Lab 10.6.1 – Creating a Small Lab Topology (Answers)
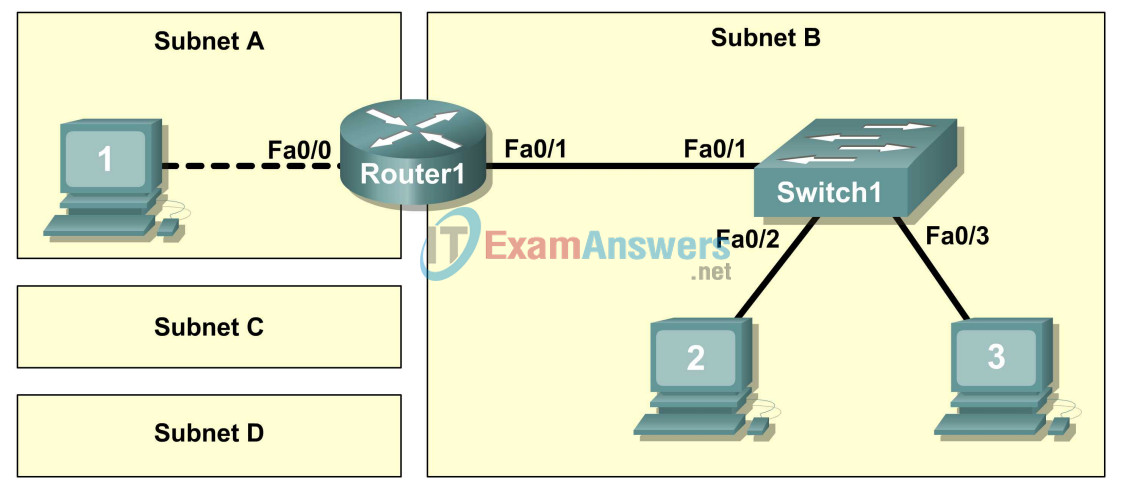
Topology Diagram
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to:
- Design the logical network.
- Configure the physical lab topology.
- Configure the logical LAN topology.
- Verify LAN connectivity.
Background
Table 1. Equipment and Hardware for Lab
| Hardware | Qty | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco Router | 1 | Part of CCNA Lab bundle |
| Cisco Switch | 1 | Part of CCNA Lab bundle |
| *Computer (host) | 3 | Lab computer |
| Cat-5 or better straight-through UTP cables | 3 | Connects Router1 and computers Host1 and Host2 to Switch1 |
| Cat-5 crossover UTP cable | 1 | Connects computer Host1 to Router1 |
Gather the necessary equipment and cables. To configure the lab, refer to the equipment and hardware listed in Table 1.
Scenario
In this lab you will create a small network that requires connecting network devices and configuring host computers for basic network connectivity. SubnetA and SubnetB are subnets that are currently needed. SubnetC and SubnetD are anticipated subnets, not yet connected to the network. The 0th subnet will be used.
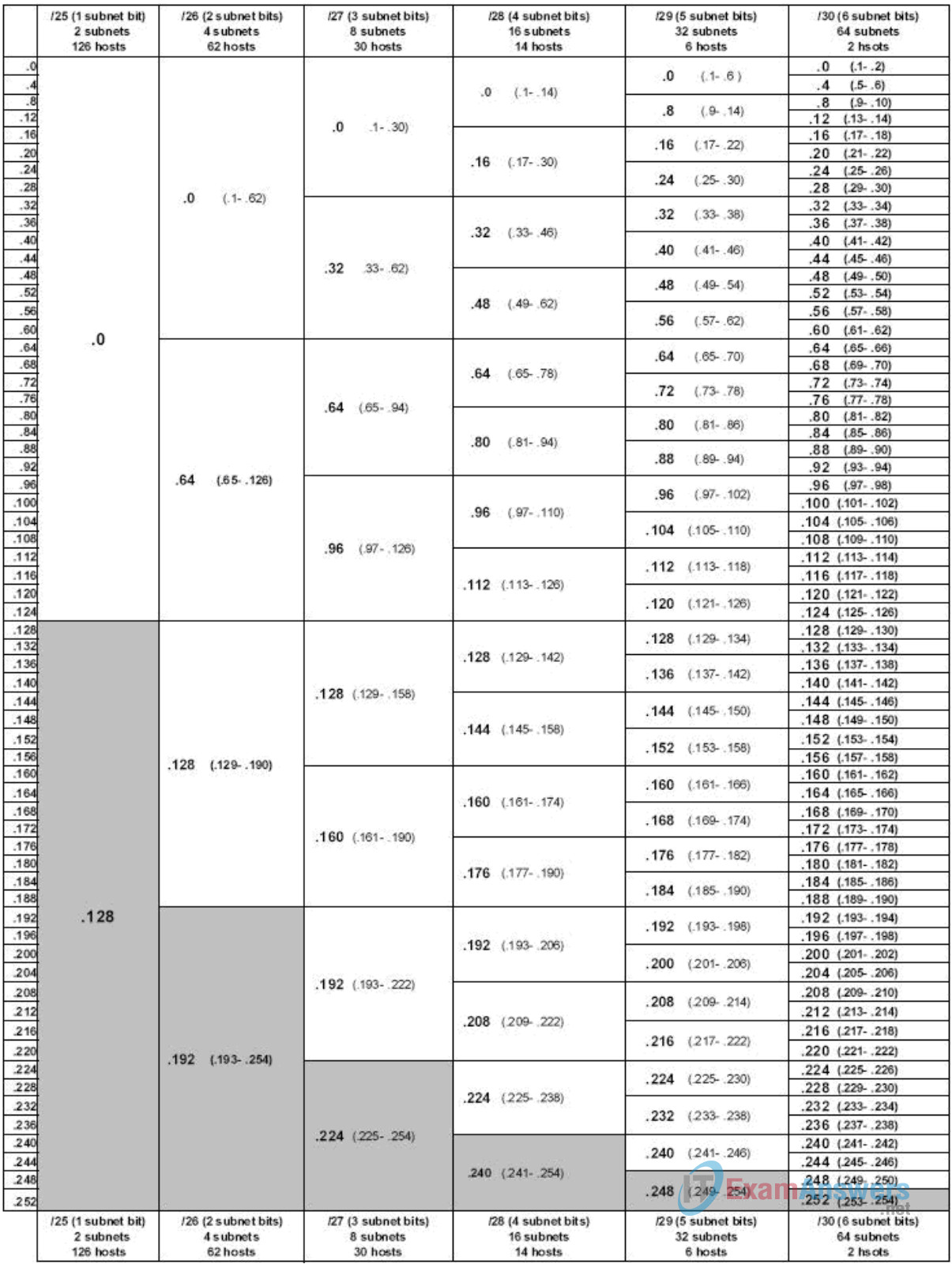
Note: Appendix 1 contains a subnet chart for the last IP address octet.
Note to Instructor: In Chapter 11 labs, students will learn how to configure a router. For this lab, the router should be configured for students. Appendix 2 contains a basic configuration for Router1. If you do not have a router that has two FastEthernet interfaces, consider configuring a loopback interface as an alternative to the FastEthernet 0/1. Another alternative would be to use two routers connected through a serial connection and use the FastEthernet interfaces from each router.
