1. A technician is attempting to explain broadband technology to a customer. Which descriptions should he use to educate the customer? (Choose two.)
- It includes dialup connections using POTS.
- It is incompatible with multiplexing.
- It uses a wide band of frequencies.
- It offers sustained speeds of 128 kbps or more.
- It requires line-of-sight connection with the service provider.
Explanation: The term broadband has several meanings, depending on the context. In this context, broadband refers to the capability to provide high-speed transmission of services (usually greater than 128 kbps), such as data, voice, and video, over the Internet and other networks using technologies such as DSL, cable, satellite, and broadband wireless. These technologies use a wide range of frequencies and multiplexing techniques.
2. When accommodating a teleworker, which type of connection should be used when mobile access during traveling is required and broadband options are available?
- Residential cable
- DSL
- Dialup
- Satellite
Explanation: With a maximum speed of 56 kbps (actual speed of 53 kbps), dialup connections are not considered a broadband technology like DSL, cable, satellite, and broadband wireless.
3. When comparing DOCSIS and Euro-DOCSIS, what is the primary difference between the two specifications?
- Flow-control mechanisms
- Maximum data rates
- Access methods
- Channel bandwidths
Explanation: Euro-DOCSIS is adapted for use in Europe. The main differences between DOCSIS and Euro-DOCSIS relate to channel bandwidths.
4. If asked to describe DSL technology, which statements would help the user develop a better understanding of the technology? (Choose three.)
- DSL is available in any location that has a telephone.
- ADSL typically has a higher download bandwidth than available upload bandwidth.
- In home installations, a splitter separates the ADSL and voice signals at the NID, allowing multiple ADSL outlets in the house.
- DSL speed can exceed the speed available with a typical T1 line.
- Transfer rates vary according to the length of the local loop.
- All varieties of DSL provide the same bandwidth, although they use different technologies to achieve upload and download.
Explanation: The different varieties of DSL provide different bandwidths, some with capabilities exceeding those of a T1 or E1 leased line. Within the variety of DSL, transfer rates are less as the distance from the central office decreases. ADSL is asymmetric DSL, which provides higher download bandwidth than upload bandwidth.
5. In a DSL installation, which devices are installed at the customer site? (Choose two.)
- CM
- DOCSIS
- DSLAM
- Microfilter
- DSL transceiver
Explanation: The customer site may include devices such as a microfilter and a DSL transceiver, which usually is a DSL modem.
6. Refer to the exhibit. On the basis of the network topology shown, which devices or software applications provide encapsulation and encryption for the VPN traffic?
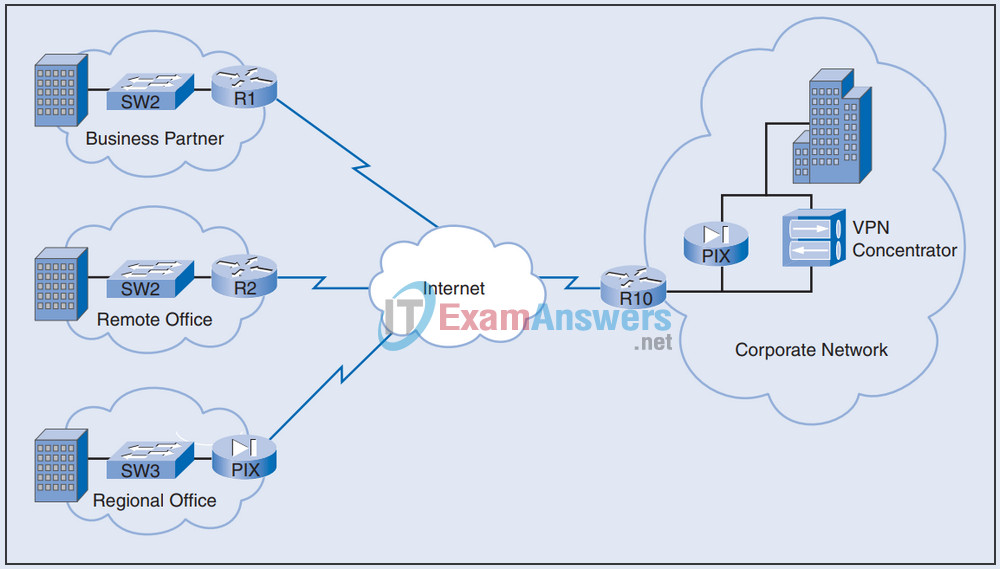
- VPN client software installed on the machines of the users at the regional office only
- PIX firewall appliance at the corporate network and regional office only
- Routers and PIX firewall appliance at the corporate network and the routers and PIX appliance at all remote locations
- LAN switches and routers at the remote locations only
- Router and PIX firewall appliance at the remote locations only
Explanation: Figure shows the regional offices with routers and PIX firewall devices. The corporate office includes a router and a PIX firewall. The PIX firewall could also be replaced by a VPN concentrator.
