1.3.4 Packet Tracer – Dynamic Routing Answers
Topology
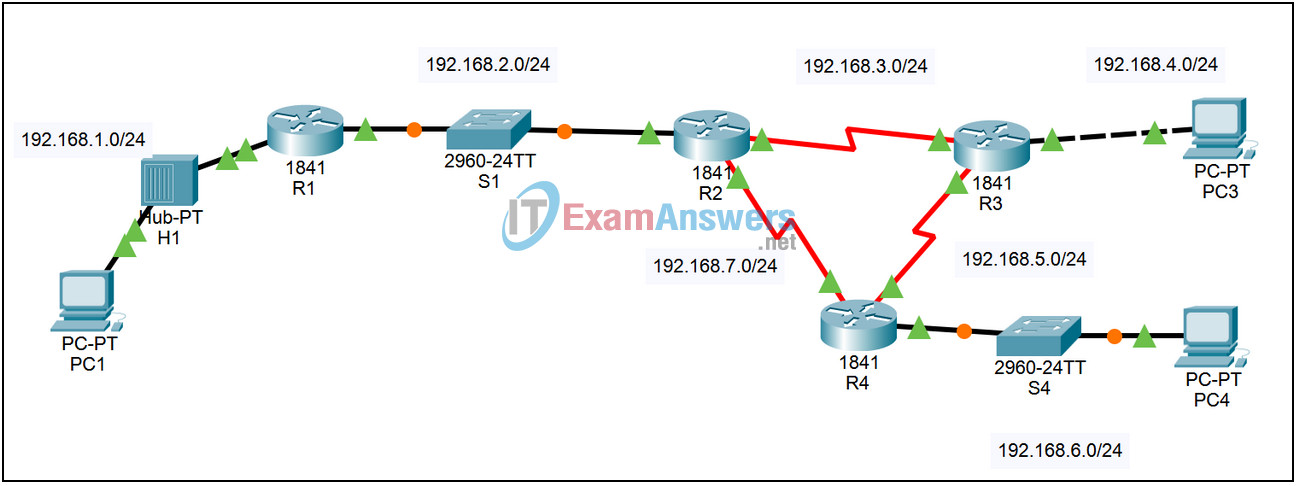
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Fa0/0 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| Fa0/1 | 192.168.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| R2 | Fa0/0 | 192.168.2.2 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.7.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.3.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| R3 | Fa0/0 | 192.168.4.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.5.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.3.2 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| R4 | Fa0/0 | 192.168.6.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.7.2 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.5.2 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| PC1 | NIC | 192.168.1.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| PC3 | NIC | 192.168.4.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.4.1 |
| PC4 | NIC | 192.168.6.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.6.1 |
Introduction
Routers can learn of remote networks statically or dynamically. This activity focuses on how remote networks are added to the routing table using static routes and a dynamic routing protocol. Static routes are configured by the network administrator and include:
- The network address.
- The subnet mask of the remote network.
- The IP address of the next-hop router or the exit interface of the local router.
Dynamic routing protocols allow routers to automatically learn about remote networks from other routers. The networks and the best path to each network are added to the routing table as they are learned via the routing protocol.
Learning Objectives:
- Describe the function of the routing table.
- Describe how a routing table can contain and use both dynamic and static routes.
Task 1: Enter RIP as the dynamic routing protocol on R2, R3, and R4.
Step 1 – Configure RIP on R2.
1. Click R2 in the workspace.
2. Select the CLI tab.
3. From the command line interface, CLI, type the following commands:
Password:cisco R2>enable Password: class R2# configure terminal R2(config)# router RIP R2(config-router)# network 192.168.2.0 R2(config-router)# network 192.168.3.0 R2(config-router)# network 192.168.7.0 R2(config-router)# end
Step 2 – Configure RIP on R3.
1. Click R3 in the workspace.
2. Select the CLI tab.
3. From the CLI type the following commands:
Password:cisco R3>enable Password: class R3# configure terminal R3(config)# router RIP R3(config-router)# network 192.168.3.0 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.4.0 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.5.0 R3(config-router)# end
Step 3 – Configure RIP on R4.
