Module Group 3: Modules 9 – 12 Group Exam Answers
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Modules 9 – 12: Data Communications and Network Services Group Exam Answers
1. A DHCP server is used to assign IP addresses dynamically to the hosts on a network. The address pool is configured with 172.30.8.0/24. There are 7 printers on this network that need to use reserved static IP addresses from the pool. How many IP addresses in the pool are left to be assigned to other hosts?
- 254
- 249
- 251
- 247
2. An employee is having connectivity issues. Why might a network technician try to ping the default gateway from the employee laptop?
- to determine if the laptop address is included in the DNS server
- to verify that an IP address was provided by the DHCP server
- to verify connectivity with the device that provides access to remote networks
- to verify that the SVI interface on the switch is configured correctly
3. How many bits make up the single IPv6 hextet :10CD:?
- 32
- 8
- 4
- 16
4. Which three pieces of information are identified by a URL? (Choose three.)
- the protocol that is being used
- the version of the browser
- the location of the resource
- the domain name that is being accessed
- the IP address of the gateway
- the MAC address of the web server
5. Which type of applications are best suited to use UDP as the transport layer protocol?
- applications that require flow control
- applications that require stateful sessions
- applications that require minimal transmission delay
- applications that require data to be reassembled in a specific order
6. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question. What is the IP address of this server?
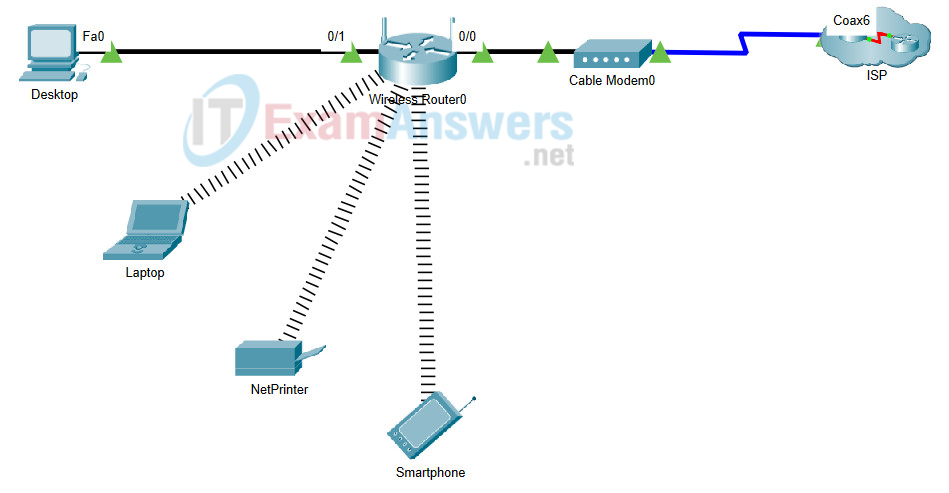
- 209.165.201.4
- 192.168.10.1
- 209.165.201.3
- 192.168.10.100
7. What type of server would use IMAP?
- DHCP
- FTP
- Telnet
- DNS
8. Which three types of nodes should be assigned static IP addresses on a network? (Choose three.)
- mobile laptops
- tablets
- desktop PCs
- gateways
- servers
- printers
9. Why is DHCP for IPv4 preferred for use on large networks?
- Large networks send more requests for domain to IP address resolution than do smaller networks.
- DHCP uses a reliable transport layer protocol.
- It prevents sharing of files that are copyrighted.
- It is a more efficient way to manage IPv4 addresses than static address assignment is.
- Hosts on large networks require more IPv4 addressing configuration settings than do hosts on small networks.
10. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 is configured to obtain a dynamic IP address from the DHCP server. PC1 has been shut down for two weeks. When PC1 boots and tries to request an available IP address, which destination IP address will PC1 place in the IP header?
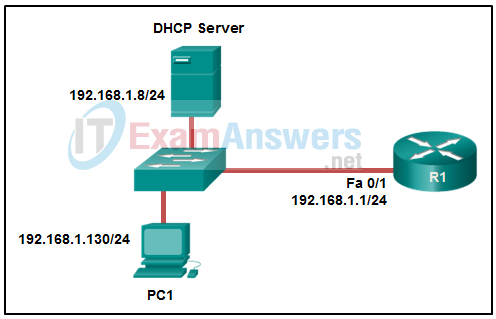
- 255.255.255.255
- 192.168.1.1
- 192.168.1.8
- 192.168.1.255
11. Which message does an IPv4 host use to reply when it receives a DHCPOFFER message from a DHCP server?
- DHCPACK
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPDISCOVER
12. A host PC is attempting to lease an address through DHCP. What message is sent by the server to let the client know it is able to use the provided IP information?