7. Which techniques can be used to secure the traffic sent over a VPN connection? (Choose two.)
- Data labeling, used to mark and separate the VPN traffic to different customers
- Data encapsulation, used to transmit data transparently from network to network through a shared network infrastructure
- Data encryption, used to code data into a different format using a secret key
- Use of a second routing protocol to transport the traffic over the VPN tunnel
- Use of a dedicated connection over the company private leased line
Explanation: VPNs secure data by encapsulating, creating a tunnel, or encrypting the data. Most VPNs can do both.
8. Match each description with its corresponding VPN characteristic:
Uses passwords, digital certificates, smart cards, and biometrics
Prevents tampering and alterations to data while data travels between the source and destination
Protects the contents of messages from interception by unauthenticated or unauthorized sources
Uses hashes
Ensures that the communicating peers are who they say they are
Uses encapsulation and encryption
A. Data confidentiality
B. Data integrity
C. Authentication
| Uses passwords, digital certificates, smart cards, and biometrics |
Authentication |
| Prevents tampering and alterations to data while data travels between the source and destination |
Data integrity |
| Protects the contents of messages from interception by unauthenticated or unauthorized sources |
Data confidentiality |
| Uses hashes |
Data integrity |
| Ensures that the communicating peers are who they say they are |
Authentication |
| Uses encapsulation and encryption |
Data confidentiality |
9. Which is an example of a tunneling protocol developed by Cisco?
Explanation: GRE is a tunneling protocol developed by Cisco Systems. It can encapsulate a variety of Layer 3 packets inside IP tunnels, creating a virtual point-to-point link to Cisco routers at remote points over an IP internetwork.
10. Match each description with its corresponding type of tunneling protocol:
Frame Relay, ATM, MPLS
The protocol that is wrapped around the original data
The protocol over which the original data was being carried
IPX, AppleTalk, IPv4, IPv6
GRE, IPsec, L2F, PPTP, L2TP
The protocol over which the information travels
A. Carrier protocol
B. Encapsulating protocol
C. Passenger protocol
| Frame Relay, ATM, MPLS |
Carrier protocol |
| The protocol that is wrapped around the original data |
Encapsulating protocol |
| The protocol over which the original data was being carried |
Passenger protocol |
| IPX, AppleTalk, IPv4, IPv6 |
Passenger protocol |
| GRE, IPsec, L2F, PPTP, L2TP |
Encapsulating protocol |
| The protocol over which the information travels |
Carrier protocol |
11. Match each description with the correct algorithm:
Encryption and decryption use the same key
Public key cryptography
Encryption and decryption use different keys
DES, 3DES, AES
RSA
Shared secret key cryptography
A. Symmetric algorithm
B. Asymmetric algorithm
| Encryption and decryption use the same key |
Symmetric algorithm |
| Public key cryptography |
Asymmetric algorithm |
| Encryption and decryption use different keys |
Asymmetric algorithm |
| DES, 3DES, AES |
Symmetric algorithm |
| RSA |
Asymmetric algorithm |
| Shared secret key cryptography |
Symmetric algorithm |
12. What type of connection is the most cost-effective to adequately support SOHO teleworker access to the Internet?
- A direct T1 link to the Internet
- 56-kbps dialup
- A one-way multicast satellite Internet system
- DSL to an ISP
Explanation: Given these choices, DSL is the most cost-effective method for broadband teleworker access to the Internet. Cable is another cost-effective technology that competes with DSL. Broadband wireless and two-way satellite Internet are becoming more common and more competitive.
