1. Which routing protocol is considered a link-state protocol?
- RIPv1
- RIPv2
- EIGRP
- IS-IS
- BGP
2. Which of the following mechanisms are used by link-state routing protocols to build and maintain routing tables? (Choose three.)
- service network advertisements
- hello packets
- link-state advertisements
- routing table broadcasts
- shortest path first algorithm
- Spanning Tree Protocol
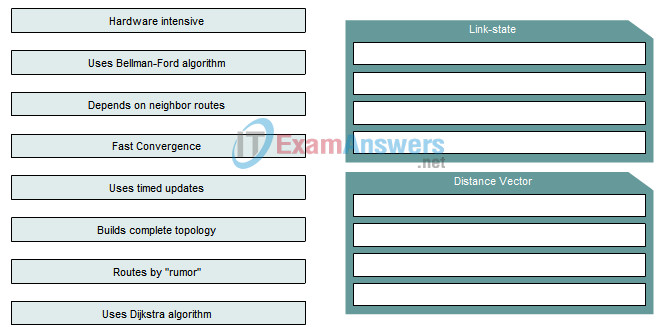
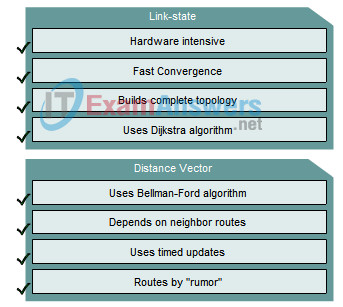
3. Drag the attributes from the left to the associated protocol on the right.
Answer
4. What is one advantage of link-state protocols over most distance-vector protocols?
- ability to route IPX
- continual route checking with periodic updates
- faster convergence
- lower hardware requirements
5. Why do link-state protocols converge faster than most distance vector protocols?
- Distance vector protocols compute their routing tables before sending any routing update, link-state protocols do not.
- Link-state protocols have lower computing requirements than distance vector protocols.
- Link-state protocols send updates out more often than distance vector protocols.
- Distance vector protocols receive more packets per update than link-state protocols.
6. Refer to the exhibit. If all routers are using a link-state routing protocol, which routers does Router A send hello packets to?
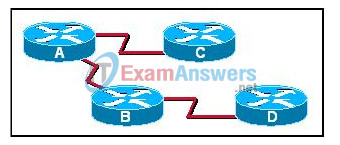
- B, C
- B, C, D
- only the DR
- only the BR and BDR
7. What information is contained in LSPs sent by link state routers to their neighbors?
- a copy of the routing table
- a copy of the topology database
- the state of directly connected links
- the most current version of the SPF tree
8. What is one disadvantage of link-state protocols over distance-vector protocols?
- slow convergence
- flat network topology
- periodic updates
- higher processing requirements
9. After two OSPF routers have exchanged Hello packets and formed an adjacency, what is the next thing to occur?
- they will take turns broadcasting their entire routing table to each other
- they will start sending Link-State Packets to each other
- they negotiate to determine who will be the root router
- they will adjust their hello timers so they don’t collide with each other
10. How does a router learn about a directly connected network?
- When the administrator configures a static route.
- When the administrator configures a dynamic routing protocol.
- When the administrator assigns an IP address and subnet mask to the interface.
- When a broadcast address is discovered on a specific interface.
