15.6.1 Packet Tracer – Configure IPv4 and IPv6 Static and Default Routes (Instructor Version)
15.6.1 Packet Tracer – Configure IPv4 and IPv6 Static and Default Routes
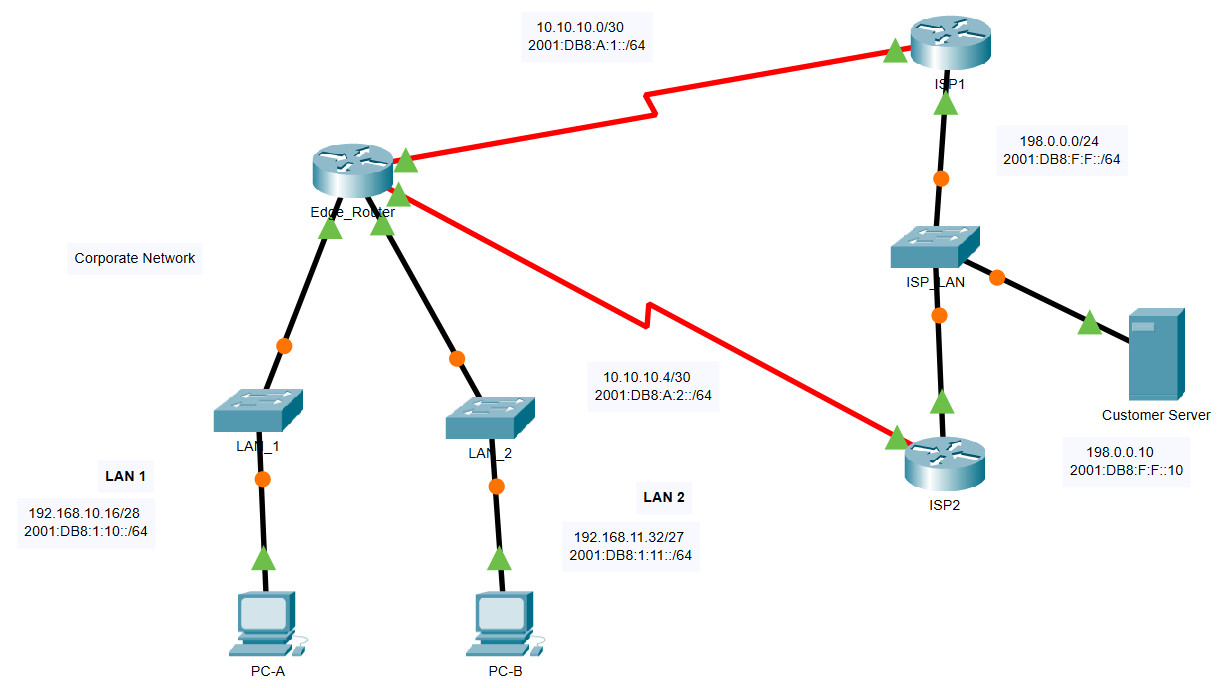
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address / Prefix |
|---|---|---|
| Edge_Router | S0/0/0 | 10.10.10.2/30 |
| 2001:db8:a:1::2/64 | ||
| S0/0/1 | 10.10.10.6/30 | |
| 2001:db8:a:2::2/64 | ||
| G0/0 | 192.168.10.17/28 | |
| 2001:db8:1:10::1/64 | ||
| G0/1 | 192.168.11.33/27 | |
| 2001:db8:1:11::1/64 | ||
| ISP1 | S0/0/0 | 10.10.10.1/30 |
| 2001:db8:a:1::1/64 | ||
| G0/0 | 198.0.0.1/24 | |
| 2001:db8:f:f::1/64 | ||
| ISP2 | S0/0/1 | 10.10.10.5/30 |
| 2001:db8:a:2::1/64 | ||
| G0/0 | 198.0.0.2/24 | |
| 2001:db8:f:f::2/64 | ||
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.10.19/28 |
| 2001:db8:1:10::19/64 | ||
| PC-B | NIC | 192.168.11.4/27 |
| 2001:db8:1:11::45 | ||
| Customer Server | NIC | 198.0.0.10 |
| 2001:db8:f:f::10 |
Objectives
In this Packet Tracer summary activity, you will configure static, default, and floating static routes for both the IPv4 and IPv6 protocols.
