1. Which statements are true about the DHCP server functions? (Choose two.)
- When a client requests an IP address, the DHCP server searches the binding table for an entry that matches the client’s MAC address. If an entry exists, the corresponding IP address for that entry is returned to the client.
- Clients can be assigned an IP address from a predefined DHCP pool for a finite lease period.
- DHCP services must be installed on a dedicated network server to define the pool of IP addresses available to the client.
- The DHCP server can answer requests and assign IP addresses for a particular subnet only.
- Each subnet in the network requires a dedicated DHCP server to assign IP addresses to the host on the subnet.
- DHCP provides clients with an IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and domain name.
2. Refer to the following configuration:
R1(config)# ip dhcp pool 10.10.10.0
What does the string 10.10.10.0 after the ip dhcp pool command specify?
- Name of the DHCP pool
- Pool of IP addresses available for lease
- Range of excluded IP addresses
- IP subnet where the DHCP server resides
3. Which statements about DHCP are true? (Choose three.)
- DHCP messages use UDP as a transport protocol.
- The DHCPOFFER message is sent by the DHCP server after receiving a DHCPDISCOVER message from a client.
- DHCP uses ports 67 and 68.
- The DHCPREQUEST message is sent by a DHCP client to locate a DHCP server.
- The DHCPACK message is sent by the DHCP server to provide the DHCP client with the DHCP server MAC address for further communications.
- All DHCP communications are broadcast.
4. Refer to the exhibit. Router R2 is configured as a DHCP server. What happens when Host A sends a DHCP request to the DHCP server?
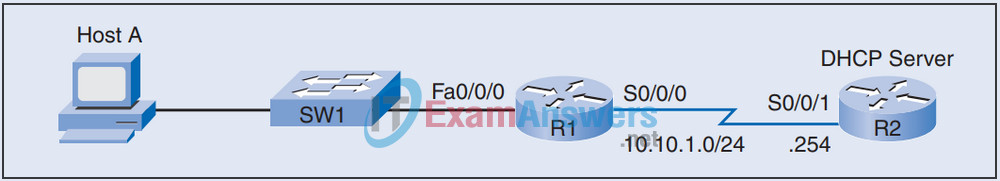
R1#show run ! interface fastethernet 0/0/0 ip helper-address 10.10.1.254 ! <output omitted>
- Router R1 drops the request.
- The request is forwarded to the DHCP server.
- The request is forwarded to the DHCP server, but the DHCP server does not respond with an IP address.
- Router R1 responds with an IP address.
5. Refer to the following output:
Router# debug ip dhcp server events DHCPD:DHCPDISCOVER received from client 0b07.1134.a029. DHCPD:assigned IP address 10.1.0.3 to client 0b07.1134.a029. DHCPD:Sending DHCPOFFER to client 0b07.1134.a029 (10.1.0.4) DHCPD:DHCPREQUEST received from client 0b07.1134.a029. DHCPD:Sending DHCPNACK to client 0b07.1134.a029. (10.1.0.3). <output omitted> Router# show ip dhcp conflict IP address Detection method Detection time 10.1.0.3 Ping Jan 01 1999 00:00 AM
Which statement is true about the DHCP exchange?
- The client was successfully configured with IP address 10.1.0.3.
- The DHCP server offered the address 10.1.0.3 to the client.
- The client requested 10.1.0.3 from the server.
- The DHCP server could not ping 10.1.0.3.
6. Refer to the following output:
NAT1# show ip nat translations Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global udp 198.18.24.211:123 192.168.254.7:123 192.2.182.4:123 192.2.182.4:123 tcp 198.18.24.211:4509 192.168.254.66:4509 192.0.2.184:80 192.0.2.184:80 tcp 198.18.24.211:4643 192.168.254.2:4643 192.0.2.71:5190 192.0.2.71:5190 tcp 198.18.24.211:4630 192.168.254.7:4630 192.0.2.71:5190 192.0.2.71:5190 tcp 198.18.24.211:1026 192.168.254.9:1026 198.18.24.4:53 198.18.24.4:53
Based on the output, which statement is true about the NAT configuration?
- Static NAT is configured.
- Dynamic NAT is configured.
- NAT Overload (PAT) is configured.
- NAT is configured incorrectly.
7. If an administrator chooses to avoid using NAT overload, what is the default timeout value for NAT translations?
- One hour
- One day
- One week
- Indefinite
8. Match each NAT characteristic with its corresponding NAT technique:
Provides one-to-one fixed mappings of local and global addresses
Assigns the translated addresses of IP hosts from a pool of public addresses
Can map multiple addresses to a single address of the external interface
Assigns unique source port numbers of an inside global address on a session-bysession basis
Allows an external host to establish sessions with an internal host
A. Dynamic NAT
B. NAT with Overload
C. Static NAT
9. Refer to the following configuration:
R1(config)# ip nat inside source static 192.168.0.100 209.165.200.2 R1(config)# interface serial0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip nat inside R1(config-if)# no shut R1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 R1(config)# interface serial0/0/2 R1(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.2 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# ip nat outside R1(config-if)# no shut
Which host or hosts will have their addresses translated by NAT?