1. Click R4 in the workspace.
2. Select the CLI tab.
3. From the CLI type the following commands:
Password:cisco R4> enable Password: class R4# configure terminal R4(config)# router RIP R4(config-router)# network 192.168.5.0 R4(config-router)# network 192.168.6.0 R4(config-router)# network 192.168.7.0 R4(config-router)# end
Task 2: Verify the static and dynamic routes.
Step 1 – Verify the routing tables on each router.
1. Click R1 in the workspace.
2. Select the CLI tab.
3. From the CLI type the following commands:
Password:cisco R1>enable Password: class R1# show ip route
(Note: The routing table should show directly connected routes and static routes, but there are no dynamic routes to remote networks)
4. Repeat the previous steps on R2, R3, and R4.
(Note: The routing tables on the other routers should show directly connected routes and combinations of static and dynamically learned routes to remote networks.)
Step 2 – Examine the routing table on R1.
1. From the CLI type the following commands:
R1# show ip route
2. Are there any static routes in the routing table? If so, list the route(s) below:
_____________________________________________________
3. If there are no routes in the routing table, retrace your steps and troubleshoot the problem.
Step 3 – Ping from R3 to PC1.
1. Click R3 in the workspace.
2. Select the CLI tab.
3. From the CLI type the following commands:
R3#ping 192.168.1.10
4. Was the ping successful?
(Hint: If the ping is not successful, check the routing tables on all three routers to see if you can determine the problem.)
Task 3: Enter a static route on R2 to reach R1’s LAN.
Follow the steps below to enter a static route on R2 to reach R1’s LAN:
Step 1 – Configuring a static route on R2.
1. Click R2 in the workspace.
2. Select the CLI tab.
3. From the CLI type the following commands:
Password:cisco R2>enable Password: class R2# show ip route
(Note: The routing table shows directly connected routes, but there are no static routes to remote networks in the routing table.)
R2# configure terminal R2(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 FastEthernet 0/0 R2(config)# end
Step 2 – Examine the routing table on R2.
1. From the CLI type the following commands:
R2# show ip route
2. Are there any static routes in the routing table? If so, list the route(s) below:
_____________________________________________________
3. If there are no routes in the routing table, retrace your steps and troubleshoot the problem.
Step 3 – Ping from R3 to PC1.
1. Click R3 in the workspace.
2. Select the CLI tab.
3. From the CLI type the following commands:
R3# ping 192.168.1.10
4. Was the ping successful?
(Hint: This ping should be successful. If the ping is not successful, check the routing tables on all three routers to determine the problem.)
Step 4 – Check results in the activity window.
Your completion rate should be 100%. If the completion rate is not 100%, use the Check Results button and troubleshoot as necessary.
Task 4: View the RIP routing updates in simulation mode.
Follow the steps below to enter simulation mode in Packet Tracer:
Step 1 – Changing from Realtime to Simulation mode.
1. Located just outside of the workspace in the lower right-hand corner there is section titled Realtime.
2. Select the Simulation tab that is located just to the upper right and behind Realtime. You should now be in Simulation mode.
Step 2 – Filter the traffic so that only RIP packets will be viewed.
1. From the simulation mode, click on button entitled Edit Filters
2. Click the last box entitled Show All/None to clear all the boxes.
3. Click on the box entitled RIP, with this box selected and only RIP traffic will be displayed.
Step 3 – Start the simulation.
1. To start the flow of traffic in the simulation, click on the button entitled Auto Capture / Play. This will start the flow of RIP updates between the Routers.
Note that R1 is not sending any RIP updates and is also dropping any RIP updates received.
Why is R1 dropping the R1 packets without sending them?
_____________________________________________________
(Hint: By clicking on one of the packets in the simulation that is being dropped by R1, additional information will be displayed about the packet and how R1 is handling the packet.)
