2.9.2 Lab – Basic Switch and End Device Configuration
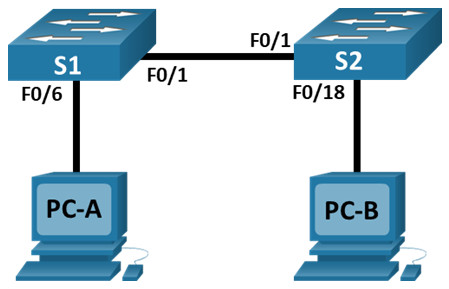
Topology
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
| S2 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 |
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.1.10 | 255.255.255.0 |
| PC-B | NIC | 192.168.1.11 | 255.255.255.0 |
Objectives
- Set Up the Network Topology
- Configure PC Hosts
- Configure and Verify Basic Switch Settings
Background / Scenario
In this lab, you will build a simple network with two hosts and two switches. You will also configure basic settings including hostname, local passwords, and login banner. Use show commands to display the running configuration, IOS version, and interface status. Use the copy command to save device configurations.
You will apply IP addressing for this lab to the PCs and switches to enable communication between the devices. Use the ping utility to verify connectivity.
Note: The switches used are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other switches and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs.
Note: Make sure that the switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. Refer to Appendix A for the procedure to initialize and reload a switch.
Required Resources
- 2 Switches (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 2 PCs (Windows with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Instructor Note: The Ethernet ports on the 2960 switches are autosensing and will accept either a straight-through or a cross-over cable for all connections. If the switches used in the topology are other than the 2960 model, then it is likely that a cross-over cable will be needed to connect the two switches.
Instructions
Step 1: Set Up the Network Topology
In this step, you will cable the devices together according to the network topology.
a. Power on the devices.
Power on all devices in the topology. The switches do not have a power switch; they will power on as soon as you plug in the power cord.
b. Connect the two switches.
Connect one end of an Ethernet cable to F0/1 on S1 and the other end of the cable to F0/1 on S2. You should see the lights for F0/1 on both switches turn amber and then green. This indicates that the switches have been connected correctly.
c. Connect the PCs to their respective switches.
Connect one end of the second Ethernet cable to the NIC port on PC-A. Connect the other end of the cable to F0/6 on S1. After connecting the PC to the switch, you should see the light for F0/6 turn amber and then green, indicating that PC-A has been connected correctly.
Connect one end of the last Ethernet cable to the NIC port on PC-B. Connect the other end of the cable to F0/18 on S2. After connecting the PC to the switch, you should see the light for F0/18 turn amber and then green, indicating that the PC-B has been connected correctly.
d. Visually inspect network connections.
After cabling the network devices, take a moment to carefully verify the connections to minimize the time required to troubleshoot network connectivity issues later.
Step 2: Configure PC Hosts
a. Configure static IP address information on the PCs according to the Addressing Table.
In PC-A, navigate to the Control Panel. In the Category view, under the Network and Internet heading, click View Network status and tasks > click Change adapter settings.
Note: There are other ways in Windows to navigate to the adapter settings.
Right-click the desired network adaptor and select Properties.
Select the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
Select Use the following IP address. Enter the IP address for PC-A (192.168.1.10) and subnet mask (255.255.255.0) as listed in the IP addressing table. You can leave default gateway blank at this time because there is no router attached to the network. Click OK to continue. Click Close to exit the Properties window.
Repeat the previous steps to assign the IP address information for PC-B.
b. Verify PC settings and connectivity.
From PC-A, open a Command Prompt to verify the PC settings and connectivity using the ipconfig /all command at the prompt.
C:\Users\Student> ipconfig /all
Windows IP Configuration
Host Name . . . . . . . . . . . . : PC-A
Primary Dns Suffix . . . . . . . :
Node Type . . . . . . . . . . . . : Hybrid
IP Routing Enabled. . . . . . . . : No
WINS Proxy Enabled. . . . . . . . : No
Ethernet adapter Ethernet0:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Description . . . . . . . . . . . : Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection
Physical Address. . . . . . . . . : 00-05-56-B3-86-BA
DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . : No
Autoconfiguration Enabled . . . . : Yes
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::a4b0:503d:84f4:f467%6(Preferred)
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.10(Preferred)
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.255
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . :
DHCPv6 IAID . . . . . . . . . . . : 50334761
DHCPv6 Client DUID. . . . . . . . : 00-01-00-01-24-EA-06-D5-00-50-56-B3-86-BA
DNS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . : fec0:0:0:ffff::1%1
fec0:0:0:ffff::2%1
fec0:0:0:ffff::3%1
NetBIOS over Tcpip. . . . . . . . : Enabled
To test the connectivity to PC-B, enter ping 192.168.1.11 at the prompt. The ping should be successful. If not, troubleshoot as necessary.