Task 1: Design the Logical Network.
Given an IP address and mask of 172.20.0.0 / 24 (address / mask), design an IP addressing scheme that satisfies the following requirements:
| Subnet | Number of Hosts |
|---|---|
| SubnetA | 2 |
| SubnetB | 6 |
| SubnetC | 47 |
| SubnetD | 125 |
Host computers from each subnet will use the first available IP address in the address block. Router interfaces will use the last available IP address in the address block.
Step 1: Design SubnetD address block.
Begin the logical network design by satisfying the requirement of SubnetD, which requires the largest block of IP addresses. Refer to the subnet chart, and pick the first address block that will support SubnetD.
Fill in the following table with IP address information for SubnetD:
| Network Address | Mask | First Host Address | Last Host Address | Broadcast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 172.20.0.0 | 255.255.255.128 | 172.20.0.1 | 172.20.0.126 | 172.20.0.127 |
What is the bit mask?
11111111.1111111.11111111.10000000
Step 2: Design SubnetC address block.
Satisfy the requirement of SubnetC, the next largest IP address block. Refer to the subnet chart, and pick the next available address block that will support SubnetC.
Fill in the following table with IP address information for SubnetC:
| Network Address | Mask | First Host Address | Last Host Address | Broadcast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 172.20.0.128 | 255.255.255.192 | 172.20.0.129 | 172.20.0.190 | 172.20.0.191 |
What is the bit mask?
