1. Which four statements are true regarding distance vector routing protocols? (Choose four.)
- Hop counts can be used for path selection.
- They scale well.
- Routing updates are broadcast at intervals.
- EIGRP can do unequal-cost load balancing.
- RIPv1 multicasts its routing updates.
- RIP sends its entire routing table to directly connected neighbors.
2. Which conditions cause distant vector routing protocols to send routing table updates? (Choose three.)
- when the hold down timer expires
- when a change occurs in the network topology
- when the update timer value expires
- when a triggered update is received from another router
- when a packet is received that is destined for an unknown network
- when there have been no routing table changes for 30 minutes
3. What are two characteristics of EIGRP updates? (Choose two.)
- include all EIGRP routes
- include the full routing table
- independent of architecture
- only triggered for route topology changes
- broadcast to affected neighbors
- bounded to affected next hop routers
4. What feature was added to RIP to help with synchronization errors?
- Holddown timer
- RIP_JITTER
- RIP_DELAY
- Jitter Control
5. Which two of the following are timers used for RIP?
- Invalid
- Refresh
- Flush
- Deadlink
- Hello
6. Which statement is true concerning the advantages of a distance vector protocol?
- periodic updates speed up convergence
- convergence times make routing loops impossible
- ease of implementation makes configuration simple
- they work well in complex networks
- their convergence times are faster than link state routing protocols
7. Which mechanism can be used to avoid a count to infinity loop?
- split horizon
- route poisoning
- holddown timers
- triggered updates
- split horizon with poison reverse
8. Refer to the exhibit. The network shown is running the RIP routing protocol. What mechanism will keep Router4 from sending updates about the 10.0.0.0 network back to Router5?
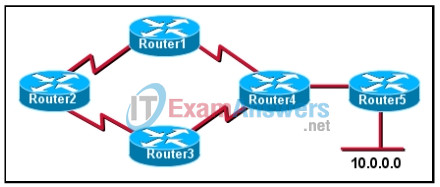
- split horizon
- poison reverse
- route poisoning
- holddown timers
- maximum hop count
9. What allows distance vector protocols to avoid routing loops by advertising a metric of infinity?
- split horizon
- route poisoning
- holddown timers
- maximum hop count
- time to live (TTL) field of IP header
10. Which field in the IP header ensures that packets will not loop endlessly on a network?
- CRC
- TOS
- TTL
- Checksome
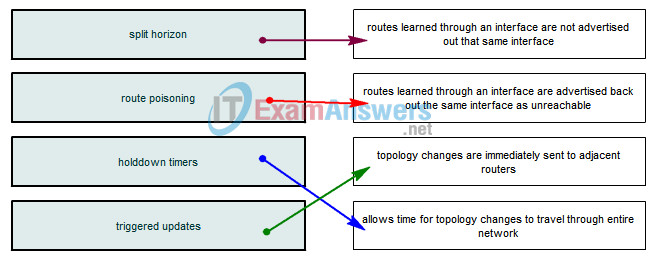
11. Drag the loop preventing mechanisms in the left column to the corresponding function in the right column.