C:\Users\Student> ping 192.168.1.11
Pinging 192.168.1.11 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.11: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.11: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.11: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.11: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.11:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
Instructor Note: If your student did not get a reply from PC-B, it may be necessary to disable the PC firewall to ping between PCs. (Navigate to Control Panel > click System and Security > click Windows Firewall > click Turn Windows Firewall on or off > click Turn off Windows Firewall (not recommended).
Instructor Note: If the first ICMP packet times out, this could be a result of the PC resolving the destination address. This should not occur if you repeat the ping as the address is now cached.
Step 3: Configure and Verify Basic Switch Settings
a. Console into the switch. Enter the global configuration mode.
Establish a console connection to the switch from PC-A using Tera Term.
You can access all switch commands in privileged EXEC mode. The privileged EXEC command set includes those commands contained in user EXEC mode, as well as the configure command through which access to the remaining command modes are gained. Enter privileged EXEC mode by entering the enable command.
Switch> enable Switch#
The prompt changed from Switch> to Switch# which indicates privileged EXEC mode.
Use the configuration terminal command to enter configuration mode.
Switch# configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Switch(config)#
The prompt changed to reflect global configuration mode.
b. Give the switch a name according to the Addressing Table.
Use the hostname command to change the switch name to S1.
Switch(config)# hostname S1
c. Prevent unwanted DNS lookups.
To prevent the switch from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were hostnames, disable the Domain Name System (DNS) lookup.
S1(config)# no ip domain-lookup
d. Enter local passwords. Use class as the privileged EXEC password and cisco as the password for console access.
To prevent unauthorized access to the switch, configure passwords.
S1(config)# enable secret class S1(config)# line con 0 S1(config-line)# password cisco S1(config-line)# login S1(config-line)# exit
e. Configure and enable the SVI according to the Addressing Table.
S1(config)# interface vlan 1 S1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 S1(config-if)# no shut
f. Enter a login MOTD banner to warn about unauthorized access.
A login banner, known as the message of the day (MOTD) banner, should be configured to warn anyone accessing the switch that unauthorized access will not be tolerated.
The banner motd command requires the use of delimiters to identify the content of the banner message. The delimiting character can be any character as long as it does not occur in the message. For this reason, symbols, such as the #, are often used.
S1(config)# banner motd # Enter TEXT message. End with the character '#'. Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited and prosecuted to the full extent of the law. # S1(config)# exit
g. Save the configuration.
Use the copy command to save the running configuration to the startup file on non-volatile random access memory (NVRAM).
S1# copy running-config startup-config Destination filename [startup-config]? [Enter] Building configuration... [OK] S1#
h. Display the current configuration.
The show running-config command displays the entire running configuration, one page at a time. Use the spacebar to advance paging. The commands configured in Steps a – h are highlighted below.
S1# show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 1409 bytes ! ! Last configuration change at 03:49:17 UTC Mon Mar 1 1993 ! version 15.0 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname S1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! no ip domain-lookup <output omitted> interface Vlan 1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip http server ip http secure-server ! banner motd ^C Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited and prosecuted to the full extent of the law. ^C ! line con 0 password cisco login line vty 0 4 login line vty 5 15 login ! end
i. Display the IOS version and other useful switch information.
Use the show version command to display the IOS version that the switch is running, along with other useful information. Again, you will need to use the spacebar to advance through the displayed information.
S1# show version Cisco IOS Software, C2960 Software (C2960-LANBASEK9-M), Version 15.0(2)SE, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport Copyright (c) 1986-2012 by Cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Sat 28-Jul-12 00:29 by prod_rel_team ROM: Bootstrap program is C2960 boot loader BOOTLDR: C2960 Boot Loader (C2960-HBOOT-M) Version 12.2(53r)SEY3, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) S1 uptime is 1 hour, 38 minutes System returned to ROM by power-on System image file is "flash:/c2960-lanbasek9-mz.150-2.SE.bin" This product contains cryptographic features and is subject to United States and local country laws governing import, export, transfer and use. Delivery of Cisco cryptographic products does not imply third-party authority to import, export, distribute or use encryption. Importers, exporters, distributors and users are responsible for compliance with U.S. and local country laws. By using this product you agree to comply with applicable laws and regulations. If you are unable to comply with U.S. and local laws, return this product immediately. A summary of U.S. laws governing Cisco cryptographic products may be found at: http://www.cisco.com/wwl/export/crypto/tool/stqrg.html If you require further assistance please contact us by sending email to [email protected]. cisco WS-C2960-24TT-L (PowerPC405) processor (revision R0) with 65536K bytes of memory. Processor board ID FCQ1628Y5LE Last reset from power-on 1 Virtual Ethernet interface 24 FastEthernet interfaces 2 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces The password-recovery mechanism is enabled. 64K bytes of flash-simulated non-volatile configuration memory. Base ethernet MAC Address : 0C:D9:96:E2:3D:00 Motherboard assembly number : 73-12600-06 Power supply part number : 341-0097-03 Motherboard serial number : FCQ16270N5G Power supply serial number : DCA1616884D Model revision number : R0 Motherboard revision number : A0 Model number : WS-C2960-24TT-L System serial number : FCQ1628Y5LE Top Assembly Part Number : 800-32797-02 Top Assembly Revision Number : A0 Version ID : V11 CLEI Code Number : COM3L00BRF Hardware Board Revision Number : 0x0A Switch Ports Model SW Version SW Image ------ ----- ----- ---------- ---------- * 1 26 WS-C2960-24TT-L 15.0(2)SE C2960-LANBASEK9-M Configuration register is 0xF
j. Display the status of the connected interfaces on the switch.