11111111.1111111.11111111.11000000
Step 3: Design SubnetB address block.
Satisfy the requirement of SubnetB, the next largest IP address block. Refer to the subnet chart, and pick the next available address block that will support SubnetB.
Fill in the following table with IP address information for SubnetB:
| Network Address | Mask | First Host Address | Last Host Address | Broadcast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 172.20.0.192 | 255.255.255.248 | 172.20.0.193 | 172.20.0.198 | 172.20.0.207 |
What is the bit mask?
11111111.1111111.11111111.11111000
Step 4: Design SubnetA address block.
Satisfy the requirement of SubnetA. Refer to the subnet chart, and pick the next available address block that will support SubnetA.
Fill in the following table with IP address information for SubnetA:
| Network Address | Mask | First Host Address | Last Host Address | Broadcast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 172.20.0.200 | 255.255.255.252 | 172.20.0.201 | 172.20.0.202 | 172.20.0.203 |
What is the bit mask?
11111111.1111111.11111111.11111100
Task 2: Configure the Physical Lab Topology.
Step 1: Physically connect devices.
Figure 1. Cabling the Network

Cable the network devices as shown in Figure 1.
What cable type is needed to connect Host1 to Router1, and why?
Both devices have similar network interfaces, and like devices require a crossover cable.
What cable type is needed to connect Host1, Host2, and Router1 to Switch1, and why?
The switch ports are dissimilar to the router and computer network interfaces. Therefore, straight-through cables are required.
If not already enabled, turn power on to all devices.
Step 2: Visually inspect network connections.
After cabling the network devices, take a moment to verify the connections. Attention to detail now will minimize the time required to troubleshoot network connectivity issues later. Ensure that all switch connections show green. Any switch connection that does not transition from amber to green should be investigated. Is the power applied to the connected device? Is the correct cable used? Is the correct cable good?
What type of cable connects Router1 interface Fa0/0 to Host1? Crossover cable
What type of cable connects Router1 interface Fa0/1 to Switch1? Straight-through cable
What type of cable connects Host2 to Switch1? Straight-through cable
What type of cable connects Host3 to Switch1? Straight-through cable
Is all equipment turned on? yes
Task 3: Configure the Logical Topology.
Step 1: Document logical network settings.
The host computer Gateway IP address is used to send IP packets to other networks. Therefore, the Gateway address is the IP address assigned to the router interface for that subnet.
From the IP address information recorded in Task 1, write down the IP address information for each computer:
| Host1 | |
|---|---|
| IP Address | 172.20.0.201 |
| IP Mask | 255.255.255.252 |
| Gateway Address | 172.20.0.202 |
| Host2 | |
|---|---|
| IP Address | 172.20.0.193 |
| IP Mask | 255.255.255.248 |
| Gateway Address | 172.20.0.198 |
| Host3 | |
|---|---|
| IP Address | 172.20.0.194 |
| IP Mask | 255.255.255.248 |
| Gateway Address | 172.20.0.198 |
Step 2: Configure Host1 computer.
On Host1, click Start > Control Panel > Network Connections. Right-click the Local Area Connection device icon and choose Properties.
On the General tab, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click the Properties button.
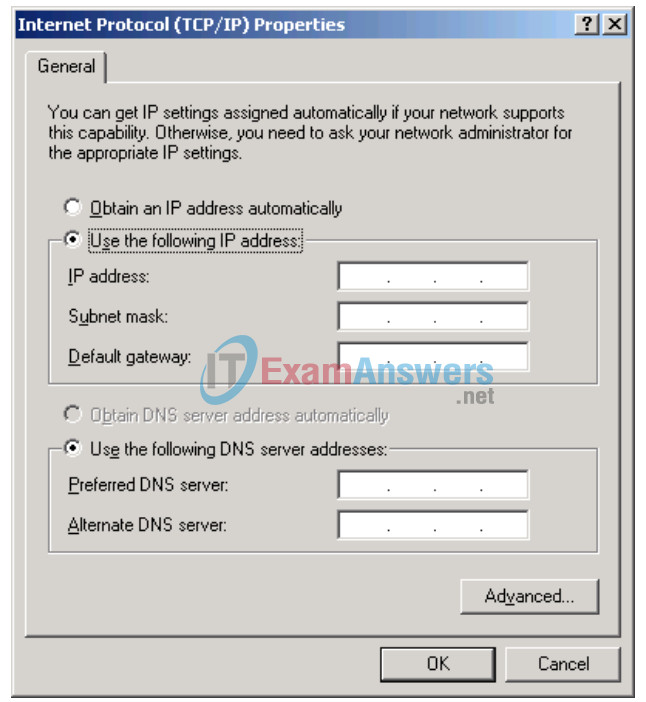
Figure 2. Host1 IP Address and Gateway Settings
Refer to Figure 2 for Host1 IP address and gateway settings. Manually enter the following information, recorded in Step 1, above:
IP address: Host1 IP address Subnet mask: Host1 subnet mask Default gateway: Gateway IP address
When finished, close the Internet Protocols (TCP/IP) Properties window by clicking OK. Close the Local Area Connection window. Depending on the Windows operating system, the computer may require a reboot for changes to be effective.