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK
13. How is a DHCPDISCOVER transmitted on a network to reach a DHCP server?
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with the broadcast IP address as the destination address.
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with the IP address of the default gateway as the destination address.
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with a multicast IP address that all DHCP servers listen to as the destination address.
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with the IP address of the DHCP server as the destination address.
14. What is the result if the default gateway address is misconfigured on a PC?
- The PC can communicate with devices in remote networks but not with those in the same network.
- The PC can communicate with devices in the same network but not with those in remote networks.
- The PC cannot communicate with any devices.
- The PC can communicate with devices both in remote networks and in the same network.
15. Which statement accurately describes dynamic NAT?
- It provides a mapping of internal host names to IP addresses.
- It provides an automated mapping of inside local to inside global IP addresses.
- It dynamically provides IP addressing to internal hosts.
- It always maps a private IP address to a public IP address.
16. What purpose does NAT64 serve in IPv6?
- It converts regular IPv6 addresses into 64-bit addresses that can be used on the Internet.
- It converts the 48-bit MAC address into a 64-bit host address that can be used for automatic host addressing.
- It enables companies to use IPv6 unique local addresses in the network.
- It translates private IPv6 addresses into public IPv6 addresses.
- It converts IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.
17. Which type of IPv6 address is not routable and used only for communication on a single subnet?
- unique local address
- unspecified address
- loopback address
- global unicast address
- link-local address
18. What is the valid most compressed format possible of the IPv6 address 2001:0DB8:0000:AB00:0000:0000:0000:1234?
- 2001:DB8:0:AB:0:1234
- 2001:DB8:0:AB00::1234
- 2001:DB8:0:AB::1234
- 2001:DB8::AB00::1234
19. What is an advantage of UDP over TCP?
- UDP communication is more reliable.
- UDP communication requires less overhead.
- UDP acknowledges received data.
- UDP reorders segments that are received out of order.
20. What layer of the TCP/IP suite makes sure that all the data packets of a message arrive safely at the destination?
- transport
- application
- network access
- internet
21. How does a client computer determine what source port number to assign to a UDP header?
- The port number is random within the range of dynamic port numbers.
- The port number is based on a well-known port number that is open on the destination device.
- The port number is based on the application that created the data.
- The port number is based on a well-known port number that is assigned to the application on the sending device.
22. What is a socket?
- the combination of a source IP address and port number or a destination IP address and port number
- the combination of the source and destination IP address and source and destination Ethernet address
- the combination of the source and destination sequence and acknowledgment numbers
- the combination of the source and destination sequence numbers and port numbers
23. What is the purpose of using a source port number in a TCP communication?
- to assemble the segments that arrived out of order
- to inquire for a nonreceived segment
- to keep track of multiple conversations between devices
- to notify the remote device that the conversation is over
24. Which two protocols are used in the process of sending and receiving emails? (Choose two.)
- HTTP
- SSH
- FTP
- POP
- SMTP
25. What is a function of a DNS server?
- It maps IP addresses to physical addresses.
- It assigns logical address information to host computers.
- It determines the IP address that is associated with a specific host domain name.
- It translates private IP addresses to public IP addresses.
26. Match the term to a function.

- web server: hosts a web page
- web client: requests a web page
- HTML: used to create web pages
- HTTPS: secure protocol that uses port 443
- HTTP: protocol commonly used by a web browser
27. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question. What message is displayed on the webpage?
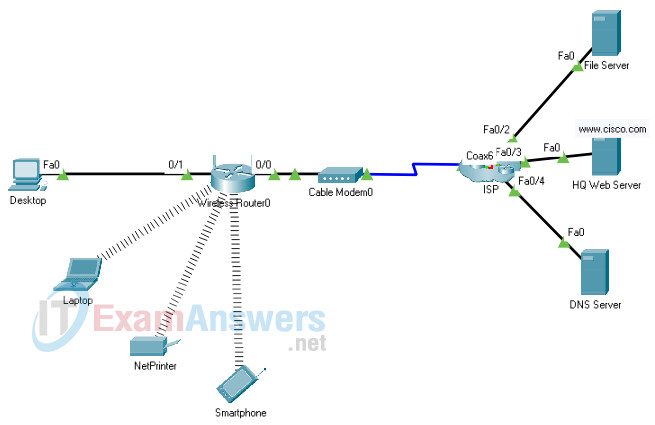
- A web server provides secure communication!
- A web server should run secure services!
- A secure web server is the way to go!
- A secure web server is running!
28. Which two applications provide virtual terminal access to remote servers? (Choose two.)
- DHCP
- SMTP
- SSH
- DNS
- Telnet

nice