13. Which wireless standard operates in both licensed and unlicensed bands of the spectrum from 2 to 6 GHz and allows for transmission rates of 70 Mbps at a range of up to 50 kilometers?
- 802.11g
- 802.11n
- 802.11b
- 802.16
- 802.11e
Explanation: The 802.16 (or WiMAX) standard allows transmissions up to 70 Mbps. 802.16 has a range of up to 30 miles (50 km). It can operate inlicensed or unlicensed bands of the spectrum from 2 to 6 GHz.
14. What do cable providers typically deploy to support high-speed transmissions of data to SOHO cable modems?
- Hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC)
- High-speed dialup cable modems
- Broadband copper coaxial
- 1000BASE-TX
Explanation: Cable operators typically deploy HFC networks to enable high-speed transmission of data to cable modems located in a SOHO. The trunks typically are fiber with coaxial distribution cable to the homes (feeders).
15. Describe the organizational, social, and environmental benefits of teleworking.
Organizational benefits:
- Continuity of operations
- Increased responsiveness
- Secure, reliable, and manageable access to information
- Cost-effective integration of data, voice, video, and applications
- Increased employee productivity, satisfaction, and retention
Social benefits:
- Increased employment opportunities for marginalized groups
- Less traveling and commuter-related stress
Environmental benefits:
- Reduced carbon footprints, for both individual workers and organizations
16. Describe the four main connection methods used by homes and SOHO businesses.
Dialup access:
- Dialup access is an inexpensive option that uses any phone line and a modem.
- It is the slowest connection option and typically is used in areas where higher-speed connections are unavailable.
DSL:
- DSL is more expensive than dialup but provides a faster connection.
- It also uses telephone lines, but unlike dialup access, DSL provides a continuous connection to the Internet.
- This connection option uses a special high-speed modem that separates the DSL signal from the telephone signal and provides an Ethernet connection to a host computer or LAN.
Cable modem:
- Cable Internet is a connection option offered by cable television service providers.
- The Internet signal is carried on the same coaxial cable that delivers cable television to homes and businesses.
- A special cable modem separates the Internet signal from the other signals carried on the cable and provides an Ethernet connection to a host computer or LAN.
Satellite:
- Satellite connection is an option offered by satellite service providers.
- The user’s computer connects through Ethernet to a satellite modem that transmits radio signals to the nearest POP within the satellite network.
17. Describe the two types of VPN networks.
Site-to-site VPNs:
- A site-to-site VPN is an extension of classic WAN networking and can connect a branch office network to a company headquarters network.
- Hosts send and receive TCP/IP traffic through a VPN “gateway,” which could be a router, PIX firewall appliance, or Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA).
- The VPN gateway is responsible for encapsulating and encrypting outbound traffic for all the traffic from a particular site and sending it through a VPN tunnel over the Internet to a peer VPN gateway at the target site.
- On receipt, the peer VPN gateway strips the headers, decrypts the content, and relays the packet toward the target host inside its private network.
Remote-access VPNs:
- Mobile users and telecommuters use remote-access VPNs extensively.
- Remote VPN connections typically take advantage of existing broadband connections.
- Each host typically has VPN client software that encapsulates and encrypts that traffic before sending it over the Internet to the VPN gateway at the edge of the target network.
- On receipt, the VPN gateway handles the data in the same way it would handle data from a site-to-site VPN.