Step 3: Configure Host2 and Host3 computers.
Repeat Step 2 for computers Host2 and Host3, using the IP address information for those computers.
Task 4: Verify Network Connectivity.
Verify with your instructor that Router1 has been configured. Otherwise, connectivity will be broken between LANs. Switch1 should have a default configuration.
Network connectivity can be verified with the Windows ping command. Open a windows terminal by clicking Start > Run. Type cmd, and press Enter.
Use the following table to methodically verify and record connectivity with each network device. Take corrective action to establish connectivity if a test fails:
| From | To | IP Address | Ping Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Host1 | Gateway (Router1, Fa0/0) | 172.20.0.202 | Should be successful |
| Host1 | Router1, Fa0/1 | 172.20.0.198 | Should be successful |
| Host1 | Host2 | 172.20.0.193 | Should be successful |
| Host1 | Host3 | 172.20.0.194 | Should be successful |
| Host2 | Host3 | 172.20.0.194 | Should be successful |
| Host2 | Gateway (Router1, Fa0/1) | 172.20.0.198 | Should be successful |
| Host2 | Router1, Fa0/0 | 172.20.0.202 | Should be successful |
| Host2 | Host1 | 172.20.0.201 | Should be successful |
| Host3 | Host2 | 172.20.0.193 | Should be successful |
| Host3 | Gateway (Router1, Fa0/1) | 172.20.0.198 | Should be successful |
| Host3 | Router1, Fa0/0 | 172.20.0.202 | Should be successful |
| Host3 | Host1 | 172.20.0.201 | Should be successful |
Note any break in connectivity. When troubleshooting connectivity issues, the topology diagram can be extremely helpful.
In the above scenario, how can a malfunctioning Gateway be detected?
If Host2 and Host3 can successfully ping each other but not Host1, it may be a Gateway issue.
Task 5: Reflection
Review any physical or logical configuration problems encountered during this lab. Be sure that you have a thorough understanding of the procedures used to verify network connectivity.
This is a particularly important lab. In addition to practicing IP subnetting, you configured host computers with network addresses and tested them for connectivity.
It is best to practice host computer configuration and verification several times. This will reinforce the skills you learned in this lab and make you a better network technician.
Task 6: Challenge
Ask your instructor or another student to introduce one or two problems in your network when you aren’t looking or are out of the lab room. Problems can be either physical (wrong UTP cable) or logical (wrong IP address or gateway). To fix the problems:
1. Perform a good visual inspection. Look for green link lights on Switch1.
2. Use the table provided in Task 3 to identify failed connectivity. List the problems:
3. Write down your proposed solution(s):
4. Test your solution. If the solution fixed the problem, document the solution. If the solution did not fix the problem, continue troubleshooting.
Task 7: Clean Up.
Unless directed otherwise by the instructor, restore host computer network connectivity, and then turn off power to the host computers.
Carefully remove cables and return them neatly to their storage. Reconnect cables that were disconnected for this lab.
Remove anything that was brought into the lab, and leave the room ready for the next class.
Appendix 1
Appendix 2
Router1 configuration
! service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption ! no ip domain-lookup ! hostname Router1 ! enable secret cisco ! ! interface FastEthernet0/0 description connection to Host1 ip address 172.20.0.202 255.255.255.252 no shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/1 description connection LAN ip address 172.20.0.198 255.255.255.248 no shutdown ! ip classless ip http server ! banner motd % ******************************************************************* This is Eagle 1 lab router Router1. Authorized access only. ******************************************************************* % ! line con 0 password cisco ! line con 0 password cisco login line aux 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login ! end