- Configure IPv4 Static and Floating Static Default Routes.
- Configure IPv6 static and floating static default routes.
- Configure IPv4 static and floating static routes to internal LANs.
- Configure IPv6 static and floating static routes to the internal LANS.
- Configure IPv4 host routes.
- Configure IPv6 host routes.
Background / Scenario
In this activity, you will configure IPv4 and IPv6 default static and floating static routes.
Note: The static routing approach that is used in this lab is used to assess your ability to configure different types of static routes only. This approach may not reflect networking best practices.
Instructions
Part 1: Configure IPv4 Static and Floating Static Default Routes
The PT network requires static routes to provide internet access to the internal LAN users through the ISPs.
In addition, the ISP routers require static routes to reach the internal LANs. In this part of the activity, you will configure an IPv4 static default route and a floating default route to add redundancy to the network.
Step 1: Configure an IPv4 static default route.
On Edge_Router, configure a directly connected IPv4 default static route. This primary default route should be through router ISP1.
Edge_Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0
Step 2: Configure an IPv4 floating static default route.
On Edge_Router, configure a directly connected IPv4 floating static default route. This default route should be through router ISP2. It should have an administrative distance of 5.
Edge_Router(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/1 5
Part 2: Configure IPv6 Static and Floating Static Default Routes
In this part of the activity, you will configure IPv6 static default and floating static default routes for IPv6.
Step 1: Configure an IPv6 static default route.
On Edge_Router, configure a next hop static default route. This primary default route should be through router ISP1.
Edge_Router(config)#ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:a:1::1
Step 2: Configure an IPv6 floating static default route.
On Edge_Router, configure a next hop IPv6 floating static default route. The route should be via router ISP2. Use an administrative distance of 5.
Edge_Router(config)#ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:a:2::1 5
Part 3: Configure IPv4 Static and Floating Static Routes to the Internal LANs
In this part of the lab you will configure static and floating static routers from the ISP routers to the internal LANs.
Step 1: Configure IPv4 static routes to the internal LANs.
a. On ISP1, configure a next hop IPv4 static route to the LAN 1 network through Edge_Router.
ISP1(config)#ip route 192.168.10.16 255.255.255.240 10.10.10.2
b. On ISP1, configure a next hop IPv4 static route to the LAN 2 network through Edge_Router.
ISP1(config)#ip route 192.168.11.32 255.255.255.224 10.10.10.2
Step 2: Configure IPv4 floating static routes to the internal LANs.
a. On ISP1, configure a directly connected floating static route to LAN 1 through the ISP2 router. Use an administrative distance of 5.
ISP1(config)#ip route 192.168.10.16 255.255.255.240 g0/0 5
b. On ISP1, configure a directly connected floating static route to LAN 2 through the ISP2 router. Use an administrative distance of 5.
ISP1(config)#ip route 192.168.11.32 255.255.255.224 g0/0 5
Part 4: Configure IPv6 Static and Floating Static Routes to the Internal LANs.
Step 1: Configure IPv6 static routes to the internal LANs.
c. On ISP1, configure a next hop IPv6 static route to the LAN 1 network through Edge_Router.
ISP1(config)#ipv6 route 2001:db8:1:10::/64 2001:db8:a:1::2
d. On ISP1, configure a next hop IPv6 static route to the LAN 2 network through Edge_Router.
ISP1(config)#ipv6 route 2001:db8:1:11::/64 2001:db8:a:1::2
Step 2: Configure IPv6 floating static routes to the internal LANs.
a. On ISP1, configure a next hop IPv6 floating static route to LAN 1 through the ISP2 router. Use an administrative distance of 5.
ISP1(config)#ipv6 route 2001:db8:1:10::/64 2001:db8:f:f::2 5
b. On ISP1, configure a next hop IPv6 floating static route to LAN 2 through the ISP2 router. Use an administrative distance of 5.