To check the status of the connected interfaces, use the show ip interface brief command. Press the spacebar to advance to the end of the list.
S1# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Vlan1 192.168.1.1 YES unset up up FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset up up FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/3 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/4 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/5 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/6 unassigned YES unset up up FastEthernet0/7 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/8 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/9 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/10 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/11 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/12 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/13 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/14 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/15 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/16 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/17 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/18 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/19 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/20 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/21 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/22 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/23 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/24 unassigned YES unset down down GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset down down GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset down down
k. Configure switch S2.
Repeat the previous steps for Switch S2. Make sure the hostname is configured as S2.
l. Record the interface status for the following interfaces.
| Interface | S1 Status | S1 Protocol | S2 Status | S2 Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0/1 | Up | Up | Up | Up |
| F0/6 | Up | Up | Down | Down |
| F0/18 | Down | Down | Up | Up |
| VLAN 1 | Up | Up | Up | Up |
m. From a PC, ping S1 and S2. The pings should be successful.
n. From a switch, ping PC-A and PC-B. The pings should be successful.
Reflection Question
Why some FastEthernet ports on the switches are up and others are down?
The FastEthernet ports are up when cables are connected to the ports unless they were manually shutdown by the administrators. Otherwise, the ports would be down.
What could prevent a ping from being sent between the PCs?
Wrong IP address, media disconnected, switch powered off or ports administratively down, firewall.
Device Configs
Switch S1 (complete)
S1#sh run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1514 bytes version 15.0 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname S1 boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! no ip domain-lookup ! spanning-tree mode pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ! interface FastEthernet0/2 ! interface FastEthernet0/3 ! interface FastEthernet0/4 ! interface FastEthernet0/5 ! interface FastEthernet0/6 ! interface FastEthernet0/7 ! interface FastEthernet0/8 ! interface FastEthernet0/9 ! interface FastEthernet0/10 ! interface FastEthernet0/11 ! interface FastEthernet0/12 ! interface FastEthernet0/13 ! interface FastEthernet0/14 ! interface FastEthernet0/15 ! interface FastEthernet0/16 ! interface FastEthernet0/17 ! interface FastEthernet0/18 ! interface FastEthernet0/19 ! interface FastEthernet0/20 ! interface FastEthernet0/21 ! interface FastEthernet0/22 ! interface FastEthernet0/23 ! interface FastEthernet0/24 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 ! interface Vlan1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! ip http server ip http secure-server ! banner motd ^C Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited and prosecuted to the full extent of the law. ^C ! line con 0 password cisco login line vty 0 4 login line vty 5 15 login end
Switch S2 (complete)
S2# sh run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1514 bytes ! version 15.0 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname S2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! no ip domain-lookup ! spanning-tree mode pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ! interface FastEthernet0/2 ! interface FastEthernet0/3 ! interface FastEthernet0/4 ! interface FastEthernet0/5 ! interface FastEthernet0/6 ! interface FastEthernet0/7 ! interface FastEthernet0/8 ! interface FastEthernet0/9 ! interface FastEthernet0/10 ! interface FastEthernet0/11 ! interface FastEthernet0/12 ! interface FastEthernet0/13 ! interface FastEthernet0/14 ! interface FastEthernet0/15 ! interface FastEthernet0/16 ! interface FastEthernet0/17 ! interface FastEthernet0/18 ! interface FastEthernet0/19 ! interface FastEthernet0/20 ! interface FastEthernet0/21 ! interface FastEthernet0/22 ! interface FastEthernet0/23 ! interface FastEthernet0/24 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 ! interface Vlan1 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 ! ip http server ip http secure-server ! banner motd ^C Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited and prosecuted to the full extent of the law. ^C line con 0 password cisco login line vty 0 4 login line vty 5 15 login end

Awesome!
This is awesome! Thanks
thx