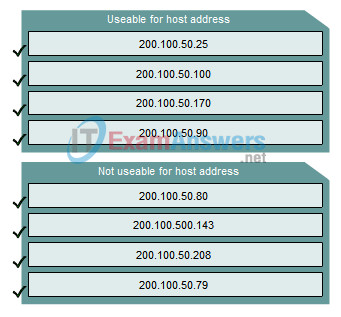
1. Determine the IP addresses that are useable for hosts on the subnetworks of the 200.100.50.0/28 network.
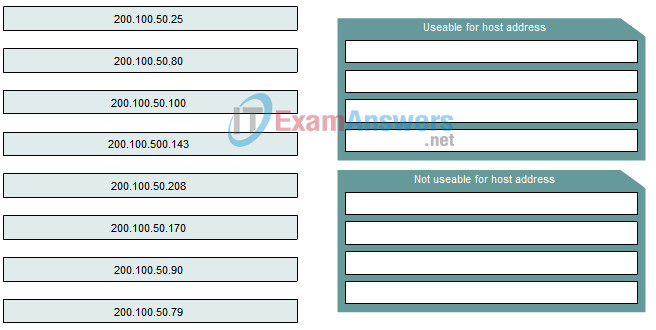
Answer
2. When is a straight-through cable used in a network?
- when connecting a router through the console port
- when connecting one switch to another switch
- when connecting a host to a switch
- when connecting a router to another router
3. Which function is a unique responsibility of the DCE devices shown in the exhibit?

- transmission of data
- reception of data
- clocking for the synchronous link
- noise cancellation in transmitted data
4. A router which terminates a serial WAN link is typically a DTE device. Under which circumstance would a router be configured as a DCE device?
- A router cannot be configured as a DCE device.
- When connecting a router directly to an analog device.
- When performing a back-to-back router scenario in a test environment.
- When the clock rate from the service provider cannot be matched by the router.
5. Which of the following are private IP addresses? (Choose three.)
- 10.1.1.1
- 172.32.5.2
- 192.167.10.10
- 172.16.4.4
- 192.168.5.5
- 224.6.6.6
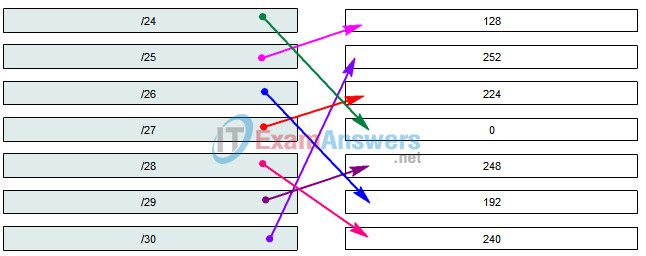
6. Match the “Slash format” number with the mask number to subnet the last octet.
7. Refer to the exhibit. What type of cable connects the two routers together without any intermediary device?

- console
- rollover
- crossover
- straight-through
8. Refer to the exhibit. Which option defines the default port configuration settings used to establish this direct serial connection between a computer and a Cisco networking device?
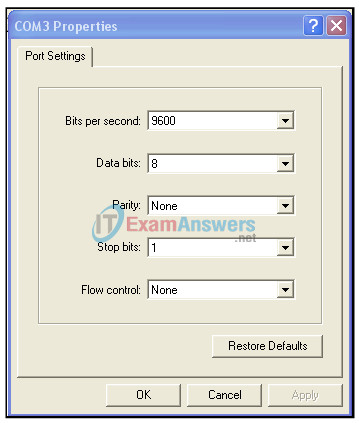
- 19,200 bps, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, no flow control
- 9600 bps, 8 data bits, even parity, 2 stop bits, hardware flow control
- 9600 bps, 16 data bits, odd parity, 1 stop bit, hardware flow control
- 19,200 bps, 8 data bits, even parity, 1 stop bit, hardware flow control
- 9600 bps, 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bit, no flow control
9. Which UTP cable lengths are specified by ANSI/TIA/EIA-568-B standards? (Choose three.)
- total end-to-end length of up to 100 meters
- up to 110 meters total end-to-end length
- horizontal cabling maximum of 90 meters
- up to 10 meters for interconnecting patch panels
- up to 5 meters for interconnecting patch panels
- up to 10 meters for connecting individual devices to wall jacks
10. What primary factor should be addressed before using wireless technology?
- FCC address assignment
- selecting an Auto-MDIX capable switch
- power supply redundancy
- identify and if possible minimize sources of RFI