- 10.1.1.2
- 192.168.0.100
- 209.165.200.2
- All hosts on the 10.1.1.0 network
- All hosts on the 192.168.0.0 network
10. Based on the following configuration, which addresses will NAT translate?
R1(config)# ip nat pool nat-pool1 209.165.200.225 209.165.200.240 netmask 255.255.255.0 R1(config)# ip nat inside source list 1 pool nat-pool1 R1(config)# interface serial0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.0.0 R1(config-if)# ip nat inside R1(config)# interface serial s0/0/2 R1(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)# ip nat outside R1(config)# access-list 1 permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255
- 10.1.1.2 to 10.1.1.255
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.0.255
- 209.165.200.240 to 209.165.200.255
- Only host 10.1.1.2
- Only host 209.165.200.255
11. Refer to the exhibit. Web server 1 is assigned a single IP address of 192.168.14.5/24. For hosts from the Internet to access web server 1, which type of NAT configuration is required on router R1?
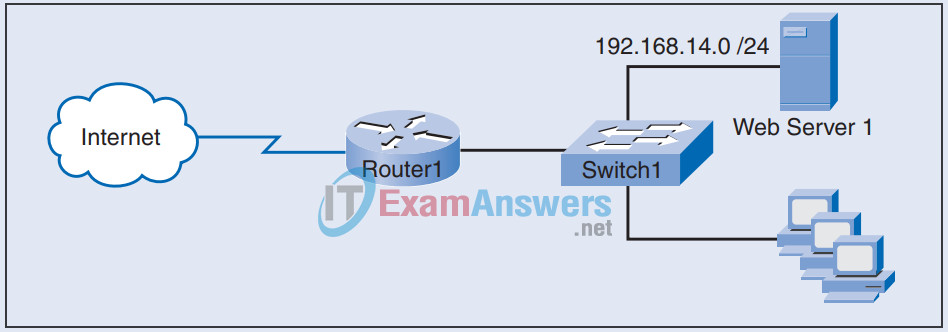
- Static NAT
- Dynamic NAT
- NAT overload
- Port address translation (PAT)
12. Which NAT solution allows external users to access an internal FTP server on a private network?
- Dynamic NAT
- Port address translation (PAT)
- NAT overload
- Static NAT
13. Given the following debug router output, what kind of address is 24.74.237.203?
s=10.10.10.3->24.74.237.203, d=64.102.252.3 [29854] s=10.10.10.3->24.74.237.203, d=64.102.252.3 [29855] s=10.10.10.3->24.74.237.203, d=64.102.252.3 [29856] s=64.102.252.3, d=24.74.237.203->10.10.10.3 [9935] s=64.102.252.3, d=24.74.237.203->10.10.10.3 [9937] s=10.10.10.3->24.74.237.203, d=64.102.252.3 [29857] s=64.102.252.3, d=24.74.237.203->10.10.10.3 [9969] s=64.102.252.3, d=24.74.237.203->10.10.10.3 [9972] s=10.10.10.3->24.74.237.203, d=64.102.252.3 [29858]
- Inside local
- Inside global
- Outside local
- Outside global
14. Which statements accurately describe the RIPng routing protocol? (Choose two.)
- RIPng has a limit of 15 hops.
- RIPng is a link-state routing protocol.
- RIPng uses UDP port 238 for updates.
- RIPng uses poison reverse.
- RIPng forwards IPv6 broadcasts.
15. Which methods of assigning an IPv6 address to an interface are automatic and can be used in conjunction with each other? (Choose two.)
- DHCPv6
- Stateless autoconfiguration
- EUI-64
- Static assignment
- DNS
16. Match each IPv6 command with its description:
ipv6 unicast-routing
ipv6 address
ip name-server
ipv6 host name
ipv6 router rip name
A. Specifies the DNS server used by the router
B. Defines a static hostname-to-address mapping
C. Configures a global IPv6 address
D. Enables IPv6 traffic forwarding between interfaces on the router
E. Enables RIPng routing on the router and identifies the RIP process
17. Given 2031:0000:0300:0000:0000:00C0:8000:130B, which options are equivalent representations of the full IPv6 address? (Choose three.)