ISP1(config)#ipv6 route 2001:db8:1:11::/64 2001:db8:f:f::2 5
If your configuration has been completed correctly, you should be able to ping the Web Server from the hosts on LAN 1 and LAN 2. In addition, if the primary route link is down, connectivity between the LAN hosts and the Web Server should still exist.
Part 5: Configure Host Routes
Users on the corporate network frequently access a server that is owned by an important customer. In this part of the activity, you will configure static host routes to the server. One route will be a floating static route to support the redundant ISP connections.
Step 1: Configure IPv4 host routes.
a. On Edge Router, configure an IPv4 directly connected host route to the customer server.
Edge_Router(config)#ip route 198.0.0.10 255.255.255.255 serial0/0/0
b. On Edger Router, configure an IPv4 directly connected floating host route to the customer sever. Use an administrative distance of 5.
Edge_Router(config)#ip route 198.0.0.10 255.255.255.255 serial0/0/1 5
Step 2: Configure IPv6 host routes.
a. On Edge Router, configure an IPv6 next hop host route to the customer server through the ISP1 router.
Edge_Router(config)#ipv6 route 2001:db8:f:f::10/128 2001:db8:a:1::1
b. On Edger Router, configure an IPv6 directly connected floating host route to the customer sever through the ISP2 router. Use an administrative distance of 5.
Correct:
Edge_Router(config)#ipv6 route 2001:db8:f:f::10/128 s0/0/1 5
Not correct:
Edge_Router(config)#ipv6 route 2001:db8:f:f::10/128 2001:db8:a:2::1 5
Answer scripts
Router Edge_Router
enable config terminal ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/1 5 ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:a:1::1 ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:a:2::1 5 ip route 198.0.0.10 255.255.255.255 serial0/0/0 ip route 198.0.0.10 255.255.255.255 serial0/0/1 5 ipv6 route 2001:db8:f:f::10/128 2001:db8:a:1::1 ipv6 route 2001:db8:f:f::10/128 s0/0/1 5
Router ISP1
enable config terminal ip route 192.168.10.16 255.255.255.240 10.10.10.2 ip route 192.168.11.32 255.255.255.224 10.10.10.2 ip route 192.168.10.16 255.255.255.240 g0/0 5 ip route 192.168.11.32 255.255.255.224 g0/0 5 ipv6 route 2001:db8:1:10::/64 2001:db8:a:1::2 ipv6 route 2001:db8:1:11::/64 2001:db8:a:1::2 ipv6 route 2001:db8:1:10::/64 2001:db8:f:f::2 5 ipv6 route 2001:db8:1:11::/64 2001:db8:f:f::2 5

The last step for Edge Router should be:
ipv6 route 2001:db8:f:f::10/128 2001:db8:a:2::1 5
Last question the incorrect part is correct actually and packet tracer will tell you this
For Step 2 the answer is 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.10.10.4 5
The ip address for the exit interface of ISP2 is 10.10.10.4 (not 10.10.10.5)
The syntax for configuring a directly connected default route is 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 {ip address | exit interface} {administrative distance}
The next hop for directly connected static routes should be tthe exit-interface not the ip address. The latter is a recursive static route.
When creating a directly connected static route, it should have the exit-interface and not the ip address as ‘next-hop’
On the last section:
b. On Edger Router, configure an IPv6 directly connected floating host route to the customer sever through the ISP2 router. Use an administrative distance of 5.
Edge_Router(config)#ipv6 route 2001:db8:f:f::10/128 2001:db8:a:2::1 5
Here is my question:
Shouldn’t it be “ ipv6 route 2001:db8:f:f::10/128 s0/0/1 5”?
So far “direct connected” routes are using exit interface, and “next hop” routes are using the remote connected router IPs.
Why use IP of next hop instead of egress interface? Or Cisco is asking for “direct connected” route, but then is checking for “next hop” route?
no- the first one is correct according to the PT lab scoring.
Correct last command- ipv6 route 2001:db8:f:f::10/128 2001:db8:a:2::1 5
how do you configure a next hop IPv4 static route to the LAN 1 network through Edge_Router?