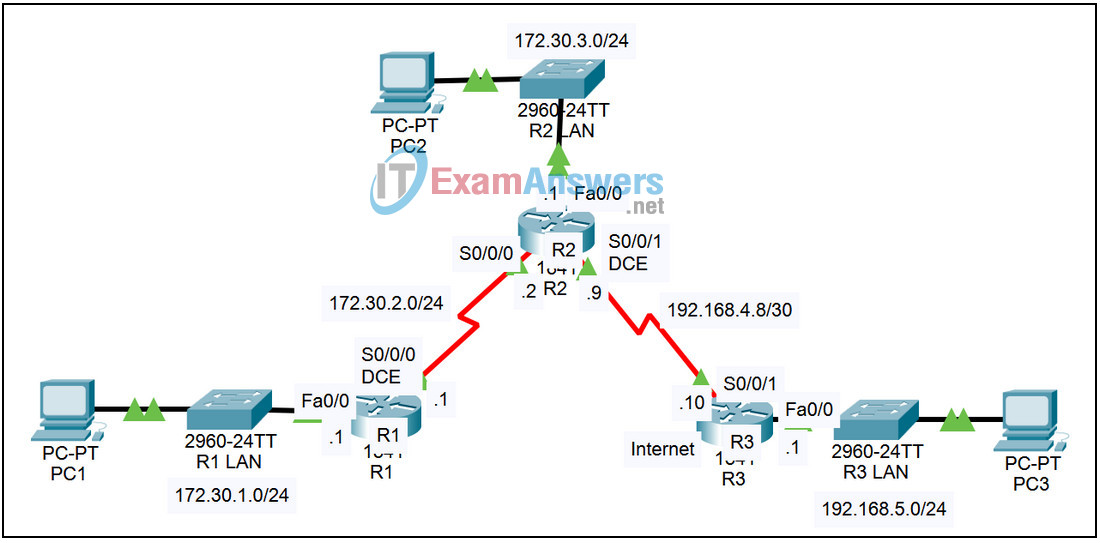
Topology
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Fa0/0 | 172.30.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 172.30.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| R2 | Fa0/0 | 172.30.3.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 172.30.2.2 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.4.9 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| R3 | Fa0/0 | 192.168.5.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.4.10 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| PC1 | NIC | 172.30.1.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.30.1.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 172.30.3.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.30.3.1 |
| PC3 | NIC | 192.168.5.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.5.1 |
Introduction:
In today’s networks, customers rarely, if ever, exchange routing updates with their ISP. Customer routers that connect to an ISP do not need a listing for every route on the Internet. Instead, these routers have a default route that sends all traffic to the ISP router when the customer router does not have a route to a destination. The ISP configures a static route pointing to the customer router for addresses inside the customer’s network. In this activity R3 will represent the router for the ISP, R2 will represent the border router that connects to the ISP, and R1 will represent an internal router within the organization.
Learning Objectives:
- Reconfigure R2 and R3 for default and static routing.
- On R2, remove the network to R3 from RIP and configure a default route.
- On R3, remove RIP and configure a static route.
- Reset the network and view the results.
- Propagate the default route in RIP.
- Configure R2 to propagate the default route in RIP.
- Examine RIP updates.
- Examine the IP routing table on R1.
- Check connectivity.
Task 1: Reconfigure routers R2 and R3 for default and static routing.
Step 1 – On R2, remove the network to R3 from RIP and configure a default route.
- Access Router R2 and enter privileged exec mode. Enter the global configuration mode. Enter the router configuration mode by issuing the command router rip.
- Issue the command no network 192.168.4.0. Issue the command exit to return to global configuration mode.
- Issue the command ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/1.
- Exit the configuration mode by using Ctrl+z. Save the configuration by issuing the command copy run start.
Step 2 – On R3, remove RIP and configure a static route.
- Access Router R3 and enter privileged exec mode. Enter the global configuration mode.
- Issue the command no router rip.
- Issue the command ip route 172.30.0.0 255.255.252.0 s0/0/1.
- Exit the configuration mode by using Ctrl+z. Save the configuration by issuing the command copy run start.
Step 3 – Reset the network and view the results.
- Click the Power Cycle Devices link below the lower left corner of the Logical Workspace to reset the network and update the routing tables.
- On each of the three routers, examine the IP routing table by issuing the command show ip route. On Router R1 there is no way to reach networks outside of 172.30.0.0/16.
Task 2: Propagate the default route in RIP.
Step 1 – Configure R2 to propagate the default route in RIP.
- Access Router R2 and enter privileged exec mode. Enter the global configuration mode. Enter the router configuration mode by issuing the command router rip.
- Issue the command default-information originate.
- Exit configuration mode by hitting Ctrl+z. Save the configuration by issuing the command copy run start.
Step 2 – Examine RIP updates.
On Router R2, examine RIP updates by issuing the command debug ip rip. Allow the command to run for several minutes and observe the updates that are sent and received. Issue the command undebug all.
Step 3 – Examine the IP routing table on R1.
On Router R1, examine the IP routing table by issuing the command show ip route. On Router R1 a default route has been learned from RIP updates.
Step 4 – Check connectivity.
Verify full connectivity by pinging from each PC to the other two PCs. All pings should succeed.