- 2031:300::C0:8:130B
- 2031:0:300::C0:8000:130B
- 2031:0:3::C0:8000:130B
- 2031:0:0300:0:0:C0:8000:130B
- 2031::300:0:0:0C0:8000:130B
- 2031::0300::C0:8:130B
18. Describe the four DHCP discovery and offer messages in sequence of operation and function.
19. Refer to the exhibit. The following has been configured on router R1:
hostname R1 ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.11.1 192.168.11.254 ip dhcp pool LAN-POOL-2 network 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 default-router 192.168.2.1 domain-name span.com
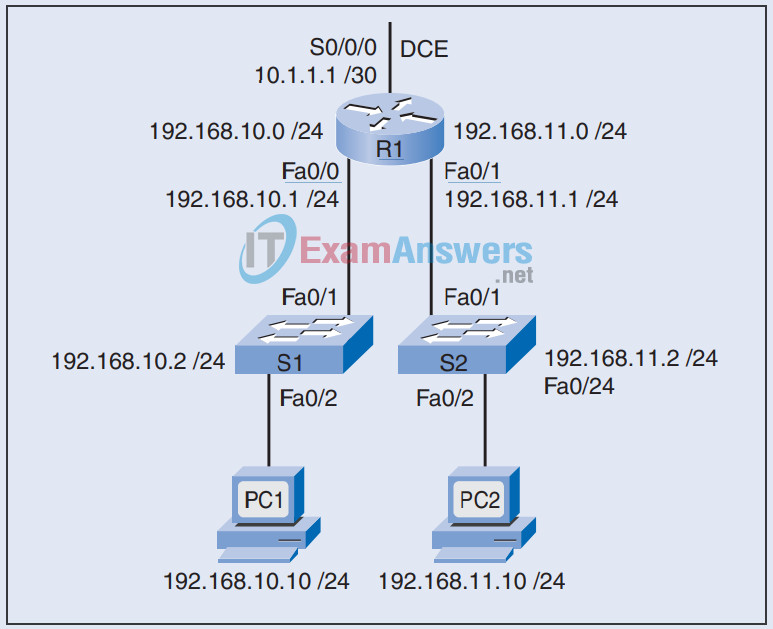
Router R1 has been configured to provide DHCP services to the hosts on network 192.168.11.0 /24, excluding the first nine IP addresses from the pool. However, after releasing and renewing its IP address, host PC2 still cannot acquire an IP address automatically. Which changes in the configuration would help this problem?
20. Refer to the exhibit. The DHCP server with an IP address of 192.168.11.5 has been configured to provide IP addresses to the hosts on network 192.168.10.0 /24. However, the hosts receive an error stating that their DHCP server request has timed out and that the DHCP server is unreachable. Which configuration commands would correct this problem?
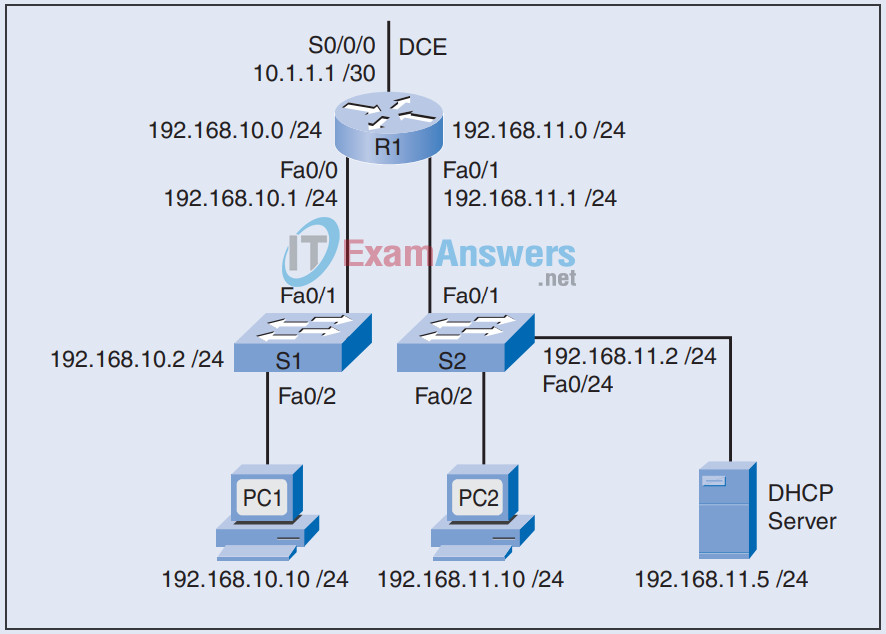
21. Describe the differences between static NAT, dynamic NAT, and NAT overload.
22. Refer to the following output:
R2# show ip nat translations
Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local
tcp 209.165.200.225:16642 192.168.10.10:16642 209.165.200.254:80
tcp 209.165.200.225:62452 192.168.11.10:62452 209.165.200.254:80
Outside global
209.165.200.254:80
209.165.200.254:80
R2# show ip nat translations verbose
Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local
tcp 209.165.200.225:16642 192.168.10.10:16642 209.165.200.254:80
Outside global
209.165.200.254:80
create 00:01:45, use 00:01:43 timeout:86400000, left 23:58:16, Map-Id(In): 1,
flags:
extended, use_count: 0, entry-id: 4, lc_entries: 0
tcp 209.165.200.225:62452 192.168.11.10:62452 209.165.200.254:80
209.165.200.254:80
create 00:00:37, use 00:00:35 timeout:86400000, left 23:59:24, Map-Id(In): 1,
flags:
extended, use_count: 0, entry-id: 5, lc_entries: 0
R2#
Router R2 has been configured to provide NAT services. On the basis of the information provided, comment on the NAT translations in the output.
23. Given 2031:0000:130F:0000:0000:09C0:876A:130B, abbreviate the IPv6 address to its shortest allowable form.
24. Describe the two main IPv4-to-IPv6 transition options, and complete the following IPv6 transition sentence:
“ _______where you can; _________where you must!”
